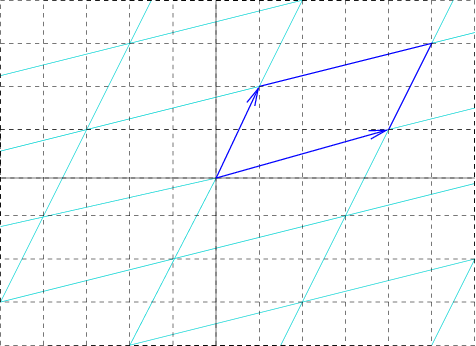
|
Supercell (crystal)
In solid-state physics and crystallography, a crystal structure is described by a unit cell repeating periodically over space. There are an infinite number of choices for unit cells, with different shapes and sizes, which can describe the same crystal, and different choices can be useful for different purposes. Say that a crystal structure is described by a unit cell U. Another unit cell S is a supercell of unit cell U, if S is a cell which describes the same crystal, but has a larger volume than cell U. Many methods which use a supercell perturbate it somehow to determine properties which cannot be determined by the initial cell. For example, during phonon calculations by the small displacement method, phonon frequencies in crystals are calculated using force values on slightly displaced atoms in the supercell. Another very important example of a supercell is the conventional cell of body-centered (bcc) or face-centered (fcc) cubic crystals. Unit cell transformation The basis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2d Supercell Example
D, or d, is the fourth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''dee'' (pronounced ), plural ''dees''. History The Semitic letter Dāleth may have developed from the logogram for a fish or a door. There are many different Egyptian hieroglyphs that might have inspired this. In Semitic, Ancient Greek and Latin, the letter represented ; in the Etruscan alphabet the letter was archaic but still retained. The equivalent Greek letter is delta, Δ. The minuscule (lower-case) form of 'd' consists of a lower-story left bowl and a stem ascender. It most likely developed by gradual variations on the majuscule (capital) form 'D', and is now composed as a stem with a full lobe to the right. In handwriting, it was common to start the arc to the left of the vertical stroke, resulting in a serif at the top of the arc. This serif was extended while the rest of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as solid-state chemistry, quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from their atomic-scale properties. Thus, solid-state physics forms a theoretical basis of materials science. Along with solid-state chemistry, it also has direct applications in the technology of transistors and semiconductors. Background Solid materials are formed from densely packed atoms, which interact intensely. These interactions produce the mechanical (e.g. hardness and Elasticity (physics), elasticity), Heat conduction, thermal, Electrical conduction, electrical, Magnetism, magnetic and Crystal optics, optical properties of solids. Depending on the material involved and the conditions in which it was formed, the atoms may be arranged in a regular, geometric patt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming 2014 the International Year of Crystallography.UN announcement "International Year of Crystallography" iycr2014.org. 12 July 2012 Crystallography is a broad topic, and many of its subareas, such as X-ray crystallography, are themselves important scientific topics. Crystallography ranges from the fundamentals of crystal structure to the mathematics of Crystal system, crystal geometry, including those that are Aperiodic crystal, not periodic or quasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional Cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessarily have unit size, or even a particular size at all. Rather, the primitive cell is the closest analogy to a unit vector, since it has a determined size for a given lattice and is the basic building block from which larger cells are constructed. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its unit cell, which is a section of the tiling (a parallelogram or parallelepiped) that generates the whole tiling using only translations. There are two special cases of the unit cell: the primitive cell and the conventional cell. The primitive cell is a unit cell corresponding to a single lattice point, it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic (crystal System)
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc) Note: the term fcc is often used in synonym for the ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp structure occurring in metals. However, fcc stands for a face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, which is not necessarily close-packed when a motif is set onto the lattice points. E.g. the diamond and the zincblende lattices are fcc but not close-packed. Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais latices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basis (linear Algebra)
In mathematics, a Set (mathematics), set of elements of a vector space is called a basis (: bases) if every element of can be written in a unique way as a finite linear combination of elements of . The coefficients of this linear combination are referred to as components or coordinates of the vector with respect to . The elements of a basis are called . Equivalently, a set is a basis if its elements are linearly independent and every element of is a linear combination of elements of . In other words, a basis is a linearly independent spanning set. A vector space can have several bases; however all the bases have the same number of elements, called the dimension (vector space), dimension of the vector space. This article deals mainly with finite-dimensional vector spaces. However, many of the principles are also valid for infinite-dimensional vector spaces. Basis vectors find applications in the study of crystal structures and frame of reference, frames of reference. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation Matrix
In linear algebra, linear transformations can be represented by matrices. If T is a linear transformation mapping \mathbb^n to \mathbb^m and \mathbf x is a column vector with n entries, then there exists an m \times n matrix A, called the transformation matrix of T, such that: T( \mathbf x ) = A \mathbf x Note that A has m rows and n columns, whereas the transformation T is from \mathbb^n to \mathbb^m. There are alternative expressions of transformation matrices involving row vectors that are preferred by some authors. Uses Matrices allow arbitrary linear transformations to be displayed in a consistent format, suitable for computation. This also allows transformations to be composed easily (by multiplying their matrices). Linear transformations are not the only ones that can be represented by matrices. Some transformations that are non-linear on an n-dimensional Euclidean space R''n'' can be represented as linear transformations on the ''n''+1-dimensional space R''n''+1. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagonal Matrix
In linear algebra, a diagonal matrix is a matrix in which the entries outside the main diagonal are all zero; the term usually refers to square matrices. Elements of the main diagonal can either be zero or nonzero. An example of a 2×2 diagonal matrix is \left begin 3 & 0 \\ 0 & 2 \end\right/math>, while an example of a 3×3 diagonal matrix is \left begin 6 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 5 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 4 \end\right/math>. An identity matrix of any size, or any multiple of it is a diagonal matrix called a ''scalar matrix'', for example, \left begin 0.5 & 0 \\ 0 & 0.5 \end\right/math>. In geometry, a diagonal matrix may be used as a '' scaling matrix'', since matrix multiplication with it results in changing scale (size) and possibly also shape; only a scalar matrix results in uniform change in scale. Definition As stated above, a diagonal matrix is a matrix in which all off-diagonal entries are zero. That is, the matrix with columns and rows is diagonal if \forall i,j \in \, i \ne j \ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Defect
A crystallographic defect is an interruption of the regular patterns of arrangement of atoms or molecules in crystalline solids. The positions and orientations of particles, which are repeating at fixed distances determined by the unit cell parameters in crystals, exhibit a periodic crystal structure, but this is usually imperfect.Ehrhart, P. (1991Properties and interactions of atomic defects in metals and alloys, volume 25 of Landolt-Börnstein, New Series III, chapter 2, p. 88, Springer, Berlin Several types of defects are often characterized: point defects, line defects, planar defects, bulk defects. Topological homotopy establishes a mathematical method of characterization. Point defects Point defects are defects that occur only at or around a single lattice point. They are not extended in space in any dimension. Strict limits for how small a point defect is are generally not defined explicitly. However, these defects typically involve at most a few extra or missing atoms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Condition
In the study of differential equations, a boundary-value problem is a differential equation subjected to constraints called boundary conditions. A solution to a boundary value problem is a solution to the differential equation which also satisfies the boundary conditions. Boundary value problems arise in several branches of physics as any physical differential equation will have them. Problems involving the wave equation, such as the determination of normal modes, are often stated as boundary value problems. A large class of important boundary value problems are the Sturm–Liouville problems. The analysis of these problems, in the linear case, involves the eigenfunctions of a differential operator. To be useful in applications, a boundary value problem should be well posed. This means that given the input to the problem there exists a unique solution, which depends continuously on the input. Much theoretical work in the field of partial differential equations is devote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |