 |
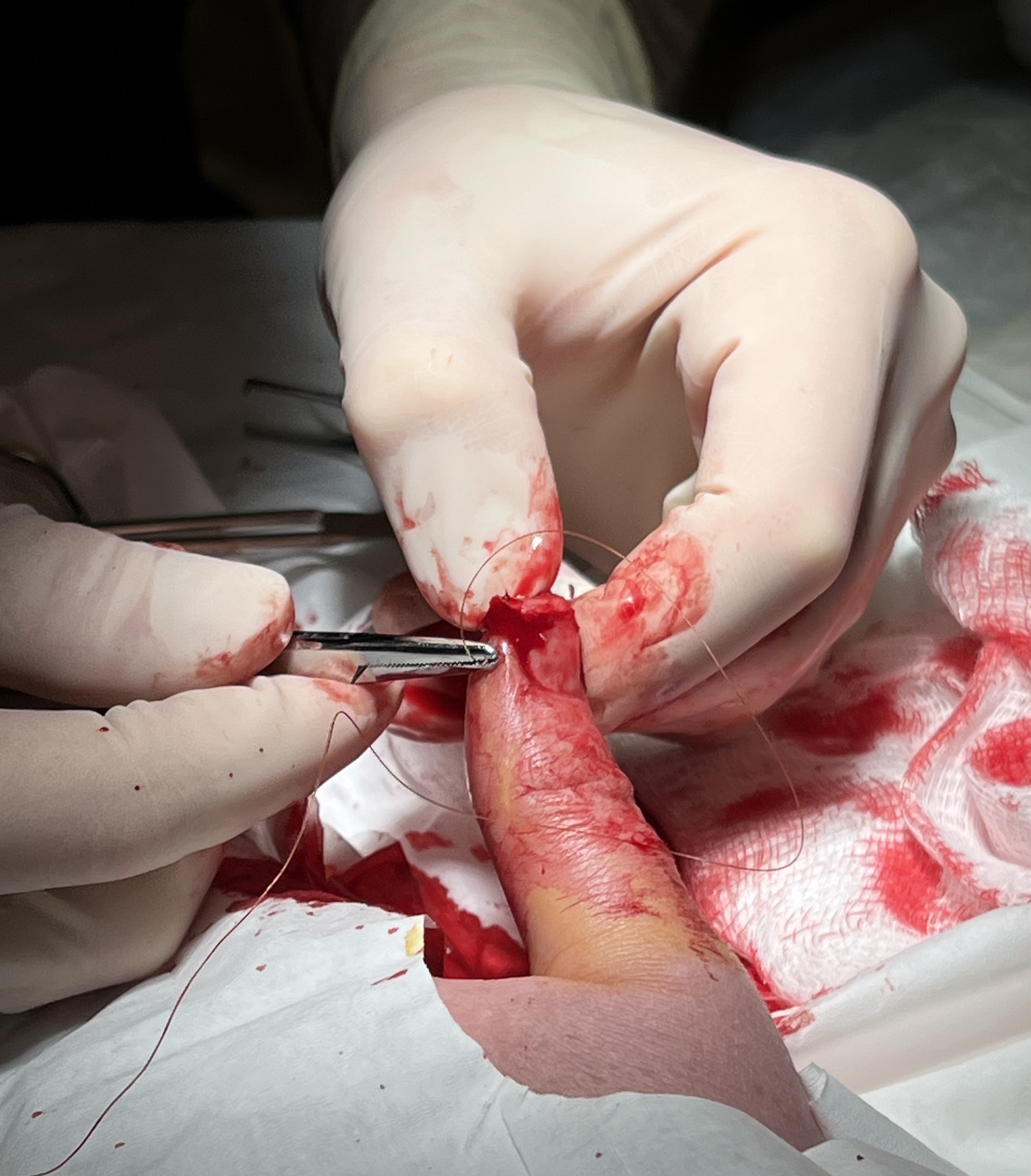
Suture (surgery)
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to different tissues, as well as the memory of the thread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene. Polypropylene belongs to the group of polyolefins and is partially crystalline and non-polar. Its properties are similar to polyethylene, but it is slightly harder and more heat-resistant. It is a white, mechanically rugged material and has a high chemical resistance. Bio-PP is the bio-based counterpart of polypropylene (PP). Polypropylene is the second-most widely produced commodity plastic (after polyethylene). In 2019, the global market for polypropylene was worth $126.03 billion. Revenues are expected to exceed US$145 billion by 2019. The sales of this material are forecast to grow at a rate of 5.8% per year until 2021. History Phillips Petroleum chemists J. Paul Hogan and Robert Banks first demonstrated the polymerization of propylene in 1951. The stereoselective polymerization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
United States Pharmacopeia
The ''United States Pharmacopeia'' (''USP'') is a pharmacopeia (compendium of drug information) for the United States published annually by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (usually also called the USP), a nonprofit organization that owns the trademark and also owns the copyright on the pharmacopeia itself. The ''USP'' is published in a combined volume with the ''National Formulary'' (a formulary) as the USP-NF. If a drug ingredient or drug product has an applicable ''USP'' quality standard (in the form of a ''USP-NF'' monograph), it must conform in order to use the designation "USP" or "NF". Drugs subject to ''USP'' standards include both human drugs ( prescription, over-the-counter, or otherwise) and animal drugs. ''USP-NF'' standards also have a role in US federal law; a drug or drug ingredient with a name recognized in ''USP-NF'' is considered adulterated if it does not satisfy compendial standards for strength, quality or purity. USP also sets standards for di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Reef Knot
The reef knot, or square knot, is an ancient and simple binding knot used to secure a rope or line around an object. It is sometimes also referred to as a Hercules knot. The knot is formed by tying a left-handed overhand knot between two ends, instead of around one end, and then a right-handed overhand knot via the same procedure, or vice versa. A common mnemonic for this procedure is "right over left; left over right", which is often appended with the rhyming suffix "... makes a knot both tidy and tight". Two consecutive overhands tied as described above of the same handedness will make a granny knot. The working ends of the reef knot must emerge both at the top or both at the bottom, otherwise a thief knot results. The reef knot is not recommended for tying two ropes together, because of the potential instability of the knot when not stabilized; something that has resulted in many deaths (see Misuse as a bend). Naming The reef knot is at least 4,000 years old. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Ladder Stitch
A ladder stitch, or mattress stitch, is a stitch which can be used to invisibly close seams from the outside of the garment or item. It is primarily used to close seams on stuffed items, such as pillows, mattresses, down coats or stuffed toys, where after the stuffing is added, there is no access to the back of the fabric. It can also be used to repair split seams on these items or garments, or to alter clothing. It can also be used in surgery Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ... to close an incision in the skin; in this context it's called a running subcuticular suture or running subcuticular closure. References Sewing stitches {{textile-arts-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Horizontal Mattress Stitch
The horizontal mattress stitch is a suture technique used to close wounds. It everts skin well and spreads tension along the wound edge. This makes it ideal for holding together fragile skin as well as skin under high tension such as the distant edges of a large laceration or as the initial holding suture in complicated repairs. The horizontal mattress is so secure that it can compromise blood supply to the tissue contained within the stitch. This can be helpful to prevent wound bleeding, but it can cause strangulation and skin necrosis if tied too tightly. Sometimes cushioning materials can be placed within the stitch to mitigate this effect. Like other mattress stitches, the horizontal mattress can sometimes leave small skin scars called "railroad marks;" for this reason it is rarely used on the face, and is removed promptly even when placed elsewhere. The knot is parallel adjacent to the wound A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves lacerated or punctured skin (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia & Dictionary Of Medicine, Nursing, And Allied Health
The ''Miller-Keane Encyclopedia & Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health'' is written for use by students and health care providers including medics, nurses, and paramedics. The entries are alphabetical and compiled with multidisciplinary collaboration. Illustrations and tables were included from the sixth edition. The latest edition is the seventh, which lists over 40,000 terms and was published in 2005. The book has been reviewed by publications including the '' American Journal of Occupational Therapy'', '' Gastroenterology Nursing'', '' Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases'', '' Hospitals & Health Networks'', and '' Hospital Topics''. References Medical dictionaries {{med-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Corner Stitch
The corner stitch is a common suture technique. It used to close wounds that are angled or Y-shaped without appreciably compromising blood supply to the wound tip. The corner stitch is a variation of the horizontal mattress stitch, and is sometimes called the "half-buried horizontal mattress stitch". The needle enters the skin on one side of the obtuse angle of the wound, passes through the deep dermis of the corner flap, and is re-inserted through the dermis of the other side of the obtuse wound angle. It finally re-emerges through the epidermis The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ... on the side of the obtuse angle, adjacent to the initial entry point. References Surgical stitches {{surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Chest Drain Stitch
A chest tube (also chest drain, thoracic catheter, tube thoracostomy or intercostal drain) is a surgical drain that is inserted through the chest wall and into the pleural space or the mediastinum in order to remove clinically undesired substances such as air (pneumothorax), excess fluid (pleural effusion or hydrothorax), blood (hemothorax), chyle (chylothorax) or pus (empyema) from the intrathoracic space. An intrapleural chest tube is also known as a Bülau drain or an intercostal catheter (ICC), and can either be a thin, flexible silicone tube (known as a "pigtail" drain), or a larger, semi-rigid, fenestrated plastic tube, which often involves a flutter valve or underwater seal. The concept of chest drainage was first advocated by Hippocrates when he described the treatment of empyema by means of incision, cautery and insertion of metal tubes. However, the technique was not widely used until the influenza epidemic of 1918 to evacuate post-pneumonic empyema, which was first do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Running Stitch
The straight or running stitch is the basic stitch in hand-sewing and embroidery, on which all other forms of sewing are based. The stitch is worked by passing the needle in and out of the fabric at a regular distance. All other stitches are created by varying the straight stitch in length, spacing, and direction. Some sources only use the term straight stitch to refer to the individual stitch or its family of related stitches, while others use it interchangeably with or in place of running stitch. Running stitch will never be used to refer to a single stitch since a single running stitch is a straight stitch. Running stitches are most often not visible as they are used to close seams. Running stitch, Holbein or double-running stitch, satin stitch and darning stitch are all classed as straight or flat stitches. Backstitch is also sometimes included in this category.Enthoven, Jacqueline: ''The Creative Stitches of Embroidery'', Van Norstrand Rheinhold, 1964, , p. 29-46 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Horizontal Mattress Stitch
The horizontal mattress stitch is a suture technique used to close wounds. It everts skin well and spreads tension along the wound edge. This makes it ideal for holding together fragile skin as well as skin under high tension such as the distant edges of a large laceration or as the initial holding suture in complicated repairs. The horizontal mattress is so secure that it can compromise blood supply to the tissue contained within the stitch. This can be helpful to prevent wound bleeding, but it can cause strangulation and skin necrosis if tied too tightly. Sometimes cushioning materials can be placed within the stitch to mitigate this effect. Like other mattress stitches, the horizontal mattress can sometimes leave small skin scars called "railroad marks;" for this reason it is rarely used on the face, and is removed promptly even when placed elsewhere. The knot is parallel adjacent to the wound A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves lacerated or punctured skin (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Vertical Mattress Stitch
The vertical mattress stitch, often called vertical Donati stitch (named after the Italian surgeon Mario Donati), is a suture type used to close skin wounds. The advantages of the vertical mattress suture are that it provides closure for both deep and superficial layers, and also allows perfect eversion and vertical opposition of the superficial skin edges. Its disadvantage is a relatively high propensity to dig into skin and cause prominent stitch mark scars. Uses The vertical mattress stitch is most commonly used in anatomic locations which tend to invert, such as the posterior aspect of the neck, and sites of greater skin laxity such as closure of lax skin after removing a dermoid cyst or reduced subcutaneous tissue (eg, the shin) that do not provide adequate subcutaneous tissue for dermal closure. It is useful for deep lacerations, where it can replace two layers of deep and superficial sutures. It can help bring the deep layers together alone, allowing several simple interru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Simple Interrupted Stitch
The simple interrupted stitch is a suturing technique used to close wounds. It is the most commonly used technique in the closure of skin. It is known as an interrupted stitch Stitch, Stitches or Stitched may refer to: Medical uses *Stitch, a surgical suture, a medical device used to hold body tissues together after an injury or surgery ** Cervical cerclage, also known as a cervical stitch *Husband stitch, a purported ... because the individual stitches aren't connected; they are separate. Placing and tying each stitch individually is time-consuming, but this technique keeps the wound together even if one suture fails. It is simple, and relatively easy to place. A surgeon's knot or knots cross the wound perpendicularly. The knots should not be left over the wound, but placed to one side in order to avoid scarring and to make the removal of the stitches easier. Image:Simple interrupted suture.svg, Procedure References {{reflist Surgical stitches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |