|
Sudo Warning
() is a shell command on Unix-like operating systems that enables a user to run a program with the security privileges of another user, by default the superuser. It originally stood for "superuser do", as that was all it did, and this remains its most common usage; however, the official Sudo project page lists it as "su 'do. The current Linux manual pages define as "substitute user", making the correct meaning of "substitute user, do", because can run a command as other users as well. Unlike the similar command su, users must, by default, supply their own password for authentication, rather than the password of the target user. After authentication, and if the configuration file (typically /etc/sudoers) permits the user access, the system invokes the requested command. The configuration file offers detailed access permissions, including enabling commands only from the invoking terminal; requiring a password per user or group; requiring re-entry of a password every time or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claim (patent)
In a patent or patent application, the claims define in technical terms the extent, i.e. the scope, of the protection conferred by a patent, or the protection sought in a patent application. The claims particularly point out the subject matter which the inventor(s) regard as their invention. In other words, the purpose of the claims is to define which subject matter is protected by the patent (or sought to be protected by the patent application). This is termed as the "notice function" of a patent claim—to warn others of what they must not do if they are to avoid patent infringement, infringement liability. The claims are of paramount importance in both patent prosecution, prosecution and lawsuit, litigation. For instance, a claim could read: * "An apparatus for catching mice, said apparatus comprising a base, a spring member coupled to the base, and ..." * "A chemical composition for cleaning windows, said composition substantially consisting of 10–15% ammonia, ..." * "Method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanity Testing
A sanity check or sanity test is a basic test to quickly evaluate whether a claim or the result of a calculation can possibly be true. It is a simple check to see if the produced material is rational (that the material's creator was thinking rationally, applying sanity). The point of a sanity test is to rule out certain classes of obviously false results, not to catch every possible error. A rule-of-thumb or back-of-the-envelope calculation may be checked to perform the test. The advantage of performing an initial sanity test is that of speedily evaluating basic function. In arithmetic, for example, when multiplying by 9, using the divisibility rule for 9 to verify that the sum of digits of the result is divisible by 9 is a sanity test—it will not catch ''every'' multiplication error, but is a quick and simple method to discover ''many'' possible errors. In computer science, a ''sanity test'' is a very brief run-through of the functionality of a computer program, system, calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Locking
File locking is a mechanism that restricts access to a computer file, or to a region of a file, by allowing only one user or process to modify or delete it at a specific time, and preventing reading of the file while it's being modified or deleted. Systems implement locking to prevent an ''interceding update'' scenario, which is an example of a race condition, by enforcing the serialization of update processes to any given file. The following example illustrates the interceding update problem: # Process A reads a customer record from a file containing account information, including the customer's account balance and phone number. # Process B now reads the same record from the same file, so it has its own copy. # Process A changes the account balance in its copy of the customer record and writes the record back to the file. # Process B, which still has the original ''stale'' value for the account balance in its copy of the customer record, updates the account balance and writes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Role-based Access Control
In computer systems security, role-based access control (RBAC) or role-based security is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users, and to implementing mandatory access control (MAC) or discretionary access control, discretionary access control (DAC). Role-based access control is a policy-neutral access control mechanism defined around roles and privileges. The components of RBAC such as role-permissions, user-role and role-role relationships make it simple to perform user assignments. A study by NIST has demonstrated that RBAC addresses many needs of commercial and government organizations. RBAC can be used to facilitate administration of security in large organizations with hundreds of users and thousands of permissions. Although RBAC is different from MAC and DAC access control frameworks, it can enforce these policies without any complication. Design Within an organization, role (computer science), roles are created for various job functions. The permiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
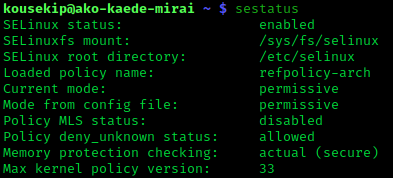
SELinux
Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a Linux kernel security module that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including mandatory access controls (MAC). SELinux is a set of kernel modifications and user-space tools that have been added to various Linux distributions. Its architecture strives to separate enforcement of security decisions from the security policy, and streamlines the amount of software involved with security policy enforcement. The key concepts underlying SELinux can be traced to several earlier projects by the United States National Security Agency (NSA). Overview The NSA Security-enhanced Linux Team describes NSA SELinux as a set of patches to the Linux kernel and utilities to provide a strong, flexible, mandatory access control (MAC) architecture into the major subsystems of the kernel. It provides an enhanced mechanism to enforce the separation of information based on confidentiality and integrity requirements, which allows th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of Desktop computer, desktop and laptop computers, it is the Usage share of operating systems#Desktop and laptop computers, second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of all Linux distributions, including ChromeOS and SteamOS. , the most recent release of macOS is MacOS Sequoia, macOS 15 Sequoia, the 21st major version of macOS. Mac OS X succeeded classic Mac OS, the primary Mac operating systems, Macintosh operating system from 1984 to 2001. Its underlying architecture came from NeXT's NeXTSTEP, as a result of NeXT#1997–2006: Acquisition by Apple, Apple's acquisition of NeXT, which also brought Steve Jobs back to Apple. The first desktop version, Mac OS X 10.0, was released on March 24, 2001. Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Distribution
A Linux distribution, often abbreviated as distro, is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro—if distributed on its own—is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers (for example, Linux Mint) to servers (for example, Red Hat Enterprise Linux) and from embedded devices (for example, OpenWrt) to supercomputers (for example, Rocks Cluster Distribution). A distro typically includes many components in addition to the Linux kernel. Commonly, it includes a package manager, an init system (such as systemd, OpenRC, or runit), GNU tools and libraries, documentation, IP network configuration utilities, the getty TTY setup program, and many more. To provide a desktop experience (most commonly the Mesa userspace graphics drivers) a display server (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Easter Egg (media)
An Easter egg is a message, image, or feature hidden in software, a video game, a film, or another—usually electronic—medium. The term used in this manner was coined around 1979 by Steve Wright, the then-Director of Software Development in the Atari Consumer Division, to describe a hidden message in the Atari video game ''Adventure (Atari 2600), Adventure'', in reference to an egg hunt, Easter egg hunt. The earliest known video game Easter egg is in the 1973 video game ''Lunar Lander (video game genre)#Graphical games, Moonlander'', in which the player tries to land a Lunar module on Moon, the Moon; if the player opts to fly the module horizontally through several of the game's screens, they encounter a McDonald's restaurant, and if they land next to it, the astronaut will visit it instead of standing next to the ship. The earliest known Easter egg in software in general is one placed in the "make" command for PDP-6/PDP-10 computers sometime in October 1967–October 1968, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root User
In computing, the superuser is a special user account used for system administration. Depending on the operating system (OS), the actual name of this account might be root, administrator, admin or supervisor. In some cases, the actual name of the account is not the determining factor; on Unix-like systems, for example, the user with a user identifier (UID) of zero is the superuser .e., uid=0 regardless of the name of that account; and in systems which implement a r model, any user with the role of superuser (or its synonyms) can carry out all actions of the superuser account. The principle of least privilege recommends that most users and applications run under an ordinary account to perform their work, as a superuser account is capable of making unrestricted, potentially adverse, system-wide changes. Unix and Unix-like In Unix-like computer OSes (such as Linux), ''root'' is the conventional name of the user who has all rights or permissions (to all files and programs) in all mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mail (Unix)
mail is a command-line email client for Unix and Unix-like operating systems. History "Electronic mail was there from the start", Douglas McIlroy writes in his article "A Research UNIX Reader: Annotated Excerpts from the Programmer’s Manual, 1971-1986", and so a command was included in the first released version of research Unix, First Edition Unix. This version of mail was capable to send (append) messages to the mailboxes of other users on the Unix system, and it helped managing (reading) the mailbox of the current user. In 1978 Kurt Shoens wrote a completely new version of mail for BSD2, referred to as Berkeley Mail. Although initially installed at , (with the earlier Unix mail still available at ), on most modern Unix and Linux systems the commands , and/or all invoke a descendant of this Berkeley Mail, which much later was the base for the standardization of a mail program by the OpenGroup, the POSIX The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX; ) is a fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo Terminal
In some operating systems, including Unix-like systems, a pseudoterminal, pseudotty, or PTY is a pair of pseudo-device endpoints (files) which establish an asynchronous, Duplex (telecommunications), bidirectional communication (IPC socket, IPC) channel (with two ports) between two or more processes. One pseudo-device in the pair, the ''master'', provides means by which a terminal emulator or remote login server (e.g. a Telnet, Berkeley r-commands, rlogin, or Secure Shell server) computer process, process controls the slave. The other pseudo-device, the ''slave'', emulates a hardware serial port device, and is used by terminal-oriented programs such as shells (e.g. Bash (Unix shell), bash) as a processes to read/write data back from/to ''master'' endpoint. PTYs are similar to bidirectional pipes. Devpts is a Linux kernel virtual file system containing pseudoterminal devices. Linux implementation is based on UNIX System V, System V-style terminals (commonly referred as UNIX 98 pse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |