|
Sura 71
A ''surah'' (; ar, سورة, sūrah, , ), is the equivalent of "chapter" in the Quran, Qur'an. There are 114 ''surahs'' in the Quran, each divided into ''ayah, ayats'' (verses). The chapters or ''surahs'' are of unequal length; the shortest surah (''Al-Kawthar'') has only three verses while the longest (''Al-Baqara'') contains 286 verses.Muhammad Mustafa Al-A'zami (2003), ''The History of The Qur'anic Text: From Revelation to Compilation: A Comparative Study with the Old and New Testaments'', p.70. UK Islamic Academy. . Of the 114 chapters in the Quran, 86 are classified as Meccan surah, Meccan, while 28 are Medinan surah, Medinan. This classification is only approximate in regard to the location of revelation; any chapter revealed after migration of Muhammad to Medina (''Hegira, Hijrah'') is termed Medinan and any revealed before that event is termed Meccan. The Meccan chapters generally deal with faith and scenes of the Afterlife, Hereafter while the Medinan chapters are more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary'' is a large American dictionary, first published in 1966 as ''The Random House Dictionary of the English Language: The Unabridged Edition''. Edited by Editor-in-chief Jess Stein, it contained 315,000 entries in 2256 pages, as well as 2400 illustrations. The CD-ROM version in 1994 also included 120,000 spoken pronunciations. History The Random House publishing company entered the reference book market after World War II. They acquired rights to the ''Century Dictionary'' and the ''Dictionary of American English'', both out of print. Their first dictionary was Clarence Barnhart's ''American College Dictionary'', published in 1947, and based primarily on ''The New Century Dictionary'', an abridgment of the ''Century''. In the late 1950s, it was decided to publish an expansion of the ''American College Dictionary'', which had been modestly updated with each reprinting since its publication. Under editors Jess Stein and Laurence Ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Jeffery
Arthur Jeffery (18 October 1892 in Melbourne, Australia – 2 August 1959 in South Milford, Canada) was a Protestant Australian professor of Semitic languages from 1921 at the School of Oriental Studies in Cairo, and from 1938 until his death jointly at Columbia University and Union Theological Seminary in New York City. He is the author of extensive historical studies of Middle Eastern manuscripts. His important works include ''Materials for the History of the Text of the Qur'an: The Old Codices'', which catalogs all surviving documented variants of the orthodox Quran text; and ''The Foreign Vocabulary of the Qur'an'', which traces the origins of 318 foreign (non-Arabic) words found in the Qur'an. Some of Jeffery's studies are included in '' The Origins of The Koran: Classic Essays on Islam’s Holy Book'', edited by Ibn Warraq. They are also discussed in Mohar Ali Muhammad Mohar Ali ( bn, মোহাম্মদ মোহার আলী); 1929–2007) was a British Ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Bell (Arabist)
Richard Bell (1876 – 1952) was a British Arabist. He was lecturer in Arabic at the University of Edinburgh and also served as Minister of Newton Wamphray, a small country parish from 1907 to 1921. On returning to Edinburgh, he spent his remaining years at the university in the study of the Qur'an The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing. .... Between 1937 and 1939 he published a translation of the Qur'an, and in 1953 his ''Introduction to the Qur'an'' was published (revised in 1970 by W. Montgomery Watt). Both works have been influential in Quranic studies in the west. He was an early investigator of Christian influences on the development of Islam. Works *''The Qur'an. Translated, with a critical re-arrangement of the Surahs'' 2 vols, Edinburgh University Press, 1937 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Nöldeke
Theodor Nöldeke (; born 2 March 1836 – 25 December 1930) was a German orientalist and scholar. His research interests ranged over Old Testament studies, Semitic languages and Arabic, Persian and Syriac literature. Nöldeke translated several important works of oriental literature and during his lifetime was considered an important orientalist. He wrote numerous studies (including on the Qur’ān) and contributed articles to the Encyclopædia Britannica. Among the projects Nöldeke collaborated on was Michael Jan de Goeje’s published edition of al-Tabari's ''Tarikh'' ("Universal History"), for which he translated the Sassanid-era section. This translation remains of great value, particularly for the extensive supplementary commentary. His numerous students included Charles Cutler Torrey, Louis Ginzberg and Friedrich Zacharias Schwally. He entrusted Schwally with the continuation of his standard work "The History of the Qur’ān". Biography Nöldeke was born in Harburg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farewell Pilgrimage
The Farewell Pilgrimage ( ar, حِجَّة ٱلْوَدَاع, Ḥijjatu Al-Wadāʿ) refers to the one Hajj pilgrimage that Muhammad performed in the Islamic year 10 AH, following the Conquest of Mecca. Muslims believe that verse 22:27 of the Quran brought about the intent to perform Hajj in Muhammad that year. When Muhammad announced this intent, approximately 100,000 of his ''Sahaba'' gathered in Medina to perform the annual pilgrimage with him. Muhammad performed Hajj al-Qiran. According to the opinion of Sunnis, Hajj al- Qirān is type of Hajj in which Umrah and Hajj are performed together. On the 9th of Dhu al-Hijjah, the Day of Arafah, Muhammad delivered the Farewell Sermon atop the Mount Arafat outside Mecca. Muhammad's pilgrimage defined several of the rituals and rites of the Hajj and is one of the most well-recorded moments of his life, later transmitted through his ''sahaba,'' who accompanied him on this occasion, observing every gesture of Muhammad, which has become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Uhud
The Battle of Uhud ( ar, غَزْوَة أُحُد, ) was fought on Saturday, 23 March 625 AD (7 Shawwal, 3 AH), in the valley north of Mount Uhud.Watt (1974) p. 136. The Qurayshi Meccans, led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, commanded an army of 3,000 men toward Muhammad's stronghold in Medina. The battle was the only battle throughout the Muslim–Quraysh War in which the Muslims did not manage to defeat their enemy and it came just a year after the Battle of Badr. Abu Sufyan became the ''de facto'' leader of the Quraish after the death of Amr ibn Hishām at Badr nine months prior. Wanting to avenge the Meccan's losses at the Battle of Badr, he marched upon Medina from Makkah on 10 December 624 AD with a force three times stronger than that of the Meccans at Badr. Another reason for the battle was to protect the trade route of Abu Sufyan's caravans. The Battle of Uhud was the second military encounter between the Meccans and the Muslims and the first one in which the Muslims were on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
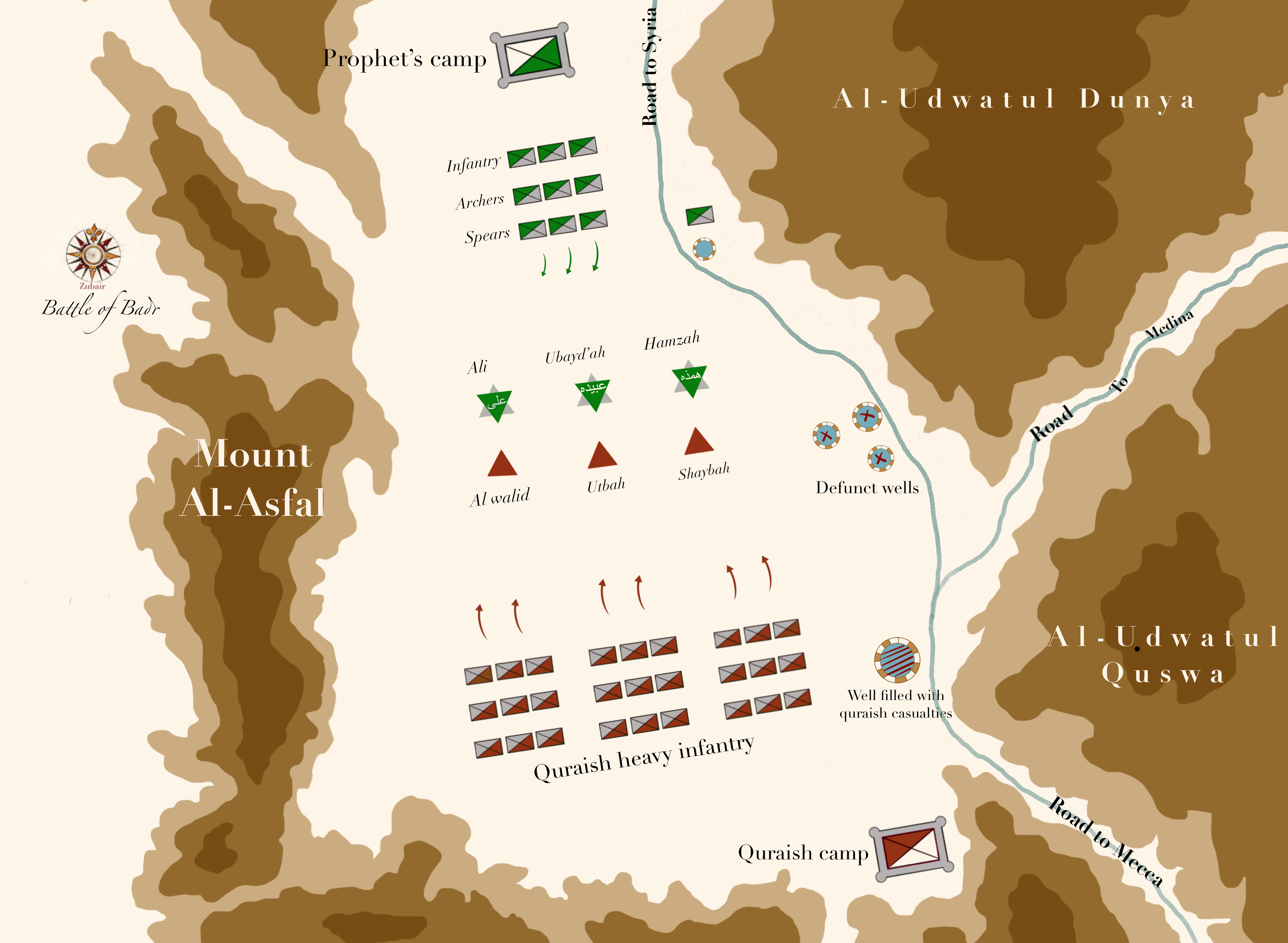
Battle Of Badr
The Battle of Badr ( ar, غَزْوَةُ بَدِرْ ), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ) in the Quran, Qur'an and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan (calendar month), Ramadan, 2 Anno Hegirae, AH), near the present-day city of Badr, Saudi Arabia, Badr, Madinah Province, Al Madinah Province in Saudi Arabia. Muhammad, commanding an army of his Companions of the Prophet, Sahaba, defeated an army of the Quraysh led by Amr ibn Hishām, better known as Abu Jahl. The battle marked the beginning of the six-year war between Muhammad and his tribe. Prior to the battle, the Muslims and the Meccans had fought several smaller skirmishes in late 623 and early 624. Muhammad took keen interest in capturing Meccan caravans after Hegira, his migration to Medina, seeing it as repayment for his people, the Muhajirun. A few days before the battle, when he learnt of a Makkan caravan returning from the Levant led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, Muhammad gathered a small E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hijra (Islam)
The Hijrah or Hijra () was the journey of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his followers from Mecca to Medina. The year in which the Hijrah took place is also identified as the epoch of the Lunar Hijri and Solar Hijri calendars; its date equates to 16 July 622 in the Julian calendar. The Arabic word ''hijra'' means "departure" or "migration", among other definitions. It has been also transliterated as Hegira in medieval Latin, a term still in occasional use in English. Early in Muhammad's preaching of Islam, his followers only included his close friends and relatives. Following the spread of his religion, Muhammad and his small faction of Muslims faced several challenges including a boycott of Muhammad's clan, torture, killing, and other forms of religious persecution by the Meccans. Toward the end of the decade, Abu Talib, Muhammad's uncle, who supported him amidst the leaders of Mecca, died. Finally, the leaders of Mecca ordered the assassination of Muhammad, which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asian
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan are all unrecognised by at least one other East Asian state due to severe ongoing political tensions in the region, specifically the division of Korea and the political status of Taiwan. Hong Kong and Macau, two small coastal quasi-dependent territories located in the south of China, are officially highly autonomous but are under Chinese sovereignty. Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau are among the world's largest and most prosperous economies. East Asia borders Siberia and the Russian Far East to the north, Southeast Asia to the south, South Asia to the southwest, and Central Asia to the west. To the east is the Pacific Ocean and to the southeast is Micronesia (a Pacific Ocean island group, class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wm Theodore De Bary
William Theodore de Bary (; August 9, 1919 – July 14, 2017) was an American Sinologist and scholar of East Asian philosophy who was a professor and administrator at Columbia University for nearly 70 years. De Bary graduated from Columbia College in 1941, where he was a student in the first year of Columbia's famed Literature Humanities course. He then briefly took up graduate studies at Harvard University before leaving to serve in American military intelligence in the Pacific Theatre of World War Two. Upon his return, he resumed his studies at Columbia, where he completed his Ph.D. in 1953. In order to create text books for the non-Western version of the Columbia humanities course, he drew together teams of scholars to translate original source material, ''Sources of Chinese Tradition'' (1960), ''Sources of Japanese Tradition'', and ''Sources of Indian Tradition''. His extensive publications made the case for the universality of Asian values and a tradition of democratic va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israr Ahmed
Israr Ahmad ( ur, اسرار احمد; 26 April 1932 – 14 April 2010) was a Pakistani Islamic theologian, philosopher, and Islamic scholar who was followed particularly in South Asia as well as by South Asian Muslims in the Middle East, Western Europe, and North America. He was the founder of Tanzeem-e-Islami, an offshoot of the Jamaat-e-Islami. He wrote about sixty books about Islam and Pakistan. As of 2017, twenty nine books have been translated into several other languages, including in English. Early life and education Israr Ahmad was born on 26 April 1932 in Agarwal family in Hisar, Punjab. His father was a civil servant in the British government who relocated his family from Hisar to Montgomery, now Sahiwal, Punjab Province of Pakistan. After graduating from a local high school, Ahmad moved to Lahore to attend the King Edward Medical University in 1950. He received his MBBS degree from King Edward Medical University in 1954 and began practising medicine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |