|
Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine
Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine, sold under the brand name Fansidar, is a combination medication used to treat malaria. It contains sulfadoxine (a sulfonamide) and pyrimethamine (an antiprotozoal). For the treatment of malaria it is typically used along with other antimalarial medication such as artesunate. In areas of Africa with moderate to high rates of malaria, three doses are recommended during the second and third trimester of pregnancy. Side effects include diarrhea, rash, itchiness, headache, and hair loss. Rarely a severe allergic reaction or rash such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, may occur. It is not generally recommended in people with a sulfonamide allergy or significant liver or kidney disease. It works by blocking malaria's ability to use folinic acid. Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine was initially approved for medical use in the United States in 1981. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is not commercially available in the United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimalarial Medication
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young children and pregnant women. As of 2018, modern treatments, including for severe malaria, continued to depend on therapies deriving historically from quinine and artesunate, both parenteral (injectable) drugs, expanding from there into the many classes of available modern drugs. Incidence and distribution of the disease ("malaria burden") is expected to remain high, globally, for many years to come; moreover, known antimalarial drugs have repeatedly been observed to elicit resistance in the malaria parasite—including for combination therapies featuring artemisinin, a drug of last resort, where resistance has now been observed in Southeast Asia. As such, the needs for new antimalarial agents and new strategies of treatment (e.g., new combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
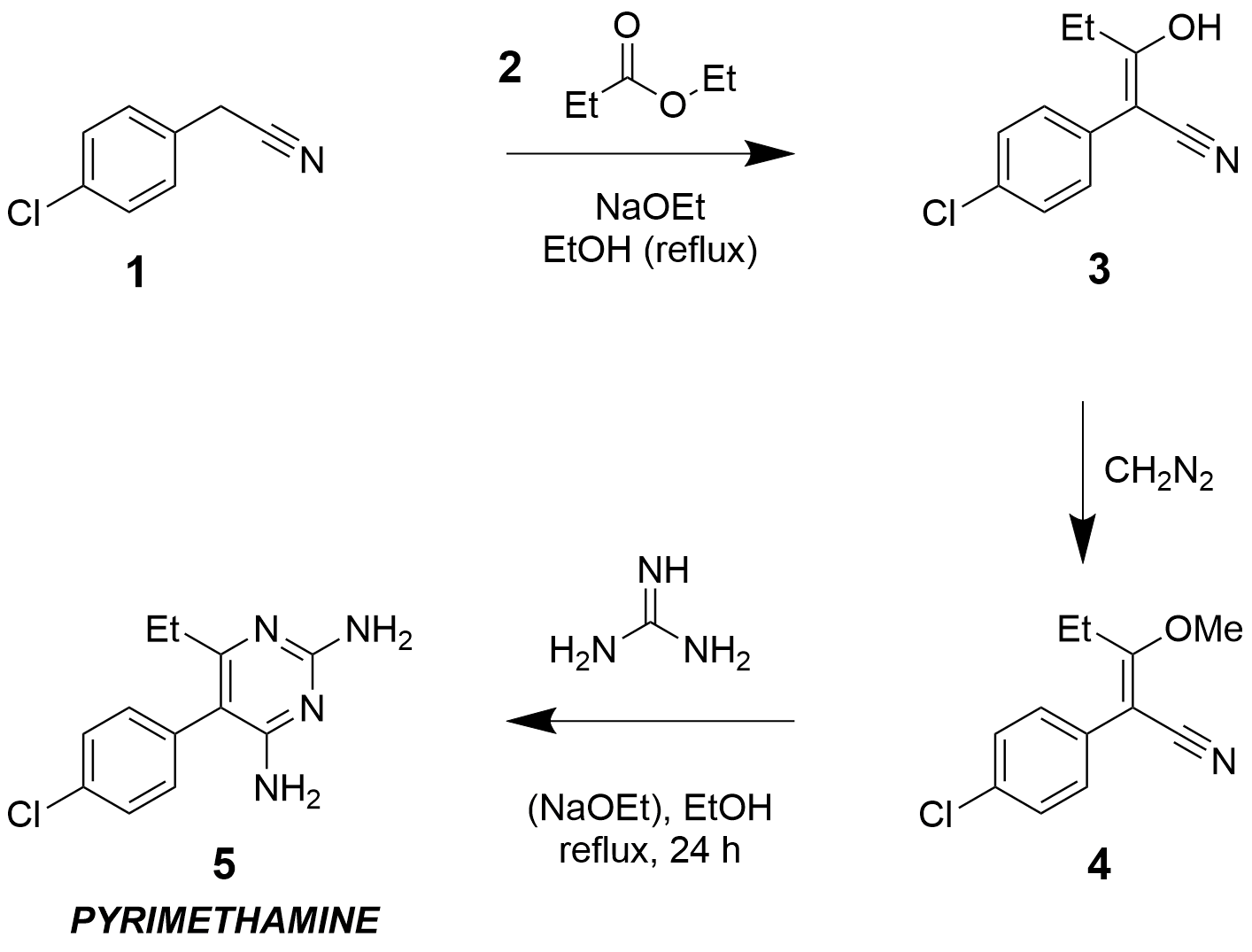
Pyrimethamine
Pyrimethamine, sold under the brand name Daraprim among others, is a medication used with leucovorin (leucovorin is used to decrease side effects of pyrimethamine; it does not have intrinsic anti-parasitic activity) to treat the parasitic diseases toxoplasmosis and cystoisosporiasis. It is also used with dapsone as a second-line option to prevent ''Pneumocystis jiroveci'' pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It was previously used for malaria but is no longer recommended due to resistance. Pyrimethamine is taken by mouth. Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset, severe allergic reactions, and bone marrow suppression. It should not be used by people with folate deficiency that has resulted in anemia. There is concern that it may increase the risk of cancer. While occasionally used in pregnancy it is unclear if pyrimethamine is safe for the baby. Pyrimethamine is classified as a folic acid antagonist. It works by inhibiting folic acid metabolism and therefore the maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
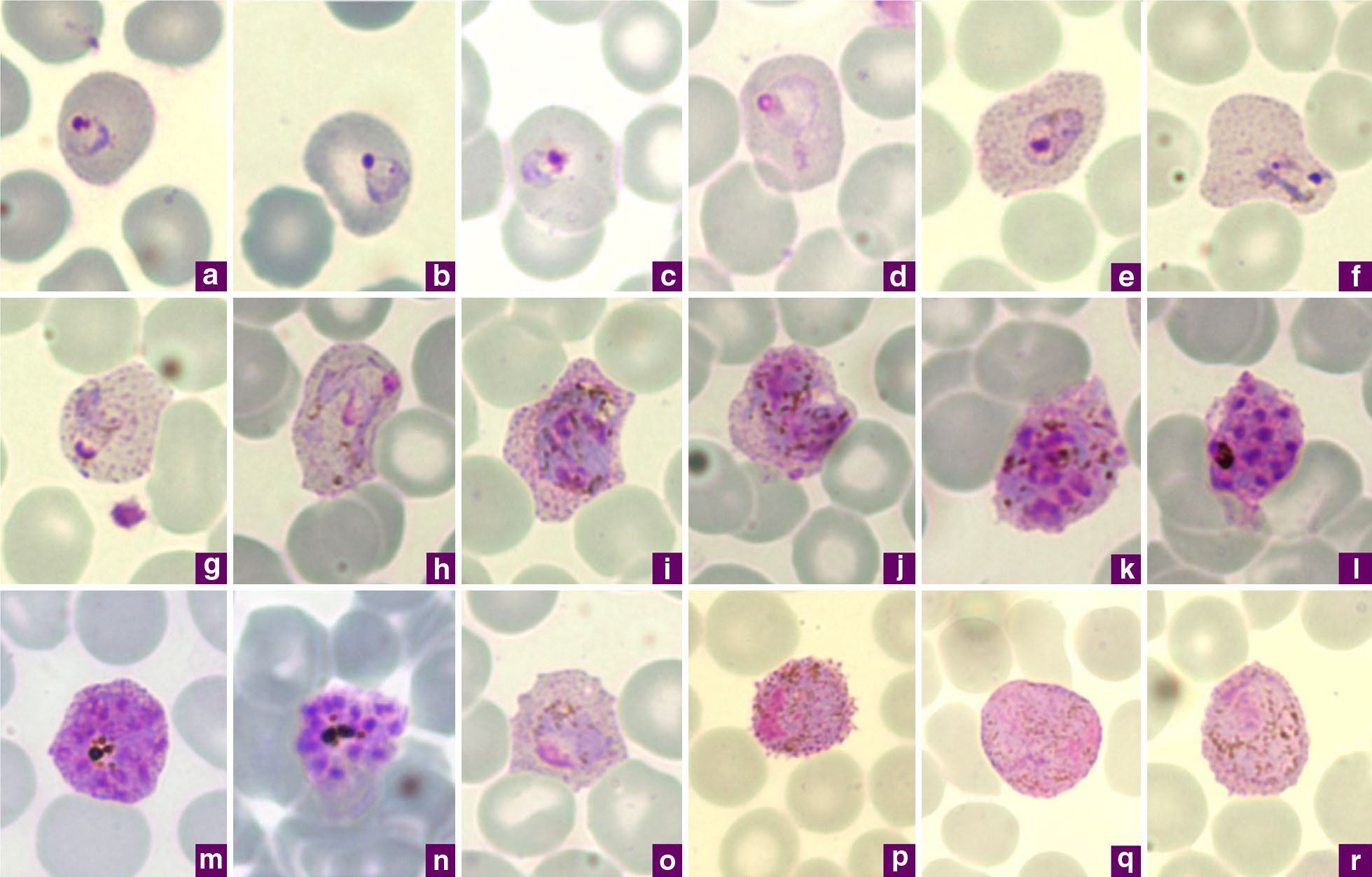
Plasmodium Vivax
''Plasmodium vivax'' is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than ''Plasmodium falciparum'', the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, ''P. vivax'' malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly (a pathologically enlarged spleen). ''P. vivax'' is carried by the female ''Anopheles'' mosquito; the males do not bite. Health Epidemiology ''Plasmodium vivax'' is found mainly in Asia, Latin America, and in some parts of Africa. ''P. vivax'' is believed to have originated in Asia, but recent studies have shown that wild chimpanzees and gorillas throughout central Africa are endemically infected with parasites that are closely related to human ''P. vivax.'' These findings indicate that human P. vivax is of African origin. ''Plasmodium vivax'' accounts for 65% of malaria cases in Asia and South America. Unlike ''Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artesunate
Artesunate (AS) is a medication used to treat malaria. The intravenous form is preferred to quinine for severe malaria. Often it is used as part of Artemisinin-based combination therapy, combination therapy, such as artesunate plus mefloquine. It is not used for the prevention of malaria. Artesunate can be given by intravenous, injection into a vein, intramuscular, injection into a muscle, by mouth, and by rectum. The most common side effects include kidney failure requiring dialysis, hemoglobinuria (the presence of hemoglobin in urine) and jaundice. Artesunate is generally well tolerated. Side effects may include a bradycardia, slow heartbeat, allergic reaction, dizziness, and low white blood cell levels. During pregnancy it appears to be a safer option, even though animal studies have found harm to the baby. Use is likely fine during breastfeeding. It is in the artemisinin class of medication. Artesunate was developed by Liu Xu (chemist), Liu Xu in 1977. It is on the WHO Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society Of Health-System Pharmacists
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) is a professional organization that represents pharmacists who serve as patient care providers in hospitals, health systems, ambulatory clinics, and other healthcare settings. The organization's nearly 58,000 members include pharmacists, student pharmacists, and pharmacy technicians. ASHP maintains a national database on U.S. drug shortages that is published on their website. Purpose The aim of the society is to support the professional practice of pharmacists in hospitals and health systems. In addition, the society advocates to government agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on public policy issues related to medication use and public health. Publications *''American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy'' *''AHFS Drug Information Book'' *''Handbook on Injectable Drugs A handbook is a type of reference work, or other collection of instructions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. The WHO was established on 7 April 1948. The first meeting of the World Health Assembly (WHA), the agency's governing body, took place on 24 July of that year. The WHO incorporated the assets, personnel, and duties of the League of Nations' Health Organization and the , including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Its work began in earnest in 1951 after a significant infusion of financial and technical resources. The WHO's mandate seeks and includes: working worldwide to promote health, keeping the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. It advocates that a billion more people should have: universal health care coverag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amodiaquine
Amodiaquine (ADQ) is a medication used to treat malaria, including ''Plasmodium falciparum'' malaria when uncomplicated. It is recommended to be given with artesunate to reduce the risk of resistance. Due to the risk of rare but serious side effects, it is not generally recommended to prevent malaria. Though, the WHO in 2013 recommended use for seasonal preventive in children at high risk in combination with sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine. The side effects of amodiaquine are generally minor to moderate and are similar to those of chloroquine. Rarely liver problems or low blood cell levels may occur. When taken in excess headaches, trouble seeing, seizures, and cardiac arrest may occur. While not extensively studied as of 2007, it appeared to be safe in pregnancy. Amodiaquine is a 4-aminoquinoline compound related to chloroquine. Amodiaquine was first made in 1948. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. While not available in the United States, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
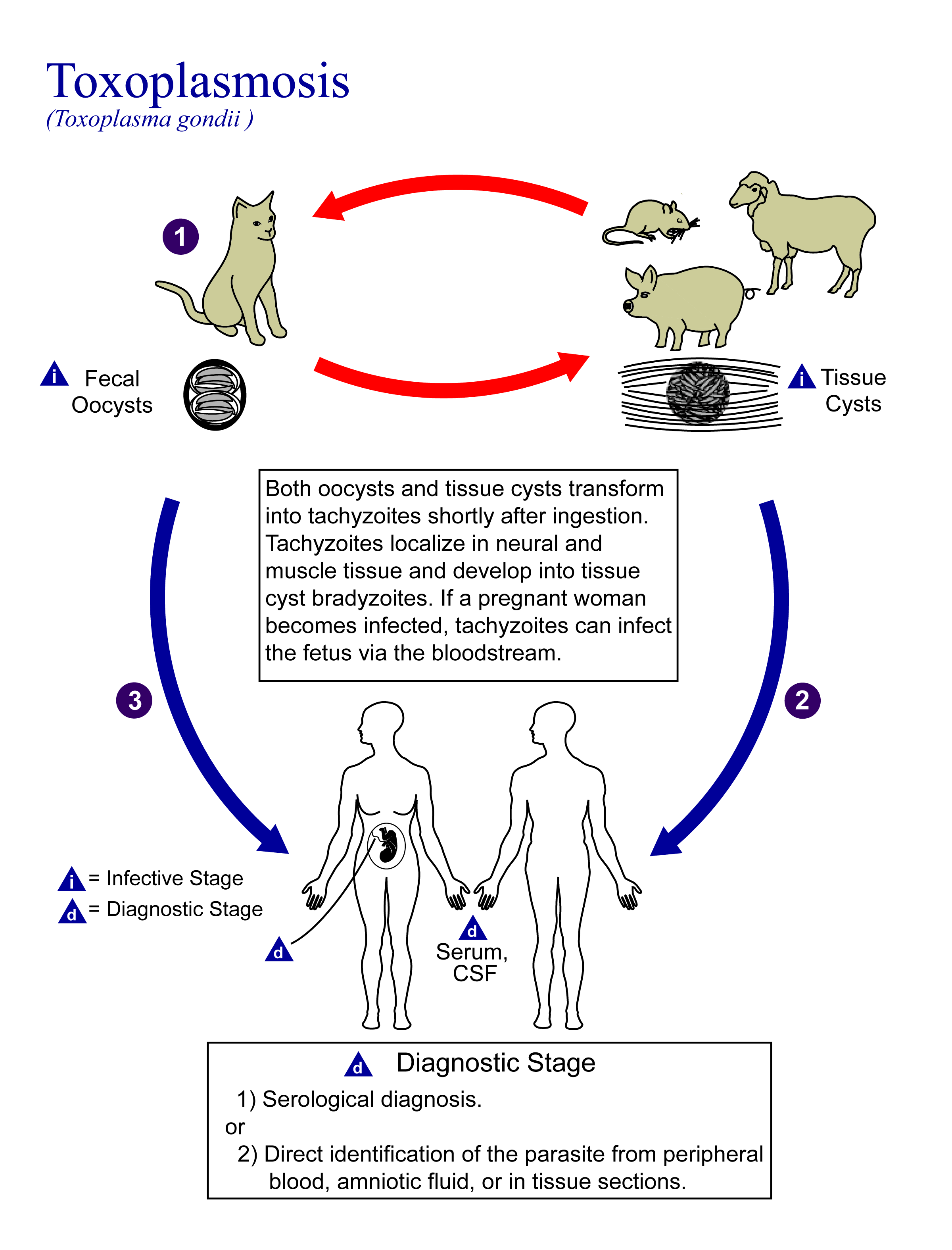
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes. In a small number of people, eye problems may develop. In those with a weak immune system, severe symptoms such as seizures and poor coordination may occur. If a person becomes infected during pregnancy, a condition known as congenital toxoplasmosis may affect the child. Toxoplasmosis is usually spread by eating poorly cooked food that contains cysts, exposure to infected cat feces, and from an infected woman to their baby during pregnancy. Rarely, the disease may be spread by blood transfusion. It is not otherwise spread between people. The parasite is known to reproduce sexually only in the cat family. However, it can infect most types of warm-blooded animals, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumocystis Jiroveci
''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' (previously ''P. carinii'') is a yeast-like fungus of the genus ''Pneumocystis''. The causative organism of ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia, it is an important human pathogen, particularly among immunocompromised hosts. Prior to its discovery as a human-specific pathogen, ''P. jirovecii'' was known as ''P. carinii''. Lifecycle The complete lifecycles of any of the species of ''Pneumocystis'' are not known, but presumably all resemble the others in the genus. The terminology follows zoological terms, rather than mycological terms, reflecting the initial misdetermination as a protozoan parasite. It is an extracellular fungus. All stages are found in lungs and because they cannot be cultured ''ex vivo'', direct observation of living ''Pneumocystis'' is difficult. The trophozoite stage is thought to be equivalent to the so-called vegetative state of other species (such as ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe''), which like ''Pneumocystis'', belong to the Taphrinomycoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
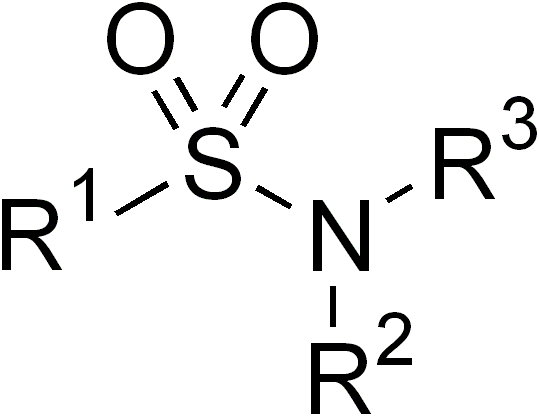
Sulfonamide (medicine)
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase (DHP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stevens–Johnson Syndrome
Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) is a type of severe skin reaction. Together with toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens–Johnson/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), it forms a spectrum of disease, with SJS being less severe. Erythema multiforme (EM) is generally considered a separate condition. Early symptoms of SJS include fever and flu-like symptoms. A few days later, the skin begins to blister and peel, forming painful raw areas. Mucous membranes, such as the mouth, are also typically involved. Complications include dehydration, sepsis, pneumonia and multiple organ failure. The most common cause is certain medications such as lamotrigine, carbamazepine, allopurinol, sulfonamide antibiotics and nevirapine. Other causes can include infections such as ''Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' and cytomegalovirus, or the cause may remain unknown. Risk factors include HIV/AIDS and systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis of Stevens–Johnson syndrome is based on involvement of les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |