|
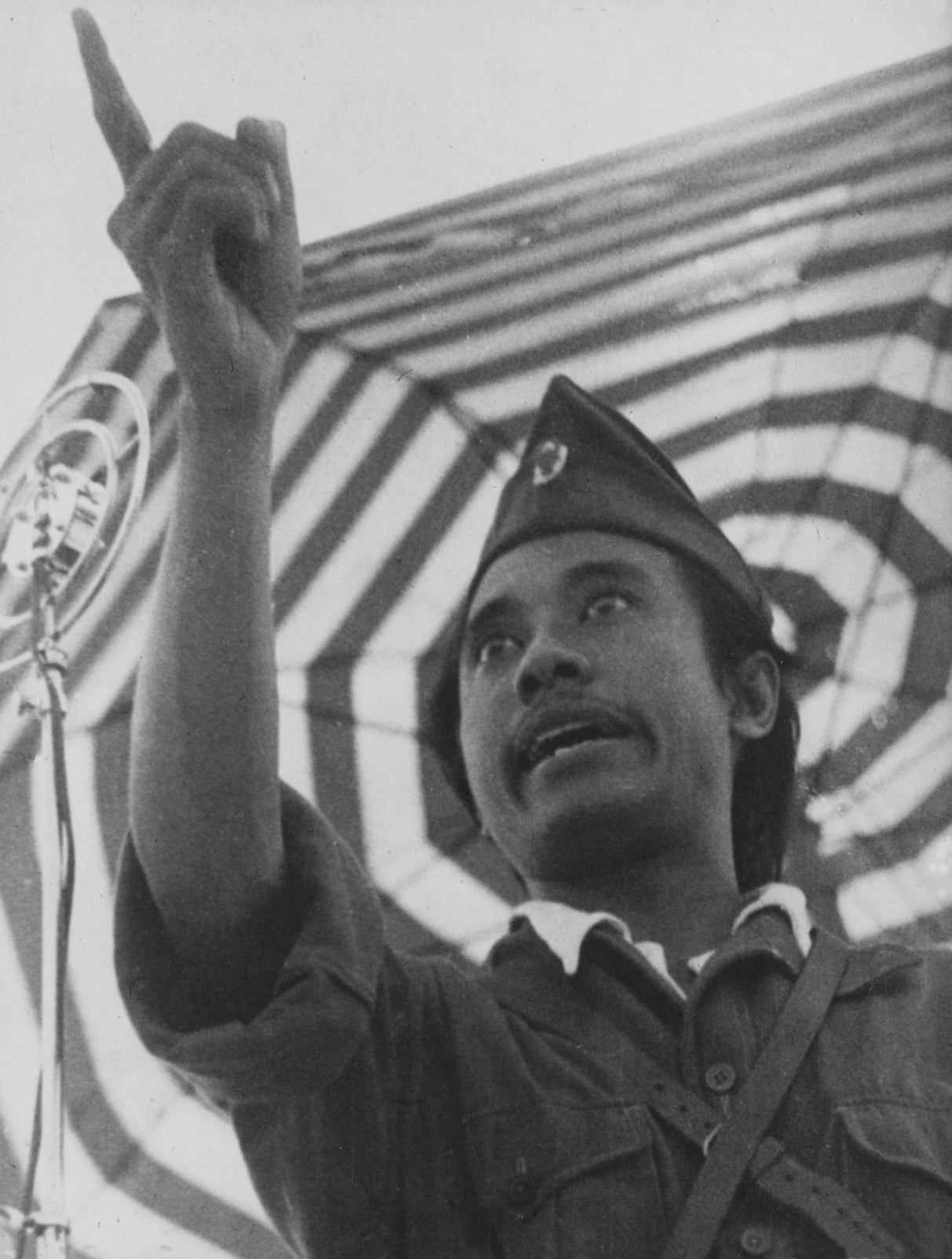
Sutomo
Sutomo (3 October 1920 – 7 October 1981), also known as Bung Tomo (meaning Comrade or Brother Tomo), is best known for his role as an Indonesian military leader during the Indonesian National Revolution against the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. He played a central role in Battle of Surabaya when the British attacked the city in October and November 1945. Early life Sutomo was born in Kampung Blauran in the centre of Surabaya to a clerk father, Kartawan Tjiptowidjojo, and mother of mixed Javanese, Sundanese and Madurese descent. He had received Dutch secondary education before the Japanese occupation. Alongside menial jobs, he joined the Indonesian Scouting organisation and at the age of seventeen as the second Pramuka Garuda; a rank achieved by only three Indonesians before the Japanese occupation during World War II. Japanese occupation During the Japanese occupation period, Sutomo was worked for the Dōmei Tsushin (the official news agency of the Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bersiap
''Bersiap'' is the name given by the Dutch to a violent and chaotic phase of the Indonesian National Revolution following the end of World War II. The Indonesian word ''bersiap'' means 'get ready' or 'be prepared'. The ''Bersiap'' period lasted from August 1945 to November 1947. In Indonesia, other terms aside from ''bersiap'' are commonly used, such as ''gedoran'' in Depok, ''ngeli'' in Banten and surrounding West Java, and ''gegeran'' and ''dombreng'' in Central Java. The period started with revolutionary violence occurring during the increasing power vacuum left by the retreating Japanese occupational forces and the gradual buildup of a British military presence but before the official handover to a Dutch military presence. The term refers to that period when Sukarno declared Indonesian independence on 17 August 1945. Thousands of Eurasian people were killed by Indonesian natives. Many people were also killed among non-European groups such as Chinese and native Indonesians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hero Of Indonesia
National Hero of Indonesia ( id, Pahlawan Nasional Indonesia) is the highest-level title awarded in Indonesia. It is posthumously given by the Government of Indonesia for actions which are deemed to be heroic, defined as "actual deeds which can be remembered and exemplified for all time by other citizens" or "extraordinary service furthering the interests of the state and people". The Ministry of Social Affairs gives seven criteria which an individual must fulfill, as follows: #Have been an Indonesian citizen who is deceased and, during his lifetime, led an armed struggle or produced a concept or product useful to the state; #Have continued the struggle throughout his life and performed above and beyond the call of duty; #Have had a wide-reaching impact through his actions; #Have shown a high degree of nationalism; #Have been of good moral standing and respectable character; #Never surrendered to his enemies; and #Never committed an act which taints his or her legacy. Nominations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
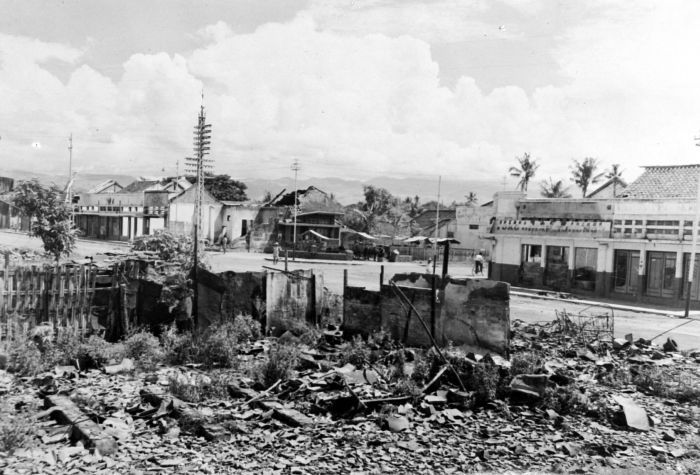
Battle Of Surabaya
The Battle of Surabaya was fought between regular infantry and militia of the Indonesian nationalist movement and British and British Indian troops as a part of the Indonesian National Revolution against the re-imposition of Dutch colonial rule. The peak of the battle was in November 1945. The battle was the largest single battle of the revolution and became a national symbol of Indonesian resistance. Considered a heroic effort by Indonesians, the battle helped galvanise Indonesian and international support for Indonesian independence. 10 November is celebrated annually as Heroes' Day (). By the time the Allied forces arrived at the end of October 1945, the ''Pemuda'' ("youth") foothold in Surabaya City was described as "a strong unified fortress". Fighting broke out on 30 October after the British commander, Brigadier A. W. S. Mallaby was killed in a skirmish. The British retaliated with a co-ordinated sweep that began on 10 November, under the cover of air attacks. Althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian National Revolution
The Indonesian National Revolution, or the Indonesian War of Independence, was an armed conflict and diplomatic struggle between the Republic of Indonesia and the Dutch Empire and an internal social revolution during Aftermath of WWII, postwar and Dutch East Indies#World War II and independence, postcolonial Indonesia. It took place between Indonesian Declaration of Independence, Indonesia's declaration of independence in 1945 and the Netherlands' Dutch–Indonesian Round Table Conference, transfer of sovereignty over the Dutch East Indies to the Republic of the United States of Indonesia at the end of 1949. The four-year struggle involved sporadic but bloody armed conflict, internal Indonesian political and communal upheavals, and two major international diplomatic interventions. Dutch military forces (and, for a while, the forces of the World War II Allies, World War II allies) were able to control the major towns, cities and industrial assets in Republican heartlands on Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian People's Revolutionary Front
Indonesian People's Revolutionary Front ( id, Barisan Pemberontakan Rakyat Indonesia), abbreviated as BPRI, is an Indonesian militia founded by Sutomo with its headquarters in Surabaya on 12 October, 1945. History The Indonesian People's Rebellion was aimed at realizing and defending the Proclamation of Indonesian Independence. The term "revolutionary front" ( id, barisan pemberontakan), and not "warrior front" ( id, barisan pejuang), was chosen because since the Dutch held power over the local population, who were ordinary people, and wanted to emphasise the fact their militia was led first and foremost by the common man. BPRI rallied the people's resistance against the Dutch who wanted to reign Indonesia after the Surrender of Japan in World War II. The most prominent role of BPRI was its involvement in the Battle of Surabaya. At that time, Sutomo delivered a speech through a radio broadcast that rallied the people in Surabaya against the army of Allied forces. Branches B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo People
The Indo people ( nl, Indische Nederlanders, or Indos) are Eurasian people living in or connected with Indonesia. In its narrowest sense, the term refers to people in the former Dutch East Indies who held European legal status but were of mixed Dutch and indigenous Indonesian descent as well as their descendants today. In the broadest sense, an Indo is anyone of mixed European and Indonesian descent. Indos are associated with colonial culture of the former Dutch East Indies, a Dutch colony in Southeast Asia and a predecessor to modern Indonesia after its proclamation of independence shortly after World War II. The term was used to describe people acknowledged to be of mixed Dutch and Indonesian descent, or it was a term used in the Dutch East Indies to apply to Europeans who had partial Asian ancestry. "Indos–people of Dutch descent who stayed in the new republic Indonesia after it gained independence, or who emigrated to Indonesia after 1949–are called 'Dutch-Indones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatah Jasin
Abdul Fattah Jasin or Fatah Jasin (26 June 19153 May 1980) was an Indonesian politician and Islamic cleric who served as Minister of Social Affairs during the Second Ali Sastroamidjojo Cabinet. Biography Early career Jasin was born in Surabaya on 26 June 1915 and received Islamic education in madrasa and pesantren. He was the son of a well-known ulama in Surabaya. After completing his education, he taught at a madrasa in Sampang before returning to Surabaya, where he taught at a madrasa affiliated with Nahdlatul Ulama. From 1939 until the Japanese takeover in 1942, he was a merchant in the city, and between 1938 and 1942 he was a member of the Gerindo political organization. Jasin was arrested and apparently sentenced to death during the Japanese occupation by the Japanese forces, but the surrender of Japan and the ensuing independence of Indonesia occurred before he could be executed. Old Order During the Indonesian National Revolution, he was for a time chief of political edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
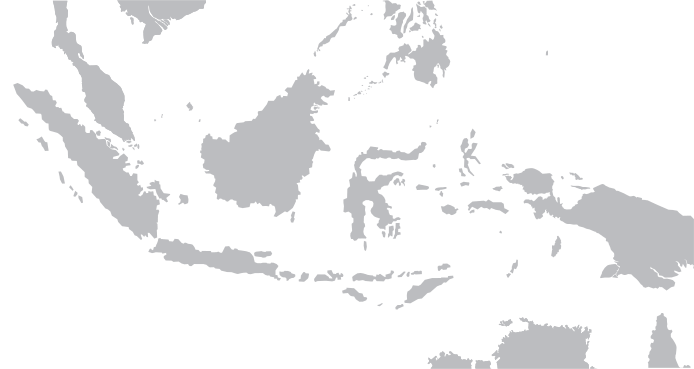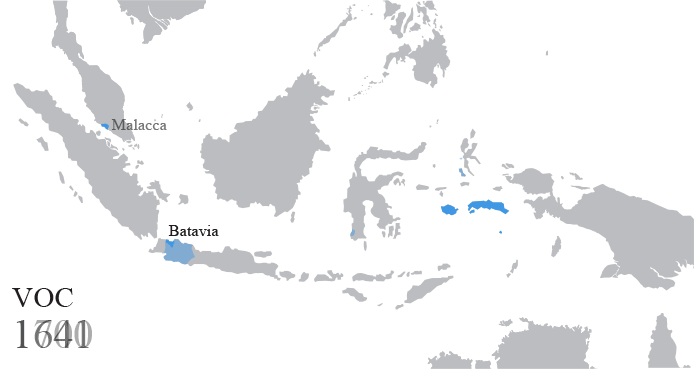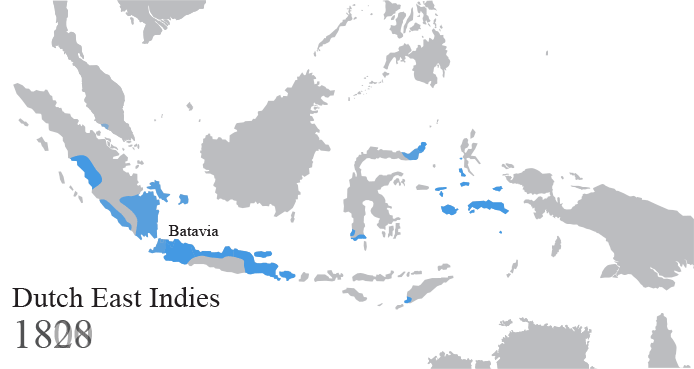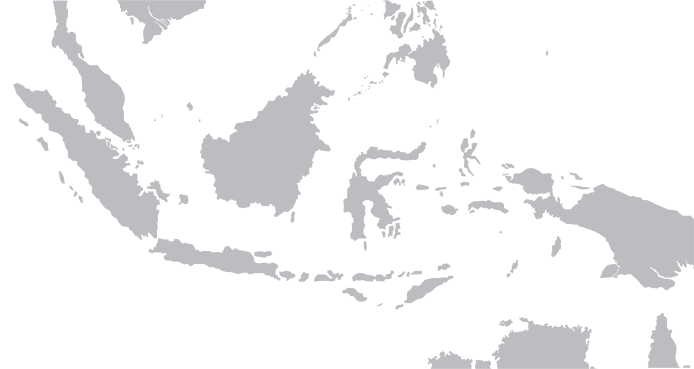
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budi Utomo
, native_name_lang = , logo = , logo_size = , logo_alt = , logo_caption = , image = , image_size = , alt = , caption = , map = , map_size = , map_alt = , map_caption = , map2 = , map2_size = , map2_alt = , map2_caption = , abbreviation = , nickname = , pronounce = , pronounce ref = , pronounce comment = , pronounce 2 = , named_after = , predecessor = , merged = , successor = , formation = 20 May 1908 , founder = , founding_location = , dissolved = 1935 , merger = , type = Nationalist organization , tax_id = , registration_id = , status = , purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pramuka Garuda
The rank insignia system of the Indonesian Scouting movement Gerakan Pramuka Indonesia is by and large militarized in traditions and outfit. Much is left to the traditions of specific groups. Some of them do not grant some of the ranks to its members, while others name them differently; the very look of the insignia may differ from group to group. Merit badges ''Tanda Kecakapan Khusus'' (TKK) are merit badge awards earned by youth members of the Gerakan Pramuka organization, based on activities within an area of study by completing Special Skills Requirements (SSR/SKK). Some special TKK are also required in order to achieve the Eagle Scout award. Members who have earned more than five merit badges display them on a sash which may be optionally worn diagonally across the front of the Boy Scout uniform from right side to left side. Sashes are usually only worn for ceremonial occasions. Level TKK for Boy Scout, and Rover Scout are divided into three levels: *For the lowest level, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dōmei Tsushin
was the official news agency of the Empire of Japan. History and development Dōmei was the end result of years of efforts by Japanese journalists and business leaders to create a national news agency in Japan that could compete with (and if necessary counter) Reuters and other internationally recognized news agencies on a global basis. After the Manchurian Incident of 1931, president Yukichi Iwanaga (岩永 裕吉 ''Iwanaga Yūkichi'') of the Nihon Shimbun Rengosha (日本新聞聯合社 Associated Press, or “Rengo”) proposed the merger of his news agency with the Nihon Dempo Tsushinsha (日本電報通信社 Japan Telegraphic News Agency, or “Dentsu”). Despite government backing for the move, the merger was resisted by Dentsu president Hoshio Mitsunaga ( 光永 星郎 ''Mitsunaga Hoshio''), who was reluctant to give up control of his company’s lucrative advertising business, and by concerns that a merger would threaten his advertising customer base – the provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_di_Republik_Indonesia%2C_p379.jpg)






_2.jpg)