|
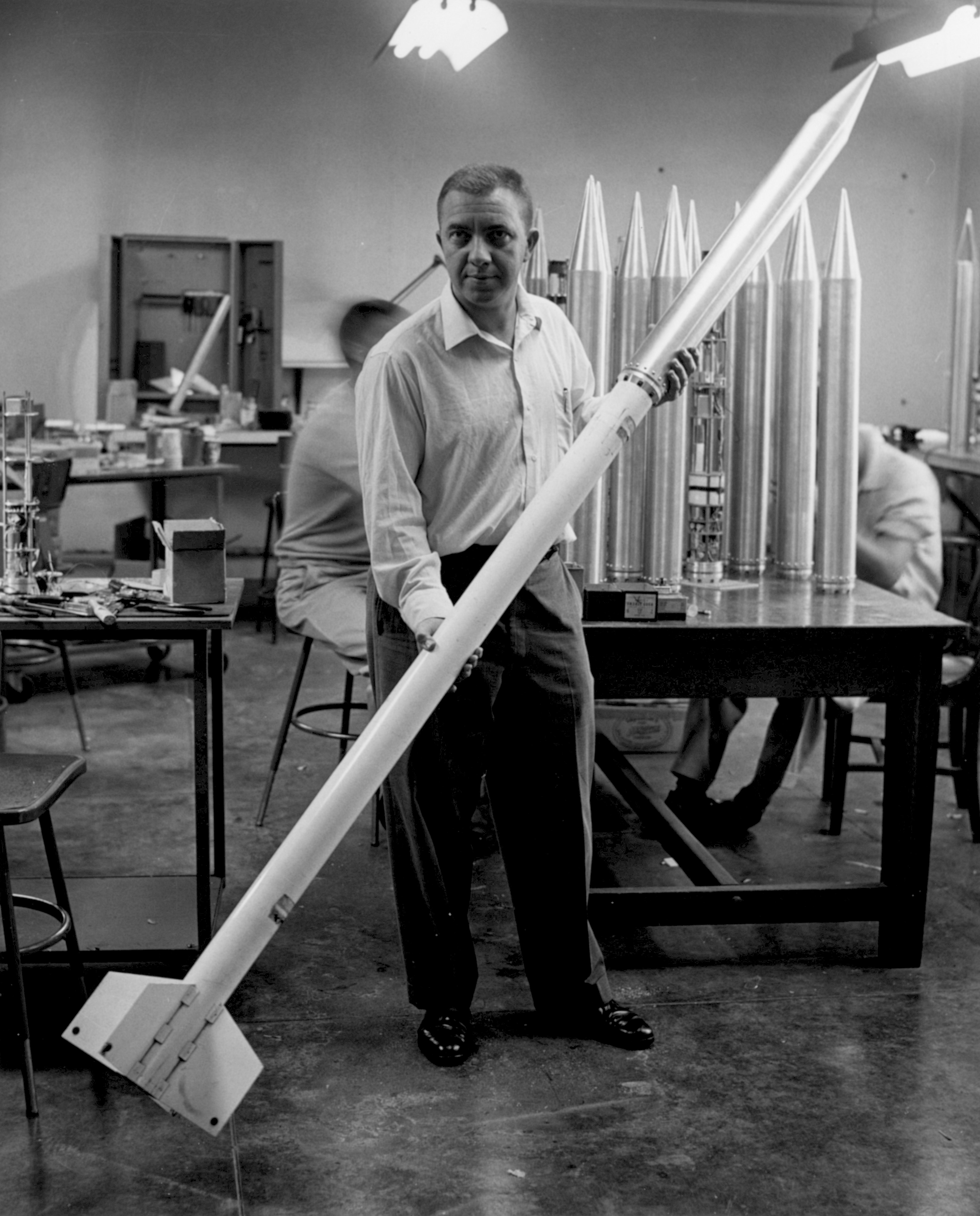
Super Loki
Loki, officially designated 76mm HEAA Rocket T220, was an American unguided anti-aircraft rocket based on the German Taifun. Like the Taifun, Loki never saw service in its original role, but later found widespread use as a sounding rocket. It was so successful in this role that several advanced versions were developed on the basic Loki layout, including the final Super Loki. Development As part of their anti-aircraft development program of 1942, the ''Luftwaffe'' began developing a number of guided missile projects. However, there was concern that these would not develop in time to be useful in the 1943/44 time frame. To fill the gap, Klaus Scheufelen suggested building a simple unguided rocket that would be fired en-masse directly up into the bomber streams. The result was the Taifun. Taifun was powered by a hypergolic mixture pressure-fed into the combustion chamber. The pressure was provided by small cordite charges that were fired into the fuel tanks, in the process burstin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redstone (rocket)
The PGM-11 Redstone was the first large American ballistic missile. A short-range ballistic missile (SRBM), it was in active service with the United States Army in West Germany from June 1958 to June 1964 as part of NATO's Cold War defense of Western Europe. It was the first US missile to carry a live nuclear warhead, in the 1958 Pacific Ocean weapons test, Hardtack Teak. The Redstone was a direct descendant of the German V-2 rocket, developed primarily by a team of German rocket engineers brought to the United States after World War II. The design used an upgraded engine from Rocketdyne that allowed the missile to carry the W39 warhead which weighed with its reentry vehicle to a range of about . Redstone's prime contractor was the Chrysler Corporation. The Redstone spawned the Redstone rocket family which holds a number of firsts in the US space program, notably launching the first US astronaut. It was retired by the Army in 1964 and replaced by the solid-fueled MGM-31 Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
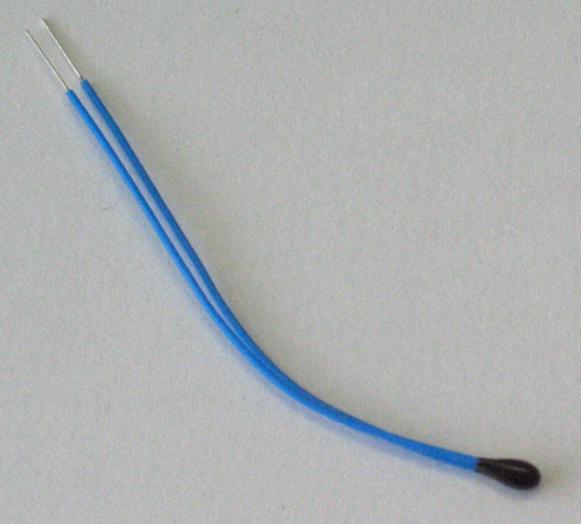
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''. Thermistors are divided based on their conduction model. Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors have ''less'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures, while Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors have ''more'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures. Hence, a PTC thermistor's resistance is directly proportional to temperature. NTC thermistor are widely used as inrush current limiters, temperature sensors, while PTC thermistors are used as self-resetting overcurrent protectors, and self-regulating heating elements. An operational temperature range of a thermistor is dependent on the probe type and is typically between −100 °C and 300 °C (−148 °F and 572 °F). Types Depending on materials used, thermistors are classified into two types: *With ''NTC'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquardt Corporation
Marquardt Corporation was an aeronautical engineering firm started in 1944 as ‘’’Marquardt Aircraft Company’’’ and initially dedicated almost entirely to the development of the ramjet engine. Marquardt designs were developed from the mid-1940s into the early 1960s, but as the ramjet disappeared from military usage, the company turned to other fields. In 1968 Marquardt was merged with CCI Inc. of Tulsa, OK. The newly merged firm became known as "CCI-Marquardt, Inc.". That name changed back to "CCI Inc." after a few years. Throughout the 1970s and 1980s pieces of Marquardt were sold off or merged with other firms. By the 1990s, one of the remnants of the company, called ''Marquardt Manufacturing Inc.'' (MMI) was embroiled in a legal suit with its predecessor organization, which had become principally a landlord who owned the buildings and land where MMI was located. By then, most of the remaining pieces of Marquardt were part of Ferranti in England which was in bankr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockoon
A rockoon (from ''rocket'' and ''balloon'') is a solid fuel sounding rocket that, rather than being immediately lit while on the ground, is first carried into the upper atmosphere by a gas-filled balloon, then separated from the balloon and ignited. This allows the rocket to achieve a higher altitude, as the rocket does not have to move under power through the lower and thicker layers of the atmosphere. The original concept was developed by Cmdr. Lee Lewis, Cmdr. G. Halvorson, S. F. Singer, and James A. Van Allen during the Aerobee rocket firing cruise of the U.S.S. ''Norton Sound'' on March 1, 1949. A serious disadvantage is that unpiloted balloons cannot be steered, and consequently the location from which the rocket is launched can be uncertain. Therefore, a large area for the fall of the rocket is required for safety reasons. Early atmospheric research ''Time'' magazine reported in 1959: "Van Allen's 'Rockoons' could not be fired in Iowa for fear that the spent rockets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Naval Research
The Office of Naval Research (ONR) is an organization within the United States Department of the Navy responsible for the science and technology programs of the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps. Established by Congress in 1946, its mission is to plan, foster, and encourage scientific research to maintain future naval power and preserve national security. It carries this out through funding and collaboration with schools, universities, government laboratories, nonprofit organizations, and for-profit organizations, and overseeing the Naval Research Laboratory, the corporate research laboratory for the Navy and Marine Corps. NRL conducts a broad program of scientific research, technology and advanced development. ONR Headquarters is in the Ballston neighborhood of Arlington, Virginia. ONR Global has offices overseas in Santiago, Sao Paulo, London, Prague, Singapore, and Tokyo. Overview ONR was authorized by an Act of Congress, Public Law 588, and subsequently approved by President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control. The United States Air Force is a military service branch organized within the Department of the Air Force, one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The Air Force through the Department of the Air Force is headed by the civilian Secretary of the Air Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
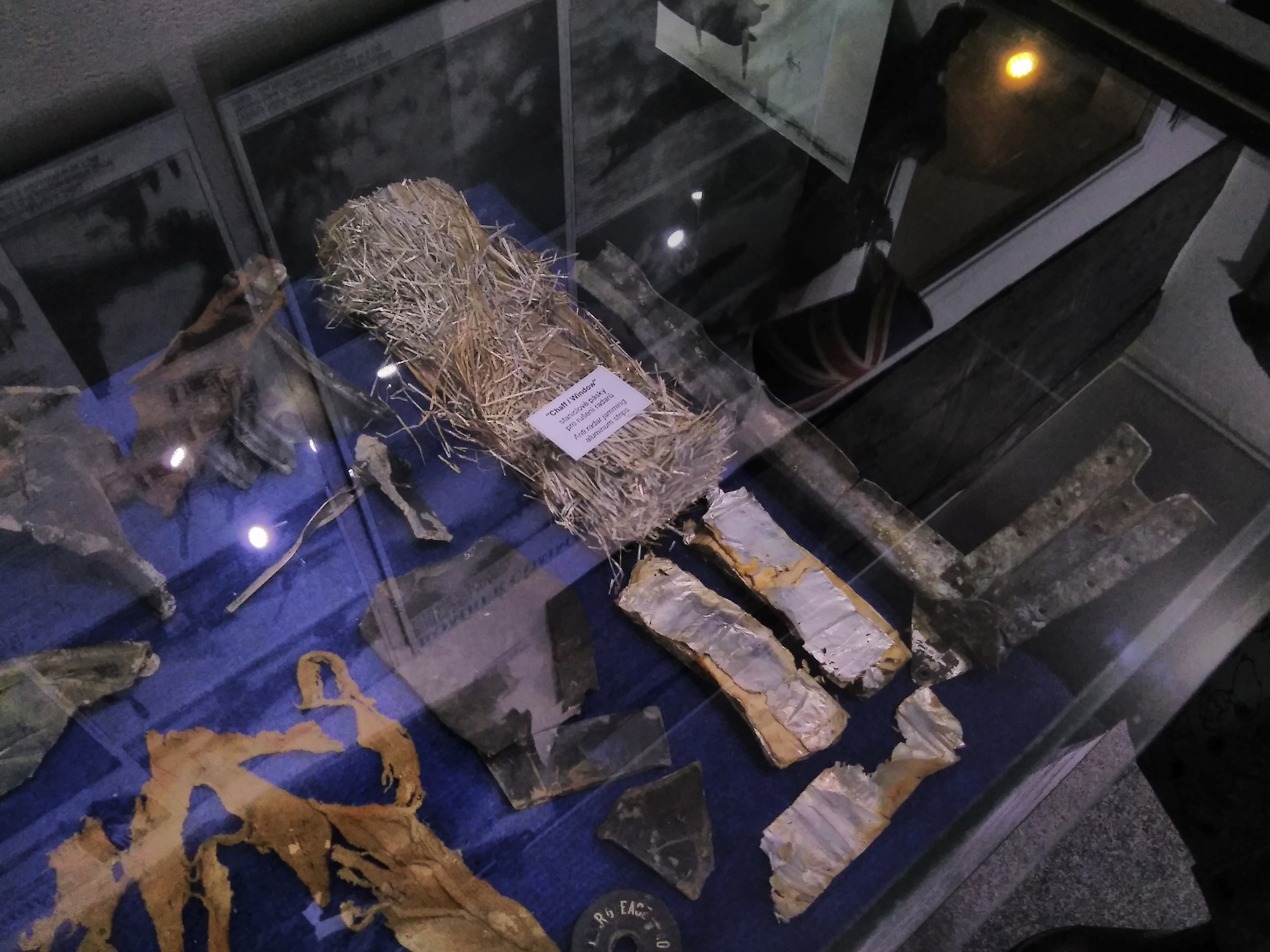
Chaff (countermeasure)
Chaff, originally called Window by the British and ''Düppel'' by the Second World War era German Luftwaffe (from the Berlin suburb where it was first developed), is a radar countermeasure in which aircraft or other targets spread a cloud of small, thin pieces of aluminium, metallized glass fibre or plastic, which either appears as a cluster of primary targets on radar screens or swamps the screen with multiple returns, in order to confuse and distract. Modern armed forces use chaff (in naval applications, for instance, using short-range SRBOC rockets) to distract radar-guided missiles from their targets. Most military aircraft and warships have chaff dispensing systems for self-defense. An intercontinental ballistic missile may release in its midcourse phase several independent warheads as well as penetration aids such as decoy balloons and chaff. Modern radar systems can distinguish chaff from target objects by measuring the Doppler shift; chaff quickly loses speed compared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockoon Van Allen
A rockoon (from ''rocket'' and ''balloon'') is a solid fuel sounding rocket that, rather than being immediately lit while on the ground, is first carried into the upper atmosphere by a gas-filled balloon, then separated from the balloon and ignited. This allows the rocket to achieve a higher altitude, as the rocket does not have to move under power through the lower and thicker layers of the atmosphere. The original concept was developed by Cmdr. Lee Lewis, Cmdr. G. Halvorson, S. F. Singer, and James A. Van Allen during the Aerobee rocket firing cruise of the U.S.S. ''Norton Sound'' on March 1, 1949. A serious disadvantage is that unpiloted balloons cannot be steered, and consequently the location from which the rocket is launched can be uncertain. Therefore, a large area for the fall of the rocket is required for safety reasons. Early atmospheric research ''Time'' magazine reported in 1959: "Van Allen's 'Rockoons' could not be fired in Iowa for fear that the spent rockets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
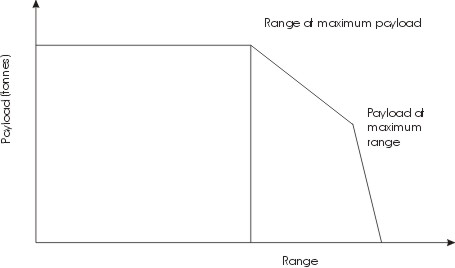
Payload (air And Space Craft)
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of the flight or mission, the payload of a vehicle may include cargo, passengers, flight crew, munitions, scientific instruments or experiments, or other equipment. Extra fuel, when optionally carried, is also considered part of the payload. In a commercial context (i.e., an airline or air freight carrier), payload may refer only to revenue-generating cargo or paying passengers. A payload of ordnance carried by a combat aircraft is sometimes alternatively referred to as the aircraft's warload. For a rocket, the payload can be a satellite, space probe, or spacecraft carrying humans, animals, or cargo. For a ballistic missile, the payload is one or more warheads and related systems; their total weight is referred to as the throw-weight. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |