|
Supraorbital Shield
{{disambig ...
Supraorbital refers to the region immediately above the eye sockets, where in humans the eyebrows are located. It denotes several anatomical features, such as: *Supraorbital artery *Supraorbital foramen *Supraorbital gland *Supraorbital nerve *Supraorbital ridge *Supraorbital vein The supraorbital vein is a vein of the forehead. It communicates with the frontal branch of the superficial temporal vein. It passes through the supraorbital notch, and merges with the angular vein to form the superior ophthalmic vein. The supra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Socket
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is , of which the eye occupies . The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves. Structure The orbits are conical or four-sided pyramidal cavities, which open into the midline of the face and point back into the head. Each consists of a base, an apex and four walls."eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2009 Openings There are two important foramina, or windows, two important fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyebrow
An eyebrow is an area of short hairs above each eye that follows the shape of the lower margin of the brow ridges of some mammals. In humans, eyebrows serve two main functions: first, communication through facial expression, and second, prevention of sweat, water, and other debris from falling down into the eye socket. It is common for people to modify their eyebrows by means of hair removal and makeup. Functions A number of theories have been proposed to explain the function of the eyebrow in humans. One approach suggests its main function is to prevent moisture (mostly sweat and rain) from flowing into the eye. Another theory holds that clearly visible eyebrows provided safety from predators when early hominid groups started sleeping on the ground. Recent research, however, suggests eyebrows in humans developed as a means of communication and that this is their primary function. Humans developed a smooth forehead with visible, hairy eyebrows capable of a wide range of movemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Artery
The supraorbital artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It passes anteriorly within the orbit to exit the orbit through the supraorbital foramen or notch alongside the supraorbital nerve, splitting into two terminal branches which go on to form anastomoses with arteries of the head. Structure Origin The supraorbital artery arises from the ophthalmic artery. Course and relations It travels anteriorly in the orbit by passing superior to the eye and medial to the superior rectus and levator palpebrae superioris. It then joins the supraorbital nerve to jointly pass between the periosteum of the roof of the orbit and the levator palpebrae superioris towards the supraorbital foramen or notch. After passing through the supraorbital foramen or notch, it often splits into a superficial branch and a deep branch. Distribution The supraorbital artery contributes arterial supply to: the superior rectus muscle, superior oblique muscle, levator palpebrae muscles, periorbita, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Foramen
The supraorbital foramen, is a bony elongated opening located above the orbit (eye socket) and under the forehead. It is part of the frontal bone of the skull. The supraorbital foramen lies directly under the eyebrow. In some people this foramen is incomplete and is then known as the supraorbital notch. Structure The supraorbital foramen is a small groove at superior and medial margin of the orbit in the frontal bone. It is part of the frontal bone of the skull. It arches transversely below the superciliary arches and is the upper part of the brow ridge. It is thin and prominent in its lateral two-thirds, but rounded in its medial third. Between these two parts, the supraorbital nerve, the supraorbital artery, and the supraorbital vein pass. The supraorbital nerve divides into superficial and deep branches after it has left the supraorbital foramen. Additional images File:Gray135.png, Frontal bone. Inner surface. File:Gray1193.svg, Side view of head, showing surface relations of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Gland
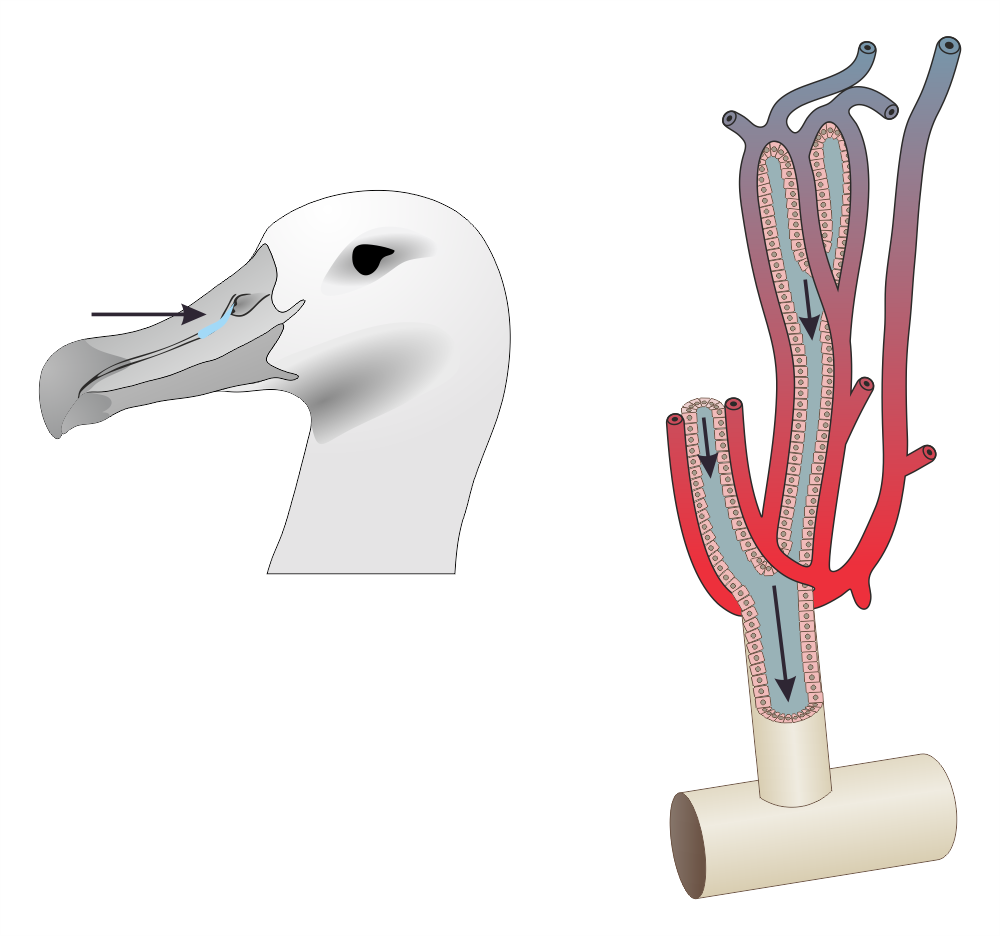
The supraorbital gland is a type of lateral nasal gland found in some species of marine birds, particularly penguins, which removes sodium chloride from the bloodstream. The gland's function is similar to that of the kidneys, though it is much more efficient at removing salt, allowing penguins to survive without access to fresh water. Contrary to popular belief, the gland does not directly convert saltwater to freshwater. The term ''supraorbital'' refers to the area just above the eye socket (which is known as the orbit). Living in saltwater environments would naturally pose a large problem for penguins because the ingestion of saltwater would be detrimental to a penguin's health. Although penguins do not directly drink water, it is taken in when they engulf prey. As a result, saltwater enters their system and must be effectively excreted. The supraorbital gland has thus enabled the penguins' survival in such environments due to its water-filtering capability. The gland is lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Nerve
The supraorbital nerve is one of two branches of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve. The other branch of the frontal nerve is the supratrochlear nerve. Structure The supraorbital nerve branches from the frontal nerve midway between the base and apex of the orbit. It travels anteriorly above the levator palpebrae superioris and exits the orbit through the supraorbital foramen (or notch) in the superior margin orbit. It exits the orbit lateral to the supratrochlear nerve. It then ascends onto the forehead beneath the corrugator supercilii and frontalis muscles and divides into a medial branch and lateral branch. Function The supraorbital nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin of the lateral forehead and upper eyelid, as well as the conjunctiva of the upper eyelid and mucosa of the frontal sinus The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Ridge
The brow ridge, or supraorbital ridge known as superciliary arch in medicine, is a bony ridge located above the eye sockets of all primates. In humans, the eyebrows are located on their lower margin. Structure The brow ridge is a nodule or crest of bone situated on the frontal bone of the skull. It forms the separation between the forehead portion itself (the squama frontalis) and the roof of the eye sockets (the pars orbitalis). Normally, in humans, the ridges arch over each eye, offering mechanical protection. In other primates, the ridge is usually continuous and often straight rather than arched. The ridges are separated from the frontal eminences by a shallow groove. The ridges are most prominent medially, and are joined to one another by a smooth elevation named the glabella. Typically, the arches are more prominent in men than in women, and vary between different ethnic groups. Behind the ridges, deeper in the bone, are the frontal sinuses. Terminology The brow ridges, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |