|
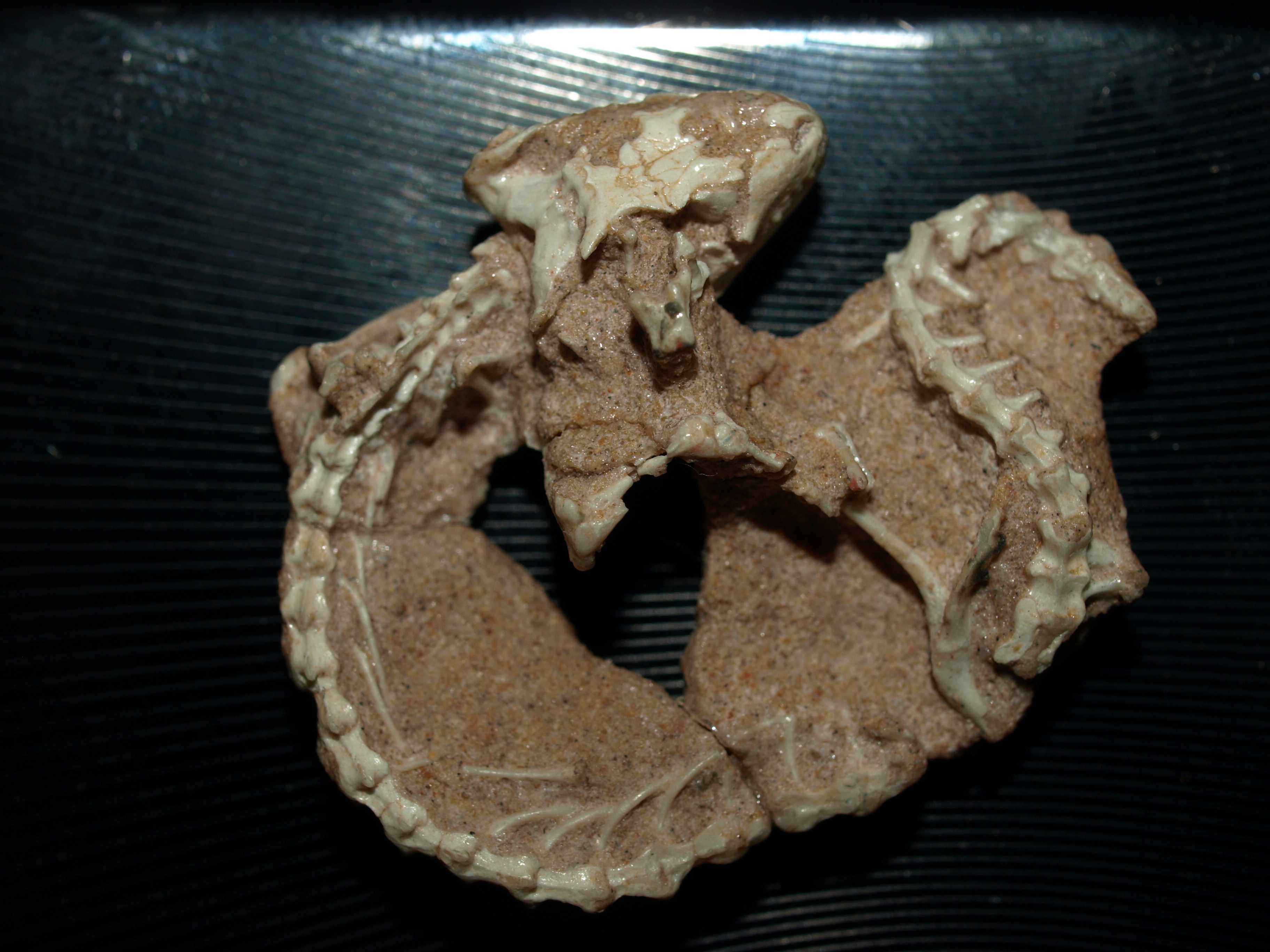
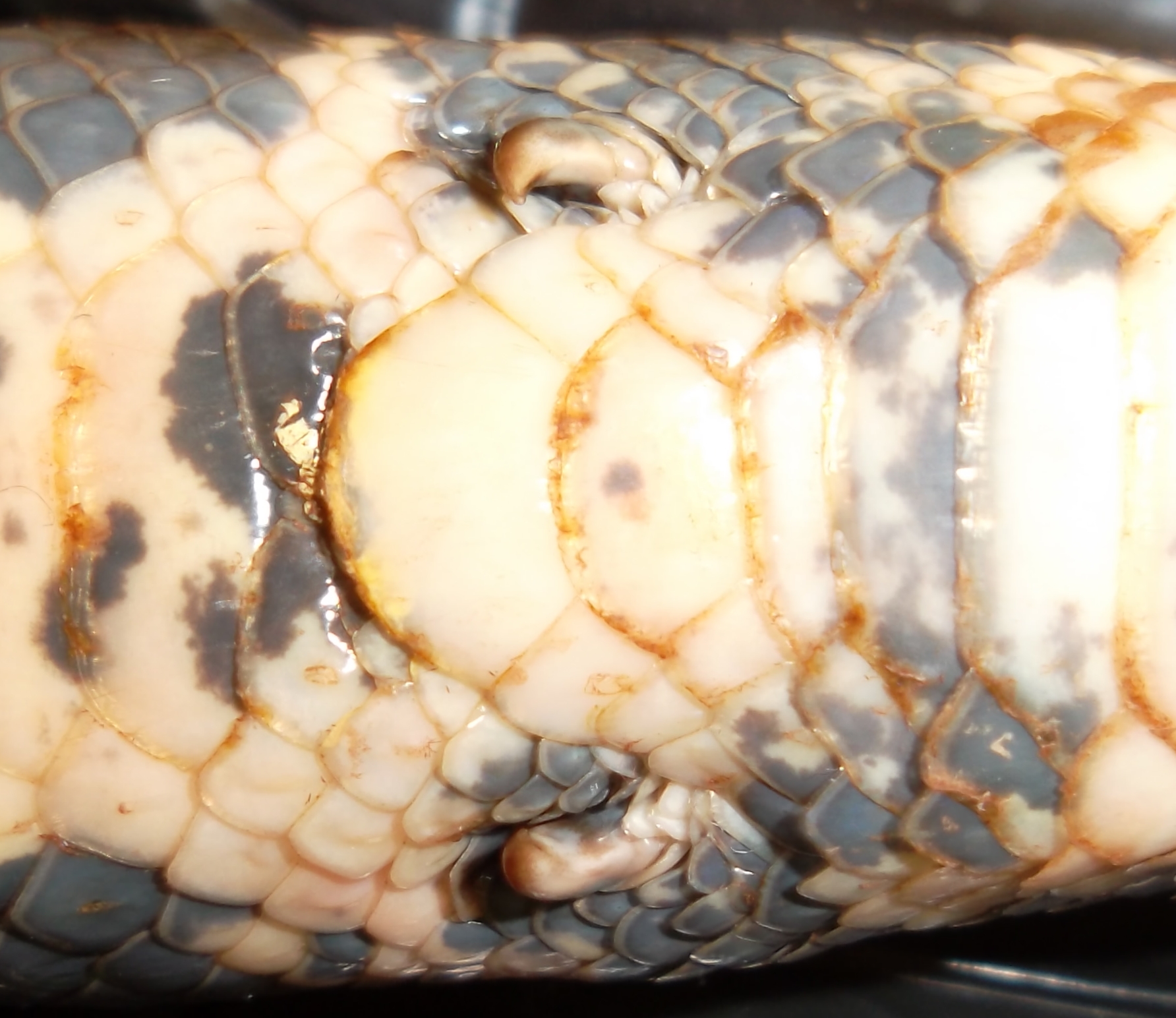
Supraocular Scales
In scaled reptiles, supraocular scales are (enlarged) scales on the crown immediately above the eye.Mallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G. 2003. True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers. Malabar, Florida: Krieger Publishing Company. 359 pp. . The size and shape of these scales are among the many characteristics used to differentiate species from each another. In many species of boids and viperids, the supraoculars are heavily fragmented. In others, such as the colubrids and elapids, they are enlarged. See also * Ocular scales * Snake scales * Anatomical terms of location Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ... References {{Reflist Snake scales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it is also the second-largest order of extant (living) vertebrates, after the perciform fish. Members of the order are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very wide to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamata is the most variably sized order of reptiles, ranging from the dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the Reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') and the now-extinct mosasaurs, which reached lengths over . Among other reptiles, squamates are most close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boidae
The Boidae, commonly known as boas or boids, are a family of nonvenomous snakes primarily found in the Americas, as well as Africa, Europe, Asia, and some Pacific Islands. Boas include some of the world's largest snakes, with the green anaconda of South America being the heaviest and second-longest snake known; in general, adults are medium to large in size, with females usually larger than the males. Five subfamilies, comprising 12 genera and 49 species, are currently recognized. The Old Tupi name for such snakes was mbói, which figures in the etymology of names such as ''jibóia'' and ''boitatá'' (the Brazilian name for the mythical giant anaconda). Description Like the pythons, boas have elongated supratemporal bones. The quadrate bones are also elongated, but not as much, while both are capable of moving freely so when they swing sideways to their maximum extent, the distance between the hinges of the lower jaw is greatly increased.Parker HW, Grandison AGC. 1977. Snakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viperids
The Viperidae (vipers) are a family of snakes found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous and have long (relative to non-vipers), hinged fangs that permit deep penetration and injection of their venom. Four subfamilies are currently recognized. They are also known as viperids. The name "viper" is derived from the Latin word ''vipera'', -''ae'', also meaning viper, possibly from ''vivus'' ("living") and ''parere'' ("to beget"), referring to the trait viviparity (giving live birth) common in vipers like most of the species of Boidae. Description All viperids have a pair of relatively long solenoglyphous (hollow) fangs that are used to inject venom from glands located towards the rear of the upper jaws, just behind the eyes. Each of the two fangs is at the front of the mouth on a short maxillary bone that can rotate back and forth. When not in use, the fangs fold back against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elapids
Elapidae (, commonly known as elapids ; grc, ἔλλοψ ''éllops'' "sea-fish") is a family of snakes characterized by their permanently erect fangs at the front of the mouth. Most elapids are venomous, with the exception of the genus Emydocephalus. Many members of this family exhibit a threat display of rearing upwards while spreading out a neck flap. Elapids are endemic to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, with terrestrial forms in Asia, Australia, Africa, and the Americas and marine forms in the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Members of the family have a wide range of sizes, from the white-lipped snake to the king cobra. Most species have neurotoxic venom which is channeled by their hollow fangs, and some may contain other toxic components in various proportions. The family includes 55 genera with some 360 species and over 170 subspecies. Description Terrestrial elapids look similar to the Colubridae; almost all have long, slender bodies with smooth scales, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocular Scales
In scaled reptiles, the ocular scales are those forming the margin of the eye.Wright AH, Wright AA. 1957. ''Handbook of Snakes''. Comstock Publishing Associates (7th printing, 1985). 1105 pp. . The name originates from the term ''oculus'' which is Latin for 'eye' and, in the broadest sense, refers to a scale associated with the eye. The numbers of these scales present, and sometimes the shapes and sizes, are some of many characteristics used to differentiate species from one another. Prefixes are usually included to indicate the positions or locations of the individual scales:Mallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G. 2003. ''True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers''. Malabar, Florida: Krieger Publishing Company. 359 pp. .Smith MA. 1943. ''The Fauna of British India, Ceylon and Burma including the whole of the Indo-Chinese Sub-region, Reptilia and Amphibia Vol III-Serpentes''. Taylor and Francis, London. page 29. * Preocular scales, or preoculars, are those lying direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake Scales
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads (cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most have only one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs about twenty-five times independently via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, although this rule is not universal (see Amphisbaenia, Dibamida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |