|
Suzuki Coupling
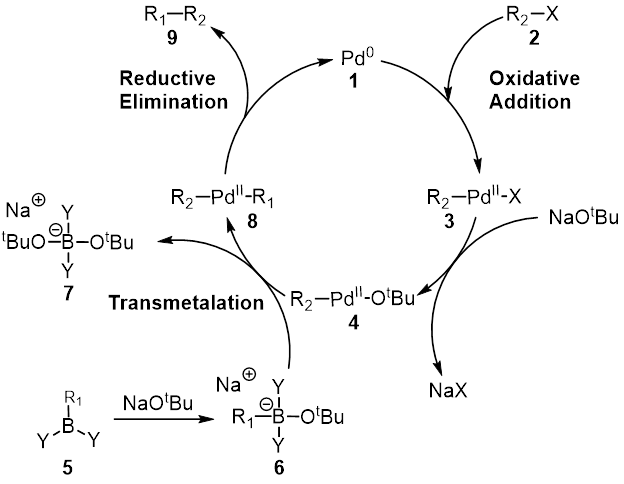
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction, classified as a cross-coupling reaction, where the coupling partners are a boronic acid and an organohalide and the catalyst is a palladium(0) complex. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of palladium-catalyzed cross-couplings in organic synthesis. This reaction is also known as the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction or simply as the Suzuki coupling. It is widely used to synthesize polyolefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. Several reviews have been published describing advancements and the development of the Suzuki reaction. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon-carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base. Reaction mechanism The mechanism of the Suzuki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akira Suzuki (chemist)
is a Japanese chemist and Nobel Prize Laureate (2010), who first published the Suzuki reaction, the organic reaction of an aryl- or vinyl- boronic acid with an aryl- or vinyl-halide catalyzed by a palladium(0) complex, in 1979. Early life and education Suzuki was born on September 12, 1930, in Mukawa, Hokkaidō, his father died when he was in high school. He studied chemistry at Hokkaido University (Hokudai) and after receiving his PhD while he worked there as assistant professor. He initially wanted to major in mathematics, his favorite subject in childhood was arithmetic.『朝日小学生新聞』2010年10月8日 It was an encounter with two books that became an opportunity to advance to the path of organic synthesis, one is ''Textbook of Organic Chemistry'' written by Louis Fieser of Harvard University, and another is ''Hydroboration'' written by Herbert C. Brown of Purdue University. Career From 1963 until 1965, Suzuki worked as a postdoctoral student with Herbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzuki Reaction Scheme ACS
is a Japan, Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Minami-ku, Hamamatsu, Japan. Suzuki manufactures automobiles, motorcycles, All-terrain vehicle, all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), outboard motor, outboard marine engines, wheelchairs and a variety of other small internal combustion engines. In 2016, Suzuki was the Automotive industry#By manufacturer, eleventh biggest automaker by production worldwide. Suzuki has over 45,000 employees and has 35 production facilities in 23 countries, and 133 distributors in 192 countries. The worldwide sales volume of automobiles is the world's tenth largest, while domestic sales volume is the third largest in the country. Suzuki's domestic motorcycle sales volume is the third largest in Japan. History In 1909, Michio Suzuki (inventor), Michio Suzuki (1887–1982) founded the Suzuki Loom Works in the small seacoast village of Hamamatsu, Japan. Business boomed as Suzuki built loom, weaving looms for Japan's giant silk industry. In 1929 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
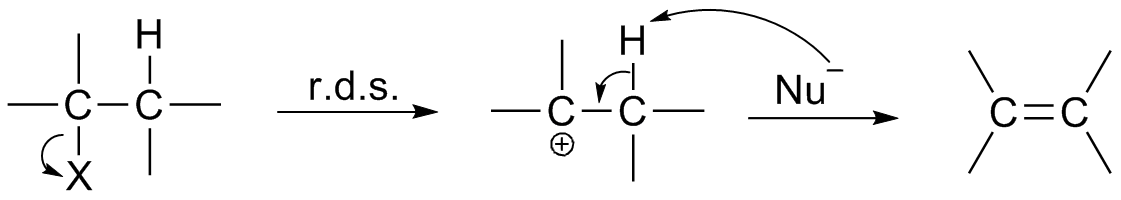
Rate Determining Step
In chemical kinetics, the overall rate of a reaction is often approximately determined by the slowest step, known as the rate-determining step (RDS or RD-step or r/d step) or rate-limiting step. For a given reaction mechanism, the prediction of the corresponding rate equation (for comparison with the experimental rate law) is often simplified by using this approximation of the rate-determining step. In principle, the time evolution of the reactant and product concentrations can be determined from the set of simultaneous rate equations for the individual steps of the mechanism, one for each step. However, the analytical solution of these differential equations is not always easy, and in some cases numerical integration may even be required. The hypothesis of a single rate-determining step can greatly simplify the mathematics. In the simplest case the initial step is the slowest, and the overall rate is just the rate of the first step. Also, the rate equations for mechanisms with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. History The terms ''nucleophile'' and '' electrophile'' were introduced by Christopher Kelk Ingold in 1933, replacing the terms ''anionoid'' and ''cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis. Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts. Enolates are unsaturated alkoxides derived by deprotonation of a bond adjacent to a ketone or aldehyde. The nucleophilic center for simple alkoxides is located on the oxygen, whereas the nucleophilic site on enolates is delocalized onto both carbon and oxygen sites. Ynolates are also unsaturated alkoxides derived from acetylenic alcohols. Phenoxides are close relatives of the alkoxides, in which the alkyl group is replaced by a derivat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Cycle
In chemistry, a catalytic cycle is a multistep reaction mechanism that involves a catalyst. The catalytic cycle is the main method for describing the role of catalysts in biochemistry, organometallic chemistry, bioinorganic chemistry, materials science, etc. Since catalysts are regenerated, catalytic cycles are usually written as a sequence of chemical reactions in the form of a loop. In such loops, the initial step entails binding of one or more reactants by the catalyst, and the final step is the release of the product and regeneration of the catalyst. Articles on the Monsanto process, the Wacker process, and the Heck reaction show catalytic cycles. A catalytic cycle is not necessarily a full reaction mechanism. For example, it may be that the intermediates have been detected, but it is not known by which mechanisms the actual elementary reactions occur. Precatalysts Precatalysts are not catalysts but are ''precursors'' to catalysts. Precatalysts are converted in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductive Elimination
Reductive elimination is an elementary step in organometallic chemistry in which the oxidation state of the metal center decreases while forming a new covalent bond between two ligands. It is the microscopic reverse of oxidative addition, and is often the product-forming step in many catalytic processes. Since oxidative addition and reductive elimination are reverse reactions, the same mechanisms apply for both processes, and the product equilibrium depends on the thermodynamics of both directions. General information Reductive elimination is often seen in higher oxidation states, and can involve a two-electron change at a single metal center (mononuclear) or a one-electron change at each of two metal centers (binuclear, dinuclear, or bimetallic). For mononuclear reductive elimination, the oxidation state of the metal decreases by two, while the d-electron count of the metal increases by two. This pathway is common for d8 metals Ni(II), Pd(II), and Au(III) and d6 metals P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ate Complex
In chemistry, an ate complex is a salt formed by the reaction of a Lewis acid with a Lewis base whereby the central atom (from the Lewis acid) increases its valence and gains a negative formal charge. (In this definition, the meaning of valence is equivalent to coordination number). Often in chemical nomenclature the term ''ate'' is suffixed to the element in question. For example, the ate complex of a boron compound is called a borate. Thus trimethylborane and methyllithium react to form the ate compound , lithium tetramethylborate(1-). This concept was introduced by Georg Wittig in 1958. Ate complexes are common for metals, including the transition metals (groups 3-11), as well as the metallic or semi-metallic elements of group 2, 12, and 13. They are also well-established for third-period or heavier elements of groups 14–18 in their higher oxidation states. Ate complexes are a counterpart to onium ions. Lewis acids form ate ions when the central atom reacts with a donor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmetalation
Transmetalation (alt. spelling: transmetallation) is a type of organometallic reaction that involves the transfer of ligands from one metal to another. It has the general form: :M1–R + M2–R′ → M1–R′ + M2–R where R and R′ can be, but are not limited to, an alkyl, aryl, alkynyl, allyl, halogen, or pseudohalogen group. The reaction is usually an irreversible process due to thermodynamic and kinetic reasons. Thermodynamics will favor the reaction based on the electronegativities of the metals and kinetics will favor the reaction if there are empty orbitals on both metals. There are different types of transmetalation including redox-transmetalation and redox-transmetalation/ligand exchange. During transmetalation the metal-carbon bond is activated, leading to the formation of new metal-carbon bonds. Transmetalation is commonly used in catalysis, synthesis of main group complexes, and synthesis of transition metal complexes. Types of transmetalation There are two main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Intermediate
In chemistry, a reaction intermediate or an intermediate is a molecular entity that is formed from the reactants (or preceding intermediates) but is consumed in further reactions in stepwise chemical reactions that contain multiple elementary steps. Intermediates are the reaction product of one elementary step, but do not appear in the chemical equation for an overall chemical equation. For example, consider this hypothetical stepwise reaction: :A + B -> C + D The reaction includes two elementary steps: :A + B -> X :X -> C + D In this example, X is a reaction intermediate. IUPAC definition The IUPAC Gold Book defines an ''intermediate'' as a compound that has a lifetime greater than a molecular vibration that is formed (directly or indirectly) from the reactants and reacts further to give (either directly or indirectly) the products of a chemical reaction. The lifetime condition distinguishes true, chemically distinct intermediates from vibrational states or such transiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Metathesis Reaction
A salt metathesis reaction, sometimes called a double displacement reaction, is a chemical process involving the exchange of bonds between two reacting chemical species which results in the creation of products with similar or identical bonding affiliations. This reaction is represented by the general scheme: :AB + CD -> AD + CB The bond between the reacting species can be either ionic or covalent. Classically, these reactions result in the precipitation of one product. In older literature, the term double decomposition is frequently encountered. The term double decomposition is more specifically used when at least one of the substances does not dissolve in the solvent, as the ligand or ion exchange takes place in the solid state of the reactant. For example: :AX(aq) + BY(s) → AY(aq) + BX(s). Types of reactions Counterion exchange Salt metathesis is a common technique for exchanging counterions. The choice of reactants is guided by a solubility chart or lattice energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |