|
Suisun Bay, California
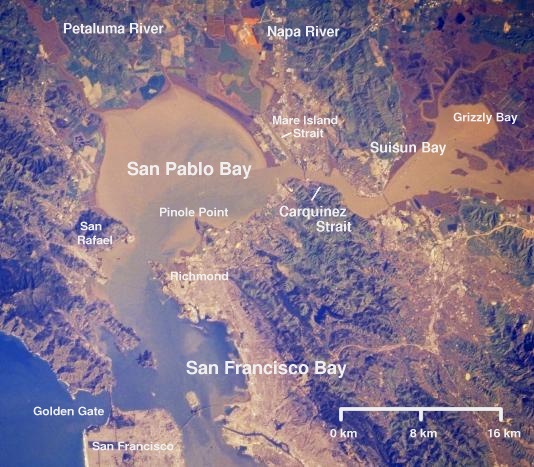
Suisun Bay ( ; Wintun for "where the west wind blows") is a shallow tidal estuary (a northeastern extension of the San Francisco Bay) in Northern California. It lies at the confluence of the Sacramento River and San Joaquin River, forming the entrance to the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta, an inverted river delta. To the west, Suisun Bay is drained by the Carquinez Strait, which connects to San Pablo Bay, a northern extension of San Francisco Bay. Suisun Marsh, the tidal marsh land to the north, is the largest marsh in California. Grizzly Bay forms a northern extension of Suisun Bay. Suisun Bay is directly north of Contra Costa County. The bay was named in 1811, after the Suisunes, a Patwin tribe of Wintun Indians. The Central Pacific Railroad built a train ferry that operated between Benicia and Port Costa, California, from 1879 to 1930. The ferry boats ''Solano'' and ''Contra Costa'' were removed from service when the nearby Martinez railroad bridge was completed in 1930. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benicia, California
Benicia ( , ) is a waterside city in Solano County, California, located in the North Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. It served as the capital of California for nearly thirteen months from 1853 to 1854. The population was 26,997 at the 2010 United States Census. The city is located along the north bank of the Carquinez Strait. Benicia is just east of Vallejo and across the strait from Martinez. Steve Young, elected in November 2020, is the mayor. History The City of Benicia was founded on May 19, 1847, by Dr. Robert Semple, Thomas O. Larkin, and Comandante General Mariano Guadalupe Vallejo, on land sold to them by General Vallejo in December 1846. It was named for the General's wife, Francisca Benicia Carillo de Vallejo, a member of the Carrillo family of California, a prominent Californio dynasty. The General intended that the city be named "Francisca" after his wife, but this name was dropped when the former city of "Yerba Buena" changed its name to "San Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
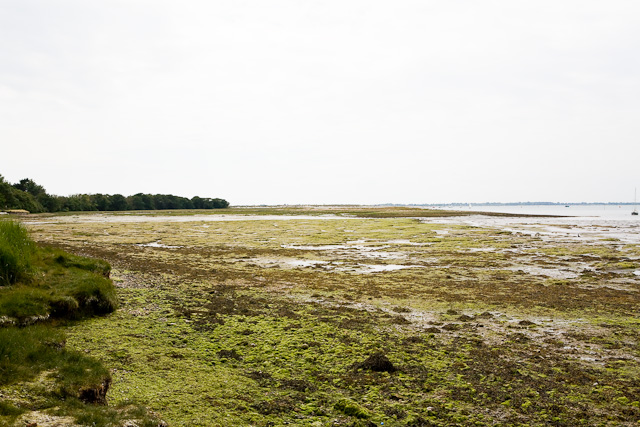
Tidal Marsh
A tidal marsh (also known as a type of "tidal wetland") is a marsh found along rivers, coasts and estuaries which floods and drains by the tidal movement of the adjacent estuary, sea or ocean. Tidal marshes are commonly zoned into lower marshes (also called intertidal marshes) and upper or high marshes, based on their elevation above sea level. A middle marsh zone also exists for tidal freshwater marshes. Tidal marshes may be further classified into back-barrier marshes, estuarine brackish marshes and tidal freshwater marshes, depending on the influence of sea level. Coastal Coastal tidal marshes are found within coastal watersheds and encompass a variety of types including fresh and salt marshes, bottomland hardwood swamps, mangrove swamps, and palustrine wetlands. Island and barrier island Tidal Marshes also form between a main shoreline and barrier islands. These elongated shifting landforms evolve parallel and in close proximity to the shoreline of a tidal marsh. Many becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Wildlife Federation
The National Wildlife Federation (NWF) is the United States' largest private, nonprofit conservation education and advocacy organization, with over six million members and supporters, and 51 state and territorial affiliated organizations (including Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands). History On March 10, 1934, U.S. Secretary of Agriculture Henry Wallace appointed political cartoonist Jay Norwood "Ding" Darling to be the chief of the U.S. Bureau of Biological Survey. Darling asked Congress repeatedly to fund environmental conservation work around the country, but Congress did not do so. Frustrated with the lack of funding to preserve and reestablish wildlife, Darling resigned from the position in late 1935. At Darling's request, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt convened the North American Wildlife Conference in Washington, D.C.. with the goal of uniting individuals, organizations, and agencies interested in the restoration and conservation of wildlife resources. The North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinder Morgan Energy Partners
Kinder Morgan Energy Partners LP () (KMEP) is a subsidiary of Kinder Morgan, Inc. The company, which is classified as an oil and gas master limited partnership (MLP), owns or operates petroleum product, natural gas, and carbon dioxide pipelines, related storage facilities, terminals, power plants and retail natural gas in the United States and Canada. History Kinder Morgan Energy Partners LP, headquartered at One Allen Center in Houston, Texas, was co-founded by Richard Kinder and William Morgan. The company began in 1997, when Kinder, a former Enron executive, and Morgan purchased the liquid pipeline assets of Enron for $40 million. It has since employed many former Enron employees, including former Enron whistleblower Jordan Mintz. Kinder Morgan is credited for bucking the trend in MLPs that traditionally deliver low double-digit total return to investors. It has produced a 26 percent compound growth rate from its founding to May of 2009. On March 1, 2002, Shares of Kinder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Train Ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train ferries are sometimes referred to as "car ferries", as distinguished from "auto ferries" used to transport automobiles. The wharf (sometimes called a "slip") has a ramp, and a linkspan or "apron", balanced by weights, that connects the railway proper to the ship, allowing for tidal or seasonal changes in water level. While railway vehicles can be and are shipped on the decks or in the holds of ordinary ships, purpose-built train ferries can be quickly loaded and unloaded by roll-on/roll-off, especially as several vehicles can be loaded or unloaded at once. A train ferry that is a barge is called a car float or rail barge. History An early train ferry was established as early as 1833 by the Monkland and Kirkintilloch Railway. To extend th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interurban
The Interurban (or radial railway in Europe and Canada) is a type of electric railway, with streetcar-like electric self-propelled rail cars which run within and between cities or towns. They were very prevalent in North America between 1900 and 1925 and were used primarily for passenger travel between cities and their surrounding suburban and rural communities. The concept spread to countries such as Japan, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, Italy and Poland. Interurban as a term encompassed the companies, their infrastructure, their cars that ran on the rails, and their service. In the United States, the early 1900s interurban was a valuable economic institution. Most roads between towns and many town streets were unpaved. Transportation and haulage was by horse-drawn carriages and carts. The interurban provided reliable transportation, particularly in winter weather, between the town and countryside. In 1915, of interurban railways were operating in the United States an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Electrification
A railway electrification system supplies electric power to railway trains and trams without an on-board prime mover or local fuel supply. Electric railways use either electric locomotives (hauling passengers or freight in separate cars), electric multiple units (passenger cars with their own motors) or both. Electricity is typically generated in large and relatively efficient generating stations, transmitted to the railway network and distributed to the trains. Some electric railways have their own dedicated generating stations and transmission lines, but most purchase power from an electric utility. The railway usually provides its own distribution lines, switches, and transformers. Power is supplied to moving trains with a (nearly) continuous conductor running along the track that usually takes one of two forms: an overhead line, suspended from poles or towers along the track or from structure or tunnel ceilings, or a third rail mounted at track level and contacted by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacramento Northern Railway
The Sacramento Northern Railway (reporting mark SN) was a electric interurban railway that connected Chico in northern California with Oakland via the California capital, Sacramento. In its operation it ran directly on the streets of Oakland, Sacramento, Yuba City, Chico, and Woodland and ran interurban passenger service until 1941 and freight service into the 1960s. History Summary The Sacramento Northern (SN) was an electrified interurban railroad in California that extended from Oakland north to Chico. A classic interurban in that it ran down the center of city streets in a number of towns, the SN was also a heavy duty electric railroad that moved considerable freight tonnage. There were three branches, one to Woodland, one to Colusa, and one to Oroville. The SN had been two separate interurban companies connecting at Sacramento until 1925. The Oakland, Antioch, and Eastern Railway was a catenary-wire powered line that ran from Oakland through a tunnel in the Oakland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Costa, California
Port Costa is a small village and census-designated place (CDP) in Contra Costa County, California, Contra Costa County, California, located in East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. Situated on the southern shore of the Carquinez Strait, the population was 190 at the 2010 census. History Port Costa was founded in 1879 as a landing for the railroad ferry ''Solano (ferry), Solano'', owned and operated by the Central Pacific Railroad.Images of America: Richmond, by Donald Bastin, Arcadia Publishing (SC), November 2003 This put Port Costa on the main route of the transcontinental railroad. The ''Solano'', later joined by the ''Contra Costa'', carried entire trains across the Carquinez Strait from Benicia to Port Costa, from whence they continued on to the Oakland Pier. Businessman George W. McNear built the Port Costa Warehouses and Dock Company west of the new ferry terminal in 1880. The valley where Port Costa now sits, at one point called Bull Valley, was part of a ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benicia
Benicia ( , ) is a waterside city in Solano County, California, located in the North Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. It served as the capital of California for nearly thirteen months from 1853 to 1854. The population was 26,997 at the 2010 United States Census. The city is located along the north bank of the Carquinez Strait. Benicia is just east of Vallejo and across the strait from Martinez. Steve Young, elected in November 2020, is the mayor. History The City of Benicia was founded on May 19, 1847, by Dr. Robert Semple, Thomas O. Larkin, and Comandante General Mariano Guadalupe Vallejo, on land sold to them by General Vallejo in December 1846. It was named for the General's wife, Francisca Benicia Carillo de Vallejo, a member of the Carrillo family of California, a prominent Californio dynasty. The General intended that the city be named "Francisca" after his wife, but this name was dropped when the former city of "Yerba Buena" changed its name to "San Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Pacific Railroad
The Central Pacific Railroad (CPRR) was a rail company chartered by Pacific Railroad Acts, U.S. Congress in 1862 to build a railroad eastwards from Sacramento, California, to complete the western part of the "First transcontinental railroad" in North America. Incorporated in 1861, CPRR ceased operation in 1885 when it was acquired by Southern Pacific Railroad as a leased line. Following the completion of the Pacific Railroad Surveys in 1855, several national proposals to build a transcontinental railroad failed because of the energy consumed by political disputes over slavery. With the secession of Southern United States, the South in 1861, the modernizers in the Republican Party (US), Republican Party controlled the US Congress. They passed Pacific Railroad Acts, legislation in 1862 authorizing the central rail route with financing in the form of land grants and government railroad bond, which were all eventually repaid with interest. The government and the railroads both shared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patwin
The Patwin (also Patween, Southern Wintu) are a band of Wintun people native to the area of Northern California. The Patwin comprise the southern branch of the Wintun group, native inhabitants of California since approximately 500 AD. The Patwin were bordered by the Yuki in the northwest; the Nomlaki (Wintun) in the north; the Konkow (Maiduan) in northeast; the Nisenan (Maiduan) and Plains Miwok in the east; the Bay Miwok to the south; the Coast Miwok in the southwest; and the Wappo, Lake Miwok, and Pomo in the west. The "Southern Patwins" lived between what is now Suisun, Vacaville, and Putah Creek. By 1800 they had been forced by Spanish and other European settlers into small tribal units: Ululatos (Vacaville), Labaytos (Putah Creek), Malacas (Lagoon Valley), Tolenas (Upper Suisun Valley), and Suisunes (Suisun Marsh and Plain). Patwin Indian remains were discovered at the Mondavi Center construction site beginning in 1999, and consequently the University of California, Davi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
_(cropped).jpg)
