|
Svydovets
The Svydovets (Ukrainian Свидовець; Polish ''Świdowiec''; Czech and Slovak ''Svidovec''; German ''Swydiwez'') is a mountain range in western Ukraine, one of the ranges of Eastern Beskids, itself belonging to the Outer Eastern Carpathians. It is a biodiversity hotspot in the Ukrainian Carpathians. The territories of the Svydovets mountain range belong to the state. The highest peak of the range is Blysnyzi mountain (1883 m). The ''Black Tisza'', the source of Tisza, is one of the more fullflowing rivers of the region, it flows out from the Svydovets. Flora and fauna The Svydovets is home to 42 plant species and 51 animal species that are listed in the Red Data Book of Ukraine as endangered. The red-listed plant species include the Rhodiola rosea, the Carpathian saxifrage, the fir clubmoss (Huperzia selago), and the stiff clubmoss (Lycopodium annotinum). The endangered animal species include the European brown bear, the Eurasian lynx, the black grouse, and the Eurasian ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Eastern Carpathians
Divisions of the Carpathians are a categorization of the Carpathian mountains system. Below is a detailed overview of the major subdivisions and ranges of the Carpathian Mountains. The Carpathians are a "subsystem" of a bigger Alps-Himalaya System that stretches from western Europe all the way to southern Asia, and are further divided into "provinces" and "subprovinces". The last level of the division, i.e. the actual mountain ranges and basins, is usually classified as "units". The main divisions are shown in the map on the right. To generalize, there are three major provinces (regions): Western Carpathians, Eastern Carpathians, and the Southern Carpathians. Naming conventions The division is largely (with many exceptions) undisputed at the lowest level (except for the Ukrainian part), but various divisions are given for the higher levels, especially for the penultimate level. A geomorphological division has been used as much as the data was available; other new physiogeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Carpathians
The Ukrainian Carpathians ( uk, Українські Карпати) are a section of the Eastern Carpathians, within the borders of modern Ukraine. They are located in the southwestern corner of Western Ukraine, within administrative territories of four Ukrainian regions (oblasts), covering northeastern part of Zakarpattia Oblast, southwestern part of Lviv Oblast, southern half of Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast and western half of Chernivtsi Oblast. They are stretching in general northwest–southeast direction, starting at the tripartite border point of Ukraine with Poland and Slovakia, and continuing towards Ukrainian border with Romania. In terms of geological classification, Ukrainian Carpathians belong to two distinctive categories, with major part belonging to the Outer Eastern Carpathians and minor part to the Inner Eastern Carpathians. Within different regional and national traditions, there are several overlapping variants of divisions and designations for various E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vorozheska
Lake Vorozheska (Ukrainian: озеро Ворожеська) is the lake in the Carpathian Mountains of Ukraine. It is a hydrological natural monument of local significance. Lake Vorozheska is located on the northern slopes of the Svydovets massif at an elevation of 1460 meters above sea level. It has glacial origin and is situated in a cirque. The lake consists of two connected bodies of water, a bigger and a smaller one. The water of the lake is clear and cool. Thickets of juniper and blueberry Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bi ... grow around it. References {{Authority control Lakes of Ukraine Protected areas of Ukraine Tourist attractions in Zakarpattia Oblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
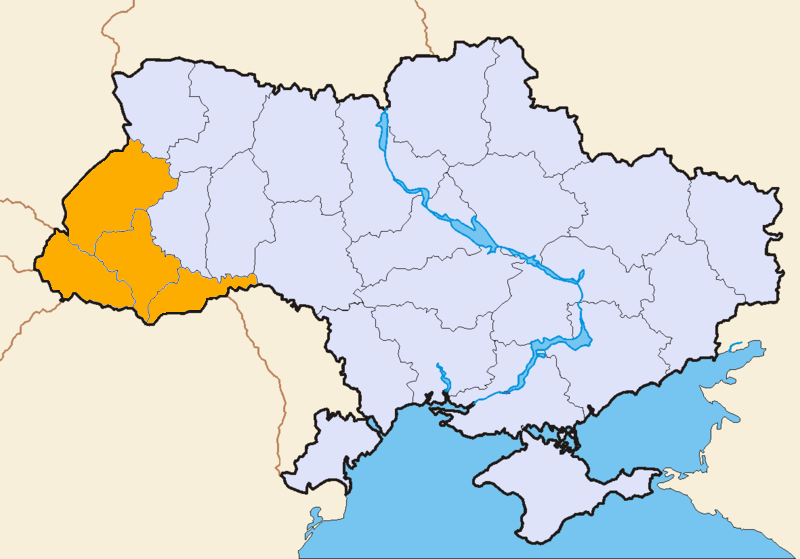
Zakarpattia Oblast
The Zakarpattia Oblast ( uk, Закарпатська область, Zakarpatska oblast) is an administrative oblast located in western Ukraine, mostly coterminous with the historical region of Carpathian Ruthenia. Its administrative centre is the city of Uzhhorod, Other major cities within the oblast include Mukachevo, Khust, Berehove, and Chop, the last of which is home to railroad transport infrastructure. Zakarpattia Oblast was established on 22 January 1946, after Czechoslovakia gave up its claim to the territory of '' Subcarpathian Ruthenia'' ( cs, Podkarpatská Rus) under a treaty between Czechoslovakia and the Soviet Union. The territory of '' Subcarpathian Ruthenia'' was then taken over by the Soviet Union and became part of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. Some scholars say that during the Ukrainian independence referendum held in 1991, Zakarpatska Oblast voters were given a separate option on whether or not they favoured autonomy for the region. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Beskids Of The Outer Eastern Carpathians
The Eastern Beskids or Eastern Beskyds ( uk, Східні Бескиди; pl, Beskidy Wschodnie; rue, Выходны Бескиды; ro, Beskizii Orientali; russian: Восточные Бескиды) are a geological group of mountain ranges of the Beskids, within the Outer Eastern Carpathians. As a continuation of the Central Beskids, this mountain range includes the far southeastern corner of Poland, the far eastern corner of Slovakia, and stretches southward through western parts of Ukraine, up to the border of Romania. In Polish and Ukrainian terminology, the range is commonly called the "Eastern Beskids" ( uk, Східні Бескиди; pl, Beskidy Wschodnie), while in Slovakia, the term ''Meadowed Mountains'' ( sk, Poloniny) is also used. The scope of those terms varies in accordance to different traditions and classifications. At the three-way border, portions of the Slovak Bukovec Mountains ( sk, Bukovské vrchy), the Polish Bieszczady Mountains ( pl, Bieszczady Za ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodpecker
Woodpeckers are part of the bird family Picidae, which also includes the piculets, wrynecks, and sapsuckers. Members of this family are found worldwide, except for Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, Madagascar, and the extreme polar regions. Most species live in forests or woodland habitats, although a few species are known that live in treeless areas, such as rocky hillsides and deserts, and the Gila woodpecker specialises in exploiting cacti. Members of this family are chiefly known for their characteristic behaviour. They mostly forage for insect prey on the trunks and branches of trees, and often communicate by drumming with their beaks, producing a reverberatory sound that can be heard at some distance. Some species vary their diet with fruits, birds' eggs, small animals, tree sap, human scraps, and carrion. They usually nest and roost in holes that they excavate in tree trunks, and their abandoned holes are of importance to other cavity-nesting birds. They sometimes com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emerald Network
The Emerald network is a network of Areas of Special Conservation Interest to conserve wild flora and fauna and their natural habitats of Europe, which was launched in 1989 by the Council of Europe as part of its work under the Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats or Bern Convention that came into force on 1 June 1982. It is to be set up in each Contracting Party or observer state to the convention. The Bern Convention is signed by the 46 member states of the Council of Europe, together with the European Union, Monaco, Burkina Faso, Morocco, Tunisia and Senegal. Algeria, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Cape Verde, Vatican City, San Marino and Russia are among non-signatories that have observer status at meetings of the committee. The European Union, as such, is also a Contracting Party to the Bern Convention. In order to fulfil its obligations arising from the convention, particularly in respect of habitat protection, it produced the Habitats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a population of approximately 675 million; it operates with an annual budget of approximately 500 million euros. The organisation is distinct from the European Union (EU), although it is sometimes confused with it, partly because the EU has adopted the original Flag of Europe, European flag, created for the Council of Europe in 1955, as well as the Anthem of Europe, European anthem. No country has ever joined the EU without first belonging to the Council of Europe. The Council of Europe is an official United Nations General Assembly observers, United Nations Observer. Being an international organization, the Council of Europe cannot make laws, but it does have the ability to push for the enf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natura 2000
Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respectively. The network includes both terrestrial and Marine Protected Areas. History In May 1992, the governments of the European Communities adopted legislation designed to protect the most seriously threatened habitats and species across Europe. The Habitats Directive complements the Birds Directive adopted earlier in 1979 and together they make up the Natura 2000 network of protected areas. The Birds Directive requires the establishment of Special Protection Areas for birds. The Habitats Directive similarly requires Sites of Community Importance which upon the agreement of the European Commission become Special Areas of Conservation to be designated for species other than birds, and for habitat types (e.g. particular types of forest, grassland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Grouse
The black grouse (''Lyrurus tetrix''), also known as northern black grouse, Eurasian black grouse, blackgame or blackcock, is a large game bird in the grouse family. It is a sedentary species, spanning across the Palearctic in moorland and steppe habitat when breeding, often near wooded areas. They will spend the winter perched in dense forests, feeding almost exclusively on the needles of conifers. The black grouse is one of 2 species of grouse in the genus '' Lyrurus'', the other being the lesser-known Caucasian grouse. The female is greyish-brown and has a cackling or warbling call. She takes all responsibility for nesting and caring for the chicks, as typical with most galliforms. The black grouse's genome was sequenced in 2014. Taxonomy and naming The black grouse was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under the binomial name ''Tetrao tetrix''. Both ''Tetrao'' and ''tetrix'' come from Ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |