|
Sweat Shops
A sweatshop or sweat factory is a crowded workplace with very poor, socially unacceptable or illegal working conditions. Some illegal working conditions include poor ventilation, little to no breaks, inadequate work space, insufficient lighting, or uncomfortably/dangerously high or low temperatures. The work may be difficult, tiresome, dangerous, climatically challenging or underpaid. Workers in sweatshops may work long hours with unfair wages, regardless of laws mandating overtime pay or a minimum wage; child labor laws may also be violated. Women make up 85 to 90% of sweatshop workers and may be forced by employers to take birth control and routine pregnancy tests to avoid supporting maternity leave or providing health benefits. The Fair Labor Association's "2006 Annual Public Report" inspected factories for FLA compliance in 18 countries including Bangladesh, El Salvador, Colombia, Guatemala, Malaysia, Thailand, Tunisia, Turkey, China, India, Vietnam, Honduras, Indonesia, Brazil, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union
The International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union (ILGWU), whose members were employed in the women's clothing industry, was once one of the largest labor unions in the United States, one of the first U.S. unions to have a primarily female membership, and a key player in the labor history of the 1920s and 1930s. The union, generally referred to as the "ILGWU" or the "ILG", merged with the Amalgamated Clothing and Textile Workers Union in the 1990s to form the Union of Needletrades, Industrial and Textile Employees (UNITE). UNITE merged with the Hotel Employees and Restaurant Employees Union (HERE) in 2004 to create a new union known as UNITE HERE. The two unions that formed UNITE in 1995 represented 250,000 workers between them, down from the ILGWU's peak membership of 450,000 in 1969. Early history The ILGWU was founded on June 3, 1900, in New York City by seven local unions, with a few thousand members between them. The union grew rapidly in the next few years but began to sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower East Side Tenement National Historic Site
The Lower East Side Tenement Museum, located at 97 and 103 Orchard Street in the Lower East Side neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, is a National Historic Site. The museum's two historical tenement buildings were home to an estimated 15,000 people, from over 20 nations, between 1863 and 2011. The museum, which includes a visitors' center, promotes tolerance and historical perspective on the immigrant experience. History The building at 97 Orchard Street was contracted by Prussian-born immigrant Lukas Glockner in 1863 and was modified several times to conform with the city's developing housing laws. When first constructed, it contained 22 apartments and a basement level saloon. Over time, four stoop-level and two basement apartments were converted into commercial retail space, leaving 16 apartments in the building. Modifications over the years included the installation of indoor plumbing (cold running water, two toilets per floor), an air shaft, and gas followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire
The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, on Saturday, March 25, 1911, was the deadliest industrial disaster in the history of the city, and one of the deadliest in U.S. history. The fire caused the deaths of 146 garment workers – 123 women and girls and 23 men – who died from the fire, smoke inhalation, or falling or jumping to their deaths. Most of the victims were recent Italian or Jewish immigrant women and girls aged 14 to 23; of the victims whose ages are known, the oldest victim was 43-year-old Providenza Panno, and the youngest were 14-year-olds Kate Leone and Rosaria "Sara" Maltese. The factory was located on the 8th, 9th, and 10th floors of the Asch Building, which had been built in 1901. Later renamed the " Brown Building", it still stands at 23–29 Washington Place near Washington Square Park, on the New York University (NYU) campus. The building has been designated a National Historic Landmark and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meat Packing Industry
The meat-packing industry (also spelled meatpacking industry or meat packing industry) handles the slaughtering, processing, packaging, and distribution of meat from animals such as cattle, pigs, sheep and other livestock. Poultry is generally not included. This greater part of the entire meat industry is primarily focused on producing meat for human consumption, but it also yields a variety of by-products including hides, dried blood, protein meals such as meat & bone meal, and, through the process of rendering, fats (such as tallow). In the United States and some other countries, the facility where the meat packing is done is called a ''slaughterhouse'', ''packinghouse'' or a ''meat-packing plant''; in New Zealand, where most of the products are exported, it is called a ''freezing works''. An abattoir is a place where animals are slaughtered for food. The meat-packing industry grew with the construction of the railroads and methods of refrigeration for meat preservation. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Jungle
''The Jungle'' is a 1906 novel by the American journalist and novelist Upton Sinclair. Sinclair's primary purpose in describing the meat industry and its working conditions was to advance socialism in the United States. However, most readers were more concerned with several passages exposing health violations and unsanitary practices in the American meat packing industry during the early 20th century, which greatly contributed to a public outcry that led to reforms including the Meat Inspection Act. The book depicts working-class poverty, lack of social supports, harsh and unpleasant living and working conditions, and hopelessness among many workers. These elements are contrasted with the deeply rooted corruption of people in power. A review by the writer Jack London called it "the ''Uncle Tom's Cabin'' of wage slavery." Sinclair was considered a muckraker, a journalist who exposed corruption in government and business. In 1904, Sinclair had spent seven weeks gathering informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upton Sinclair
Upton Beall Sinclair Jr. (September 20, 1878 – November 25, 1968) was an American writer, muckraker, political activist and the 1934 Democratic Party nominee for governor of California who wrote nearly 100 books and other works in several genres. Sinclair's work was well known and popular in the first half of the 20th century, and he won the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction in 1943. In 1906, Sinclair acquired particular fame for his classic muck-raking novel, ''The Jungle'', which exposed labor and sanitary conditions in the U.S. meatpacking industry, causing a public uproar that contributed in part to the passage a few months later of the 1906 Pure Food and Drug Act and the Meat Inspection Act. In 1919, he published ''The Brass Check'', a muck-raking exposé of American journalism that publicized the issue of yellow journalism and the limitations of the "free press" in the United States. Four years after publication of ''The Brass Check'', the first code of ethics for journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
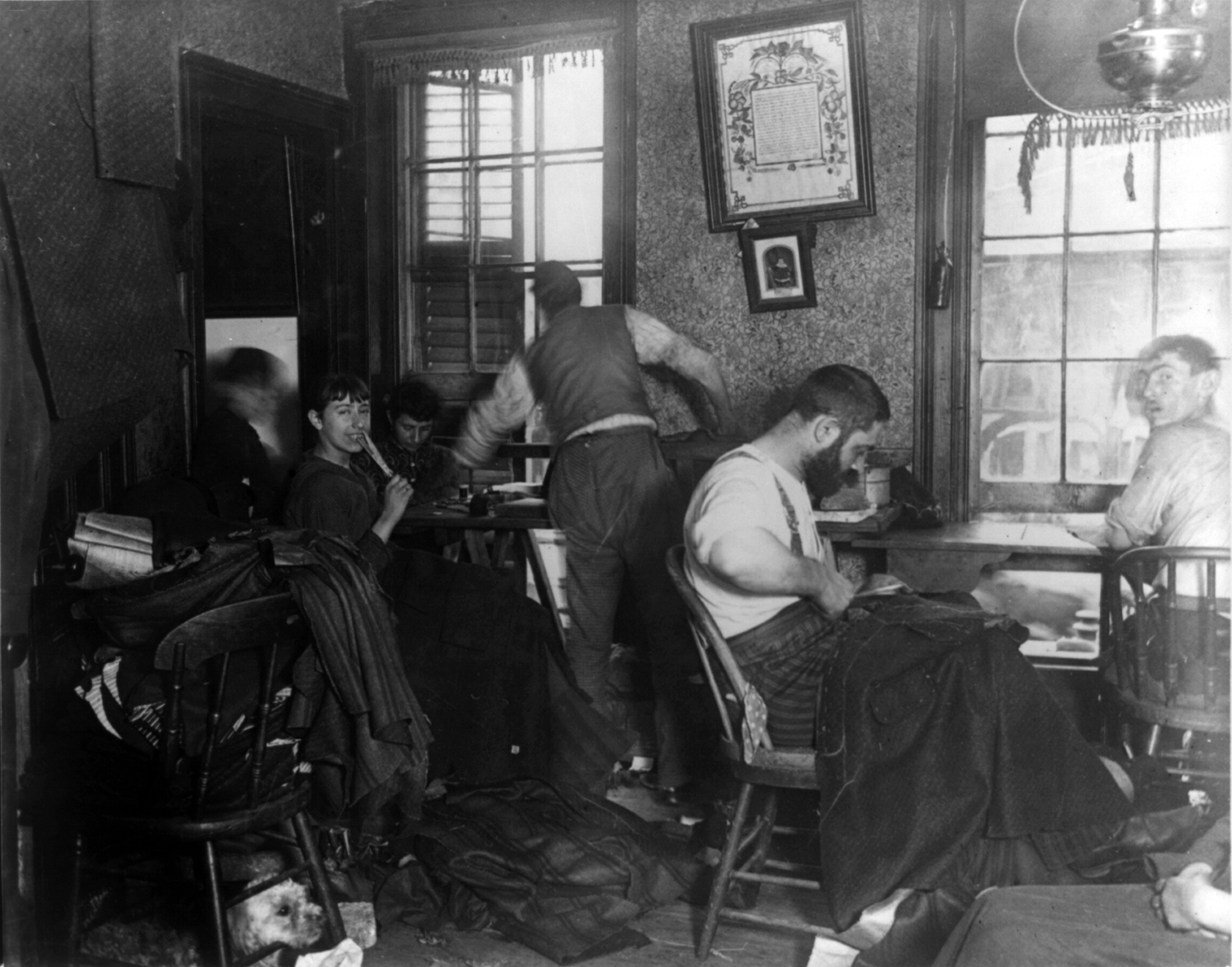
How The Other Half Lives
''How the Other Half Lives: Studies among the Tenements of New York'' (1890) is an early publication of photojournalism by Jacob Riis, documenting squalid living conditions in New York City slums in the 1880s. The photographs served as a basis for future "muckraking" journalism by exposing the slums to New York City's upper and middle classes. They inspired many reforms of working-class housing, both immediately after publication as well as making a lasting impact in today's society. Background 19th century, New York City In the 1880s many people in upper- and middle-class society were unaware of the dangerous conditions in the slums among poor immigrants. After the Civil War, the country transformed into an industrial superpower and became largely urban. Also, a wave of unskilled southern European, eastern European, Asian, and Jewish immigrants came to settle in the "promised land" of the United States. This migration was vastly different from the previous booms due to the influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photo Journalism
Photojournalism is journalism that uses images to tell a news story. It usually only refers to still images, but can also refer to video used in broadcast journalism. Photojournalism is distinguished from other close branches of photography (such as documentary photography, social documentary photography, war photography, street photography and celebrity photography) by having a rigid ethical framework which demands an honest but impartial approach that tells a story in strictly journalistic terms. Photojournalists contribute to the news media, and help communities connect with one other. They must be well-informed and knowledgeable, and are able to deliver news in a creative manner that is both informative and entertaining. Similar to a writer, a photojournalist is a reporter, but they must often make decisions instantly and carry photographic equipment, often while exposed to significant obstacles, among them immediate physical danger, bad weather, large crowds, and limited phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Riis
Jacob August Riis ( ; May 3, 1849 – May 26, 1914) was a Danish-American social reformer, "muckraking" journalist and social documentary photographer. He contributed significantly to the cause of urban reform in America at the turn of the twentieth century. He is known for using his photographic and journalistic talents to help the impoverished in New York City; those impoverished New Yorkers were the subject of most of his prolific writings and photography. He endorsed the implementation of "model tenements" in New York with the help of humanitarian Lawrence Veiller. Additionally, as one of the most famous proponents of the newly practicable casual photography, he is considered one of the fathers of photography due to his very early adoption of flash. While living in New York, Riis experienced poverty and became a police reporter writing about the quality of life in the slums. He attempted to alleviate the bad living conditions of poor people by exposing their living condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressivism In The United States
Progressivism in the United States is a political philosophy and reform movement in the United States advocating for policies that are generally considered left-wing, left-wing populist, libertarian socialist, social democratic, and environmentalist. In mainstream American politics, progressives generally advocate for a universal healthcare system, wage equity and labor rights, economic justice, social justice, opposition to the military-industrial complex, corporate regulation, the abolition of capital punishment, and action on climate change. It reached its height early in the 20th century. Middle class and reformist in nature, it arose as a response to the vast changes brought by modernization such as the growth of large corporations, pollution and corruption in American politics. Historian Alonzo Hamby describes American progressivism as a "political movement that addresses ideas, impulses, and issues stemming from modernization of American society. Emerging at the end of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)