|
Suzuki GSX-S750
The Suzuki GSX-S750 is a standard motorcycle made by Suzuki since 2015. The , Multivalve, 16-valve, Straight-four engine, inline-four, sports-bike-derived engine was modified and re-tuned for more usable torque at lower RPM for commuting and cruising at slower speeds. The GSX-S750's predecessor, the Suzuki GSR750, GSR750, was sold in the European markets since 2011, while Suzuki sold the same motor bike with a different body model in the USA under the GSX-S750 name in 2015 and 2016. Comparing the GSX-S750 with the GSR750, the changes made to GSX-S750 include a new exhaust to comply with Euro 4 and California emission standards, a new tapered handlebar, new swing-arm, a revised air box, and ventilation holes in the bottom of each cylinder to reduce pumping loss and improve power. It uses a 43 tooth rear sprocket compared to the GSR's 42, to improve acceleration, and top gear was lengthened to keep the top speed the same (250 km/h +/- or 155 mph +/-). It will be illegal to registe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-lock Braking System
An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety anti-skid braking system used on aircraft and on land vehicles, such as cars, motorcycles, trucks, and buses. ABS operates by preventing the wheels from locking up during braking, thereby maintaining tractive contact with the road surface and allowing the driver to maintain more control over the vehicle. ABS is an automated system that uses the principles of threshold braking and cadence braking, techniques which were once practiced by skillful drivers before ABS was widespread. ABS operates at a much faster rate and more effectively than most drivers could manage. Although ABS generally offers improved vehicle control and decreases stopping distances on dry and some slippery surfaces, on loose gravel or snow-covered surfaces ABS may significantly increase braking distance, while still improving steering control. Since ABS was introduced in production vehicles, such systems have become increasingly sophisticated and effective. Mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycle World
''Cycle World'' is a motorcycling magazine in the United States. It was founded in 1962 by Joe Parkhurst, who was inducted to the Motorcycle Hall of Fame as "the person responsible for bringing a new era of objective journalism" to the US. ''Cycle World'' was the largest motorcycling magazine in the world. The magazine is headquartered in Irvine, California. Regular contributors include Peter Egan and Nick Ienatsch. Previous or occasional contributors have included gonzo journalist and author Hunter S. Thompson, journalist and correspondent Henry N. Manney III, and professional riding coach Ken Hill. Parkhurst sold ''Cycle World'' to CBS in 1971. CBS executive Peter G. Diamandis and his associates bought CBS Magazines from CBS in 1987, forming Diamandis Communications, which was acquired by Hachette Magazines the following year, 1988. In 2011, Hachette sold the magazine to Hearst Corporation, which in turn sold ''Cycle World'' to Bonnier Corporation Bonnier LLC (formerl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
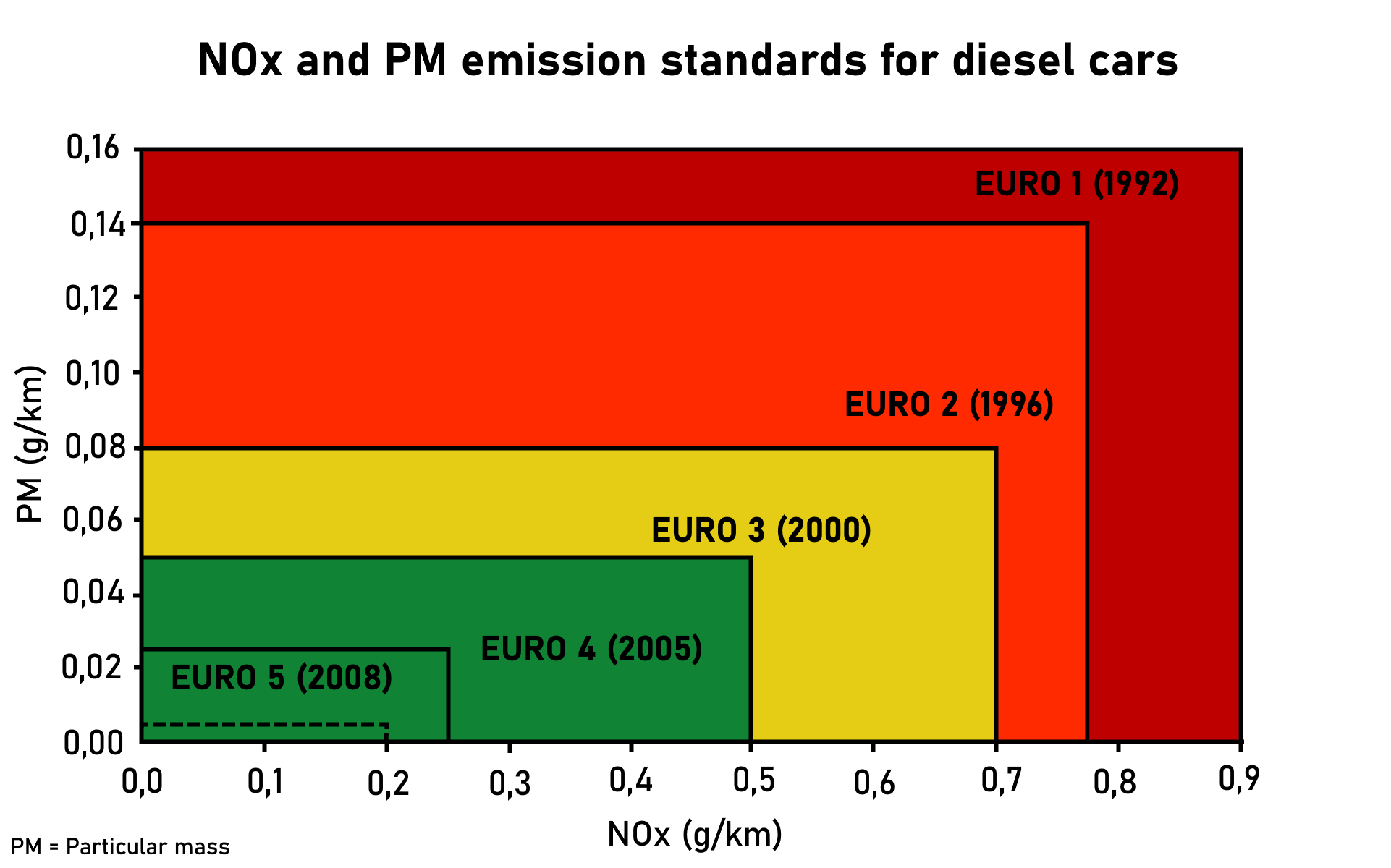
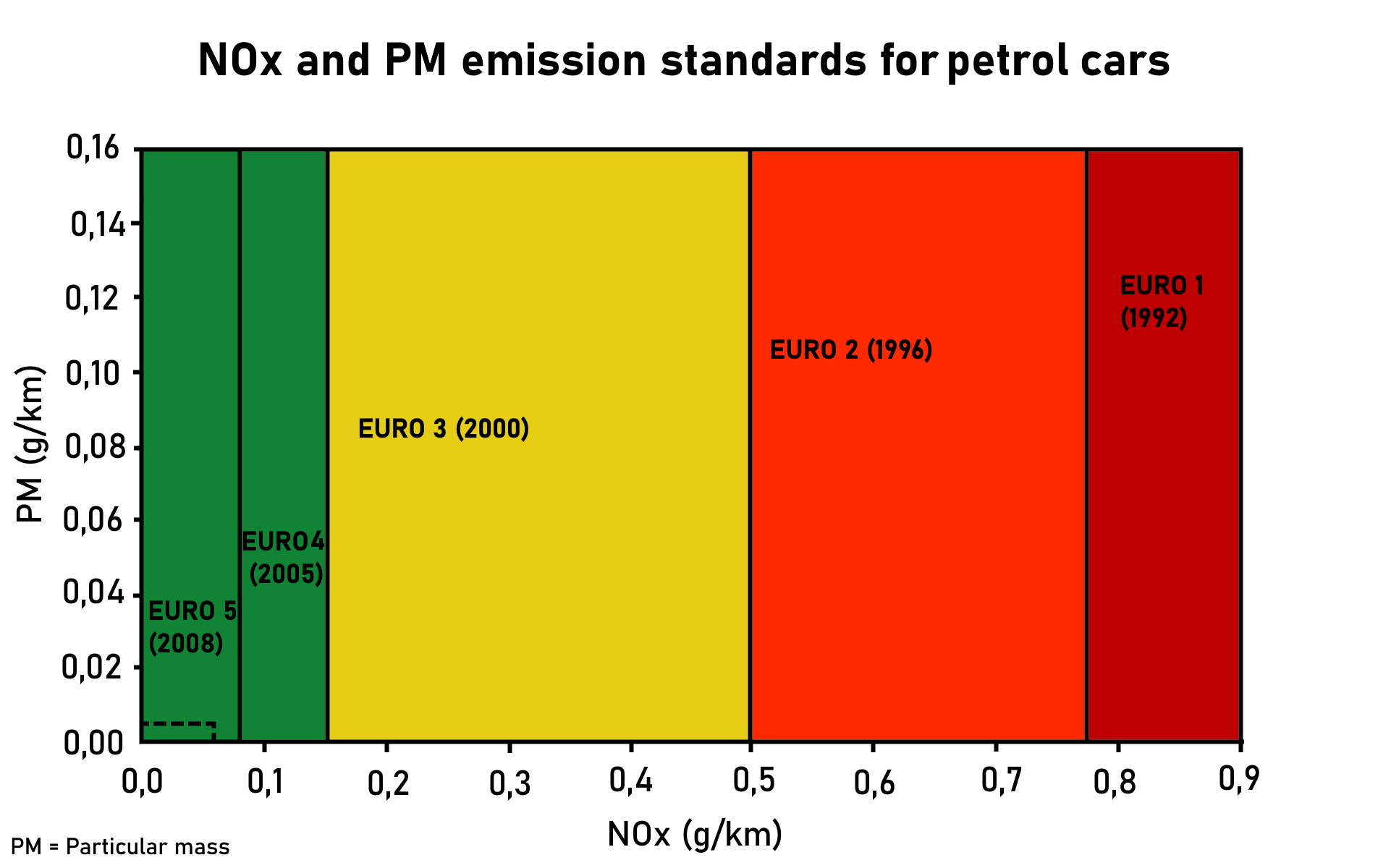
European Emissions Standards
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards for pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and EEA member states and the UK, and ships in EU waters. The standards are defined in a series of European Union directives staging the progressive introduction of increasingly stringent standards. , the standards do not include non-exhaust emissions such as particulates from tyres and brakes. Details of Euro 7 have been postponed to 12 October 2022. Background In the European Union, emissions of nitrogen oxides (), total hydrocarbon (THC), non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), carbon monoxide (CO) and particulate matter (PM) are regulated for most vehicle types, including cars, trucks (lorries), locomotives, tractors and similar machinery, barges, but excluding seagoing ships and aeroplanes. For each vehicle type, different standards apply. Compliance is determined by running the engine at a standardised test cycle. Non-com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Emission Standards
United States vehicle emission standards are set through a combination of legislative mandates enacted by Congress through Clean Air Act (CAA) amendments from 1970 onwards, and executive regulations managed nationally by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and more recently along with the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). These standard cover common motor vehicle air pollution, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate emissions, and newer versions have incorporated fuel economy standards. In nearly all cases, these agencies set standards that are expected to be met on a fleet-wide basis from automobile and other vehicle manufacturers, with states delegated to enforce those standards but not allowed to set stricter requirements. California has generally been the exception, having been granted a waiver and given allowance to set stricter standards as it had established its own via the California Air Resources Board prior to the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro 4
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards for pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and EEA member states and the UK, and ships in EU waters. The standards are defined in a series of European Union directives staging the progressive introduction of increasingly stringent standards. , the standards do not include non-exhaust emissions such as particulates from tyres and brakes. Details of Euro 7 have been postponed to 12 October 2022. Background In the European Union, emissions of nitrogen oxides (), total hydrocarbon (THC), non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), carbon monoxide (CO) and particulate matter (PM) are regulated for most vehicle types, including cars, trucks (lorries), locomotives, tractors and similar machinery, barges, but excluding seagoing ships and aeroplanes. For each vehicle type, different standards apply. Compliance is determined by running the engine at a standardised test cycle. Non-co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Motorcycle
The six main types of motorcycles are generally recognized as ''standard'', ''cruiser'', ''touring'', ''sports'', ''off-road'', and ''dual-purpose''. ''Sport touring'' is sometimes recognized as a seventh category or integrated with the ''touring'' category. Although there are many names and systems for classifying types of motorcycles based on their characteristics and usage, there are generally six categories recognized by most motorcycle manufacturers and organizations. Strong distinctions are usually made between the six main types of motorcycles and other motorcycles. Scooter, moped, underbone, miniature, pocket, electric, and three-wheeled motorcycles are generally excluded from the main categories but other classification schemes may include these as types of motorcycles. There is no universal system for classifying all types of motorcycles. There are strict classification systems enforced by competitive motorcycle sport sanctioning bodies, or legal definitions of a mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzuki GSX-R750
The Suzuki GSX-R750 is a sports motorcycle made by Suzuki. It was introduced at the Cologne Motorcycle Show in October 1984 as a motorcycle of the GSX-R series. Air and oil cooled The air and oil-cooled models can be divided into the first-generation and the second-generation colloquially referred to as 'slabbies' and 'slingshots' respectively. The 1985-1987 models featured very flat bodies compared to modern sport-bikes, hence the term 'slab-sided'. 1988-1991 (1992 USA) models are sometimes referred to as slingshots because the carburetors introduced in 1988 were marketed as slingshot carburetors (slingshot describes the cross-section of the semi-flat slide carbs). GSX-R750 (F) 1985 (The Classic) The original model featured a lightweight aluminum alloy frame, vacuum carburetors, twin discs with 4-pot calipers, and tyres both front and rear. To save weight, the designers specified an air-and-oil-cooled engine, rather than a water-cooled engine. The seat has separate front an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescopic Fork
A telescopic fork is a form of motorcycle front suspension whose use is so common that it is virtually universal. The telescopic fork uses fork tubes and sliders which contain the springs and dampers. The main advantages of the telescopic fork are that (i) it is simple in design and relatively cheap to manufacture and assemble; (ii) it is lighter than older designs using external components and linkage systems; and (iii) it has a clean and simple appearance that bikers find attractive. Telescopic forks sometimes have gaiters to protect the fork tubes from abrasion and corrosion. A more modern (and more expensive) version of the conventional telescopic fork is the inverted or "USD" (upside-down) fork. BMW's patented telelever front suspension appears at first glance to be conventional telescopic fork, but the fork tubes contain neither springs nor damping. Instead, a wishbone and an inboard monoshock perform suspension duties, and the forks serve to locate the front wheel an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pops Yoshimura
Hideo "Pops" Yoshimura (October 7, 1922 – March 29, 1995) was a Japanese motorcycle tuner, race team owner, and manufacturer of speciality motorcycle accessories. He is remembered for his ties to the beginnings of Superbike racing and the Yoshimura factory racing team. __TOC__ Motorcycling career Born in Fukuoka City, Japan, Yoshimura was called into military service during the Second World War where he was trained as an aircraft mechanic. After the war, he began tuning motorcycles for American servicemen stationed in Japan and in 1954, he opened his first shop, with his wife and children helping him. In 1971, he moved his business to Los Angeles at the beginning of the four-cylinder superbike era. He gained a reputation as an excellent motorcycle tuner. In 1976 the AMA introduced a racing class for production based bikes and Yoshimura established himself by entering fast, reliable Kawasaki Z1 bikes. In 1978 he switched to Suzuki bikes and began winning races. Steve McLaughlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-four Engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the exceptions of the flat-four engines produced by Subaru and Porsche) and the layout is also very common in motorcycles and other machinery. Therefore the term "four-cylinder engine" is usually synonymous with straight-four engines. When a straight-four engine is installed at an inclined angle (instead of with the cylinders oriented vertically), it is sometimes called a slant-four. Between 2005 and 2008, the proportion of new vehicles sold in the United States with four-cylinder engines rose from 30% to 47%. By the 2020 model year, the share for light-duty vehicles had risen to 59%. Design A four-stroke straight-four engine always has a cylinder on its power stroke, unlike engines with fewer cylinders where there is no power stroke occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |