|
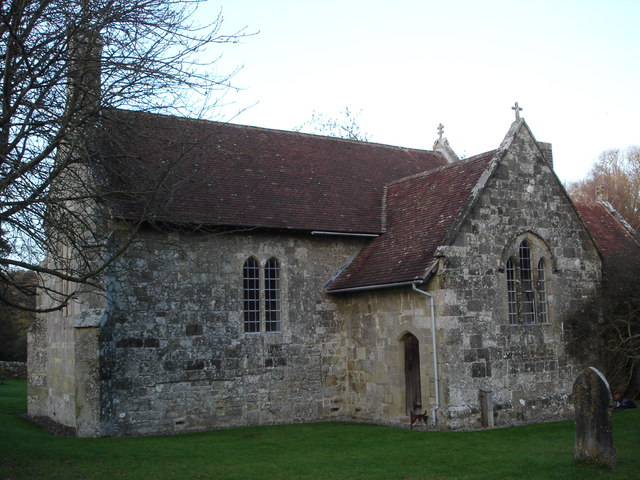
Swallowcliffe
Swallowcliffe is a small village and civil parish in Wiltshire, England, about southeast of Tisbury and west of Salisbury. The village lies about half a mile north of the A30 Shaftesbury- Wilton road which crosses the parish. Geography Swallowcliffe lies on the southern edge of the Vale of Wardour. The parish is composed of chalk escarpments and greensand terraces to the south and upper greensand wooded hills to the south-west; also to the northeast, where Swallowcliffe Wood is prominent. Cutting through the hills south to north is the spring-filled valley where the village first developed. In the south, Swallowcliffe Down rises to a height of 221 metres at a spur of White Sheet Hill, and the parish boundary is an ancient ridgeway. History There is a Neolithic long barrow, 95m in length, in the southwest of the parish on Swallowcliffe Down, where the boundaries of Swallowcliffe, Ansty, and Alvediston parishes now meet. The Iron Age hillfort known as Castle Ditches li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansty, Wiltshire
Ansty is a small village and civil parish in southwest Wiltshire, England, about east of Shaftesbury. The village is just north of the A30, between Shaftesbury and Salisbury. The parish includes the hamlet of Ansty Coombe. History In the southern part of the parish is White Sheet Hill, on which there are Bronze Age barrows including a long barrow. In the eastern part of the parish there is bowl barrow. The barrow may be older than the pagan Saxon burial from the 7th century AD that has been found in it. Grave goods excavated from the burial include a diadem, palm cups, enamelled ironwork and an incense burner. Domesday Book in 1086 recorded two estates at ''Anestioe'', with altogether 17 households. The village developed in a sheltered valley where springs form a stream which flows north to join the Nadder at Tisbury. One of the springs feeds a pond north of the church, which was made as a fish-pond before 1769 by constructing an earth dam. The village lies on both sides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tisbury, Wiltshire
Tisbury is a large village and civil parish approximately west of Salisbury in the English county of Wiltshire. With a population at the 2011 census of 2,253 it is a centre for communities around the upper River Nadder and Vale of Wardour. The parish includes the hamlets of Upper Chicksgrove and Wardour. Tisbury is the largest settlement within the Cranborne Chase and West Wiltshire Downs Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (larger nearby settlements such as Salisbury and Shaftesbury are just outside it). Prehistory The area has some paleoanthropological significance. Evidence of early human activity comes from the Middle Gravel at Swanscombe, Kent, a 400,000-year-old stratum, in which skull fragments of a young woman were found. Along with the remains were several fragments of Pseudodiplocoenia oblonga (also known as Isastraea oblonga), one of four Upper Jurassic species of coral unique to the Upper Portlandian of Tisbury. This indicates that the group to which the woman be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiltshire Council
Wiltshire Council is a council for the unitary authority of Wiltshire (excluding the separate unitary authority of Swindon) in South West England, created in 2009. It is the successor authority to Wiltshire County Council (1889–2009) and the four district councils of Kennet, North Wiltshire, Salisbury, and West Wiltshire, all of which were created in 1974 and abolished in 2009. Establishment of the unitary authority The ceremonial county of Wiltshire consists of two unitary authority areas, Wiltshire and Swindon, administered respectively by Wiltshire Council and Swindon Borough Council. Before 2009, Wiltshire was administered as a non-metropolitan county by Wiltshire County Council, with four districts, Kennet, North Wiltshire, Salisbury, and West Wiltshire. Swindon, in the north of the county, had been a separate unitary authority since 1997, and on 5 December 2007 the Government announced that the rest of Wiltshire would move to unitary status. This was later put in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
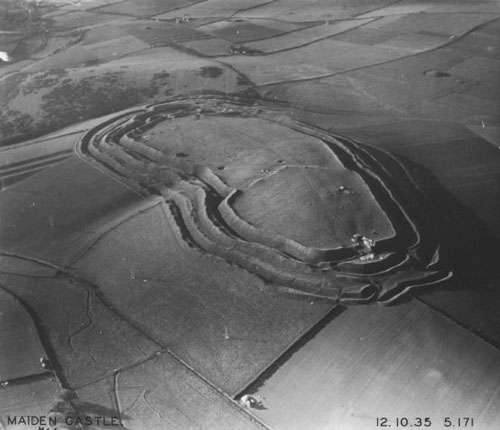
Hillfort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of earthworks, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. Hillforts developed in the Late Bronze and Early Iron Age, roughly the start of the first millennium BC, and were used in many Celtic areas of central and western Europe until the Roman conquest. Nomenclature The spellings "hill fort", "hill-fort" and "hillfort" are all used in the archaeological literature. The ''Monument Type Thesaurus'' published by the Forum on Information Standards in Heritage lists ''hillfort'' as the preferred term. They all refer to an elevated site with one or more ramparts made of earth, stone and/or wood, with an external ditch. Many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Depression Of British Agriculture
The Great Depression of British Agriculture occurred during the late nineteenth century and is usually dated from 1873 to 1896. Contemporaneous with the global Long Depression, Britain's agricultural depression was caused by the dramatic fall in grain prices that followed the opening up of the American prairies to cultivation in the 1870s and the advent of cheap transportation with the rise of steamships. British agriculture did not recover from this depression until after the Second World War. Other countries in Western Europe such as the Netherlands experienced the same agricultural crisis (1878–1895) as a result of the market being flooded by cheap grain from the United States and Canada.Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "landbouwpolitiek § geschiedenis", "Leeuwarden §3. geschiedenis". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum. Background In 1846 Parliament repealed the Corn Laws, which had imposed a tariff on imported grain, and thereby ''de facto'' instituted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public House
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was used to differentiate private houses from those which were, quite literally, open to the public as "alehouses", "taverns" and "inns". By Georgian times, the term had become common parlance, although taverns, as a distinct establishment, had largely ceased to exist by the beginning of the 19th century. Today, there is no strict definition, but CAMRA states a pub has four characteristics:GLA Economics, Closing time: London's public houses, 2017 # is open to the public without membership or residency # serves draught beer or cider without requiring food be consumed # has at least one indoor area not laid out for meals # allows drinks to be bought at a bar (i.e., not only table service) The history of pubs can be traced to Roman taverns in B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanning (leather)
Tanning is the process of treating Skinning, skins and Hide (skin), hides of animals to produce leather. A tannery is the place where the skins are processed. Tanning hide into leather involves a process which permanently alters the protein structure of skin, making it more durable and less susceptible to decomposition and coloring. Before tanning, the skins are dehaired, degreased, desalted and soaked in water over a period of six hours to two days. Historically this process was considered a noxious or "odoriferous trade" and relegated to the outskirts of town. Historically, tanning used tannin, an acidic chemical compound from which the tanning process draws its name, derived from the bark of certain trees. An alternative method, developed in the 1800s, is chrome tanning, where chromium salts are used instead of natural tannins. History The English word for tanning is from medieval Latin , derivative of (oak bark), from French (tanbark), from old-Cornish (red oak). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Francia, West Franks and Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Romans. The term is also used to denote emigrants from the duchy who conquered other territories such as England and Sicily. The Norse settlements in West Francia followed a series of raids on the French northern coast mainly from Denmark, although some also sailed from Norway and Sweden. These settlements were finally legitimized when Rollo, a Scandinavian Viking leader, agreed to swear fealty to Charles the Simple, King Charles III of West Francia following the Siege of Chartres (911), siege of Chartres in 911. The intermingling in Normandy produced an Ethnic group, ethnic and cultural "Norman" identity in the first half of the 10th century, an identity which continued to evolve over the ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estate Maps
Estate maps were maps commissioned by landed gentry, individual landowners or institutions, to show their Estate (land), extensive landed property, typically including fields, Designed landscape, parkland and buildings. They were used for display and estate management and were fashionable from the 16th to the 19th century. History In England and Wales, estate maps began to be produced in large numbers during the 16th century. The availability of new estates as a result of the Dissolution of the Monasteries gave increased impetus to their production. Estate maps continued in popularity until the middle of the 19th century, when large scale tithe maps, tithe and Ordnance Survey maps became available. The English country house#Decline, decline of many country estates led to the dismantling of many of the traditional landed estates in the early to mid 20th century. A few maps were drawn prior to the 16th century, but these were ad hoc, for a particular purpose. Before the emergence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Pembroke
Earl of Pembroke is a title in the Peerage of England that was first created in the 12th century by King Stephen of England. The title, which is associated with Pembroke, Pembrokeshire in West Wales, has been recreated ten times from its original inception. Due to the number of creations of the Earldom, the original seat of Pembroke Castle is no longer attached to the title. , the current holder of the earldom is William Herbert, 18th Earl of Pembroke, which is the 10th creation of the title. For the past 400 years, his family's seat has been Wilton House, Wiltshire. The Earls of Pembroke also hold the title Earl of Montgomery, created for the younger son of Henry Herbert, 2nd Earl of Pembroke before he succeeded as the 4th Earl in 1630. The current Earls of Pembroke also carry the subsidiary titles: Baron Herbert of Cardiff, of Cardiff in the County of Glamorgan (1551), Baron Herbert of Shurland, of Shurland in the Isle of Sheppey in the County of Kent (1605), and Baron Herbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enclosure
Enclosure or Inclosure is a term, used in English landownership, that refers to the appropriation of "waste" or " common land" enclosing it and by doing so depriving commoners of their rights of access and privilege. Agreements to enclose land could be either through a formal or informal process. The process could normally be accomplished in three ways. First there was the creation of "closes", taken out of larger common fields by their owners. Secondly, there was enclosure by proprietors, owners who acted together, usually small farmers or squires, leading to the enclosure of whole parishes. Finally there were enclosures by Acts of Parliament. The primary reason for enclosure was to improve the efficiency of agriculture. However, there were other motives too, one example being that the value of the land enclosed would be substantially increased. There were social consequences to the policy, with many protests at the removal of rights from the common people. Enclosure riots a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened within Britain, and the identity was not merely imported. Anglo-Saxon identity arose from interaction between incoming groups from several Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes, both amongst themselves, and with Celtic Britons, indigenous Britons. Many of the natives, over time, adopted Anglo-Saxon culture and language and were assimilated. The Anglo-Saxons established the concept, and the Kingdom of England, Kingdom, of England, and though the modern English language owes somewhat less than 26% of its words to their language, this includes the vast majority of words used in everyday speech. Historically, the Anglo-Saxon period denotes the period in Britain between about 450 and 1066, after Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
