|
Sweden V Belarus
Sweden, ; fi, Ruotsi; fit, Ruotti; se, Ruoŧŧa; smj, Svierik; sje, Sverji; sju, Sverje; sma, Sveerje or ; yi, שוועדן, Shvedn; rmu, Svedikko; rmf, Sveittiko. formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country and the fifth-largest country in Europe. The capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of ; around 87% of Swedes reside in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden’s urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Because the country is so long, ranging from 55°N to 69°N, the climate of Sweden is diverse. Sweden has been inhabited since prehistoric times, . The inhabitants emerged into history as the Geats ( sv, Götar, links=no) and Swedes (), which together constituted the sea-fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Sweden
The coat of arms of the Kingdom of Sweden ( sv, Sveriges riksvapen) has a greater and a lesser version. Regulated usage The usage of the coats of arms is regulated by Swedish Law, Actbr>1970:498 which states (in unofficial translation) that "in commercial activities, the coats of arms, the flag or other official insignia of Sweden may not be used in a trademark or other insignias for products or services without proper authorisation. This includes any mark or text referring to the Swedish State which this can give the commercial mark a sign of official endorsement. This includes municipal coats of arms which are registered." Any representation consisting of three crowns ordered two above one are considered to be the lesser coat of arms, and its usage is therefore restricted by law 1970:498. Variants The arms of Sweden were first formally codified by law in 1908. This law also formally codifies the differences between the "greater" and "lesser" arms. The present law prescribi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Language Council
The Language Council of Sweden ( sv, Språkrådet) is the primary regulatory body for the advancement and cultivation of the Swedish language. The council is a department of the Swedish government's Institute for Language and Folklore ( sv, Institutet för språk och folkminnen). The council asserts control over the language through the publication of various books with recommendations in spelling and grammar as well as books on linguistics intended for a general audience, the sales of which are used to fund its operation. The council also works with four of the five official minority languages in Sweden: Finnish, Meänkieli, Yiddish, and Romani (Sámi excluded) alongside the Swedish Sign Language. Between 1965 and 2007, the council published the quarterly journal ''Språkvård'' (lit. "Language care"). The journal published articles about the use and development of the Swedish language, Q&As about spelling and grammar as well as guidelines for the use of Swedish in various contex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1995 Enlargement Of The European Union
The 1995 enlargement of the European Union saw Austria, Finland, and Sweden accede to the European Union (EU). This was the EU's fourth enlargement and came into effect on 1 January of that year. All these states were previous members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and had traditionally been less interested in joining the EU than other European countries. Norway had negotiated to join alongside the other three but following the signing of the treaty, membership was turned down by the Norwegian electorate in the 1994 national referendum. Switzerland also applied for membership on 26 May 1992, but withdrew it after a negative referendum result on 6 December 1992 (and that was not changed after a second negative referendum result on 4 March 2001). Closer links The three states, plus Norway and Switzerland (which never joined due to their referendum results) began to look at stronger ties with the EU (which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
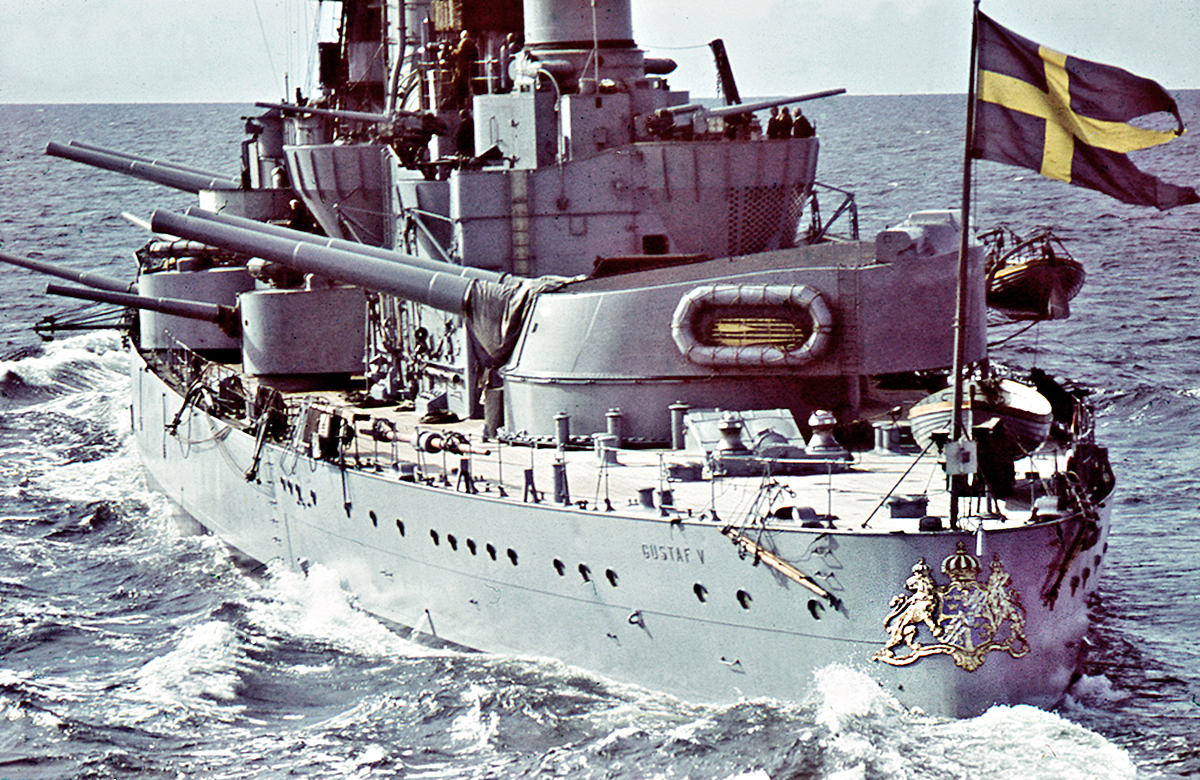
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually taken as the reign of Gustavus Adolphus, who ascended the throne in 1611, and its end as the loss of territories in 1721 following the Great Northern War. After the death of Gustavus Adolphus in 1632, the empire was controlled for lengthy periods by part of the high nobility, such as the Oxenstierna family, acting as regents for minor monarchs. The interests of the high nobility contrasted with the uniformity policy (i.e., upholding the traditional equality in status of the Swedish estates favoured by the kings and peasantry). In territories acquired during the periods of ''de facto'' noble rule, serfdom was not abolished, and there was also a trend to set up respective estates in Sweden proper. The Great Reduction of 1680 put an end to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and sv, Kalmarunionen; fi, Kalmarin unioni; la, Unio Calmariensis) was a personal union in Scandinavia, agreed at Kalmar in Sweden, that from 1397 to 1523 joined under a single monarch the three kingdoms of Denmark, Sweden (then including most of present-day Finland), and Norway, together with List of possessions of Norway#Former dependencies and homelands, Norway's overseas colonies Norway retained none of its prior possessions, however. Christian I pledged the Northern Isles to Scotland as insurance for his daughter’s dowery in 1468; when the dowery wasn’t paid the islands transferred to perpetual Scottish sovereignty in 1470. Following the Union’s dissolution, all remaining overseas possessions brought into the Union by Norway became property of the Danish monarch; who retained ownership following the transfer of the Kingdom of Norway from the Danish crown to Swedish crown (discussed in further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Sweden
The history of Sweden can be traced back to the melting of the Northern Polar Ice Caps. From as early as 12000 BC, humans have inhabited this area. Throughout the Stone Age, between 8000 BC and 6000 BC, early inhabitants used stone-crafting methods to make tools and weapons for hunting, gathering and fishing as means of survival. Written sources about Sweden before AD 1000 are rare and short, usually written by outsiders. It was not until the 14th century that longer historical texts were produced in Sweden. It is therefore usually accepted that Swedish recorded history, in contrast with pre-history, starts around the 11th century, when sources are common enough that they can be contrasted with each other. The modern Swedish state was formed over a long period of unification and consolidation. Historians have set different standards for when it can be considered complete, resulting in dates from the 6th to 16th centuries. Some common laws were present from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riksdag
The Riksdag (, ; also sv, riksdagen or ''Sveriges riksdag'' ) is the legislature and the supreme decision-making body of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members (), elected proportionally and serving, since 1994, fixed four-year terms. The 2022 Swedish general election is the most recent general election. The constitutional mandates of the Riksdag are enumerated in the ''Instrument of Government'' (), and its internal workings are specified in greater detail in the Riksdag Act ().Instrument of Government as of 2012. Retrieved on 16 November 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulf Kristersson
Ulf Hjalmar Ed Kristersson (born 29 December 1963) is a Swedish politician who has been serving as Prime Minister of Sweden since October 2022. He has been the leader of the Moderate Party (M) since October 2017 and a member of the Riksdag (MP) for Södermanland County since 2014 and for Stockholm County from 1991 to 2000. He previously served as Minister for Social Security from 2010 to 2014 and as Chairman of the Moderate Youth League from 1988 to 1992. On 11 December 2014, he was appointed Shadow Finance Minister of the Moderate Party and economic policy spokesperson. On 1 October 2017 Kristersson was elected party leader of the Moderate Party after Anna Kinberg Batra stepped down. Under his leadership, M has opened up to the Sweden Democrats (SD) and, by late 2021, had formed an informal right-wing alliance with them and two center-right parties of the dissolved Alliance. In the 2022 Swedish general election, that bloc obtained a majority in the Riksdag, leading to Krister ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Minister Of Sweden
The prime minister ( sv, statsminister ; literally translating to "Minister of State") is the head of government of Sweden. The prime minister and their cabinet (the government) exercise executive authority in the Kingdom of Sweden and are subject to the Parliament of Sweden. The prime minister is nominated by the Speaker of the Riksdag and elected by the chamber by simple majority, using negative parliamentarianism. The Riksdag Elections in Sweden, holds elections every four years, in the even year between leap years. Unlike most prime ministers in parliamentary systems, the prime minister is both ''de jure'' and ''de facto'' chief executive. This is because the Basic Laws of Sweden#Instrument of Government, Instrument of Government explicitly vests executive power in the Government of Sweden, government, of which the prime minister is the leader. History Before 1876, when the office of a single prime minister was created, Sweden did not have a ''head of government'' separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andreas Norlén
Per Olof Andreas Norlén (; born 6 May 1973) is a Swedish politician and member of the Moderate Party who has served as Speaker of the Riksdag since September 2018. He has been a Member of the Riksdag (MP) for Östergötland County (Riksdag constituency), Östergötland County since October 2006. Norlén has previously been a member of the Konstitutionsutskottet, Committee on the Constitution, 2014–2018 as chair of the committee. Career Following the first sitting of the Riksdag since the 2018 Swedish general election on 24 September, Norlén was elected the Speaker of the Riksdag. After the centre-left Löfven I Cabinet lost a vote of no confidence, Norlén began the task of nominating candidates for Stefan Löfven's successor as Prime Minister, according to the Swedish Basic Laws of Sweden#Instrument of Government, Instrument of Government. The lengthy work of finding a prime minister that could be tolerated by the Riksdag was concluded on 18 January 2019 when Löfven was appoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speaker Of The Riksdag
The speaker of the Riksdag ( sv, Riksdagens talman) is the speaker (politics), presiding officer of the national unicameral legislature in Sweden. The Riksdag underwent profound changes in 1867, when the medieval Riksdag of the Estates was abolished. The new form of the Riksdag included bicameral system, two elected chambers, each with its own speaker. Since the ''de facto'' introduction of parliamentarism in 1917, the Riksdag has properly functioned as the institution to which the prime minister and the Government of Sweden, government are held accountable. In 1971 the institution was transformed into a unicameral legislature with 350 members, reduced to 349 in 1976 to avoid parliamentary deadlocks. Since 1975, in accordance with the Basic Laws of Sweden#Instrument of Government, Instrument of Government of 1974, it is the speaker and no longer the Monarchy of Sweden, monarch who appoints and dismisses the Prime Minister of Sweden, prime minister. The current speaker is Andreas N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl XVI Gustaf
Carl XVI Gustaf (Carl Gustaf Folke Hubertus; born 30 April 1946) is King of Sweden. He ascended the throne on the death of his grandfather, Gustaf VI Adolf, on 15 September 1973. He is the youngest child and only son of Prince Gustaf Adolf, Duke of Västerbotten, and Princess Sibylla of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. His father died on 26 January 1947 in an airplane crash in Denmark when Carl Gustaf was nine months old. Upon his father's death, he became second in line to the throne, after his grandfather, the then Crown Prince Gustaf Adolf. Following the death of his great-grandfather, King Gustaf V, in 1950, Gustaf Adolf ascended the throne and thus Carl Gustaf became Sweden's new crown prince and heir apparent to the throne at the age of four. Shortly after he became king in September 1973, the new 1974 Instrument of Government took effect, formally stripping Carl XVI Gustaf of his remaining executive power. As a result, he no longer performs many of the duties normally accorded to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |