|
Sucralfate
Sucralfate, sold under various brand names, is a medication used to treat stomach ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), radiation proctitis, and stomach inflammation and to prevent stress ulcers. Its usefulness in people infected by ''H. pylori'' is limited. It is used by mouth (for upper GIT ulcers) and rectally (for radiation proctitis). Common side effects include constipation. Serious side effects may include bezoar formation and encephalopathy. Use appears to be safe in pregnancy and breastfeeding. How it works is unclear but is believed to involve binding to the ulcer and protecting it from further damage. Sucralfate was approved for medical use in the United States in 1981. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 182nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2million prescriptions. Medical uses Sucralfate is used for the treatment of active duodenal ulcers not related to the use of nonsteroidal anti-infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include dental corrosion, dysphagia, heartburn, odynophagia, regurgitation, non-cardiac chest pain, extraesophageal symptoms such as chronic cough, hoarseness, reflux-induced laryngitis, or asthma. On the long term, and when not treated, complications such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus may arise. Risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, and taking certain medications. Medications that may cause or worsen the disease include benzodiazepines, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, NSAIDs, and certain asthma medicines. Acid reflux is due to poor closure of the lower esophageal sphincter, which is at the junction between the stomach and the esoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NSAID
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease. The term ''non-steroidal'', common from around 1960, distinguishes these drugs from corticosteroids, which during the 1950s had acquired a bad reputation due to overuse and side-effect problems after their initial introduction in 1948. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes (the COX-1 and COX-2 isoenzymes). In cells, these enzymes are involved in the synthesis of key biological mediators, namely prostaglandins, which are involved in inflammation, and thromboxanes, which are involved in blood clotting. There are two general types of NSAIDs available: non-selective, and COX-2 selective. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Society Of Oral Oncology
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations". International may also refer to: Music Albums * ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * ''International'' (New Order album), 2002 * ''International'' (The Three Degrees album), 1975 *''International'', 2018 album by L'Algérino Songs * The Internationale, the left-wing anthem * "International" (Chase & Status song), 2014 * "International", by Adventures in Stereo from ''Monomania'', 2000 * "International", by Brass Construction from ''Renegades'', 1984 * "International", by Thomas Leer from ''The Scale of Ten'', 1985 * "International", by Kevin Michael from ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * "International", by McGuinness Flint from ''McGuinness Flint'', 1970 * "International", by Orchestral Manoeuvres in the Dark from '' Dazzle Ships'', 1983 * "International (Serious)", by Estelle from '' All of Me'', 2012 Politics * Political international, any transnational organization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizing radiation works by damaging the DNA of cancerous tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
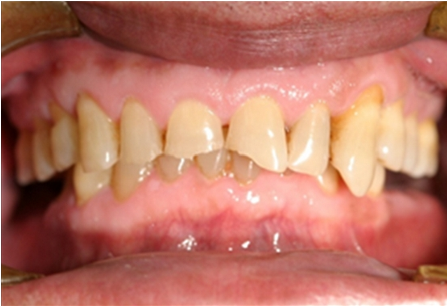
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is inflammation of the mouth and lips. It refers to any inflammatory process affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips, with or without oral ulceration. In its widest meaning, stomatitis can have a multitude of different causes and appearances. Common causes include infections, nutritional deficiencies, allergic reactions, radiotherapy, and many others. When inflammation of the gums and the mouth generally presents itself, sometimes the term ''gingivostomatitis'' is used, though this is also sometimes used as a synonym for herpetic gingivostomatitis. The term is derived from the Greek ''stoma'' (), meaning "mouth", and the suffix ''-itis'' (), meaning "inflammation". Causes Nutritional deficiency Malnutrition (improper dietary intake) or malabsorption (poor absorption of nutrients into the body) can lead to nutritional deficiency states, several of which can lead to stomatitis. For example, deficiencies of iron, vitamin B2 (riboflavin), vitamin B3 (niacin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
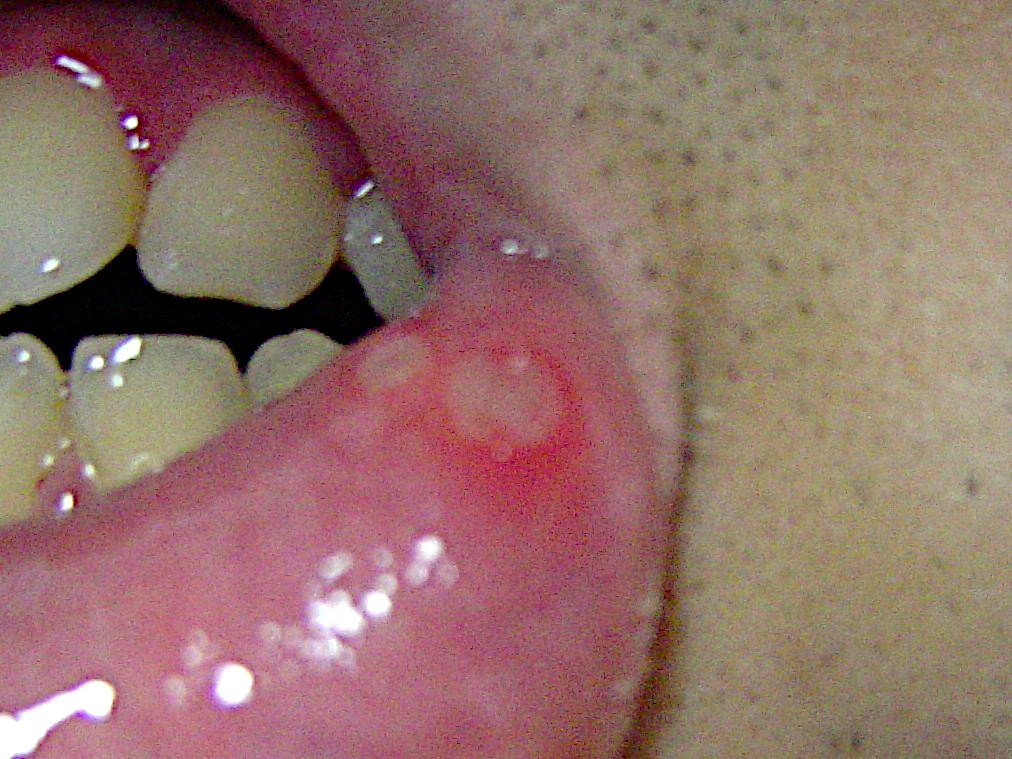
Aphthous Ulcer
Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals. The informal term ''canker sore'' is also used, mainly in North America, although it may also refer to other types of mouth ulcers. The cause is not completely understood but involves a T cell-mediated immune response triggered by a variety of factors which may include nutritional deficiencies, local trauma, stress, hormonal influences, allergies, genetic predisposition, certain foods, dehydration, some food additives, or some hygienic chemical additives like SDS (common in toothpaste). These ulcers occur periodically and heal completely between attacks. In the majority of cases, the individual ulcers last about 7–10 days, and ulceration episodes occur 3–6 times per year. Most appear on the non-keratinizing epithelial surfaces in the mouth – i.e. anywhere excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranitidine
Ranitidine, sold under the brand name Zantac among others, is a medication used to decrease stomach acid production. It is commonly used in treatment of peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. It can be given by mouth, injection into a muscle, or injection into a vein. In September 2019, the probable carcinogen ''N''-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) was discovered in ranitidine products from a number of manufacturers, resulting in recalls. In April 2020, ranitidine was withdrawn from the United States market and suspended in the European Union and Australia due to these concerns. Common side effects include headaches and pain or burning if given by injection. Serious side effects may include liver problems, a slow heart rate, pneumonia, and the potential of masking stomach cancer. It is also linked to an increased risk of ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis. Ranitidine is an H2 histamine receptor antagonist that works by blockin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns". Standard indicators of the quality of life include wealth, employment, the environment, physical and mental health, education, recreation and leisure time, social belonging, religious beliefs, safety, security and freedom. QOL has a wide range of contexts, including the fields of international development, healthcare, politics and employment. Health related QOL (HRQOL) is an evaluation of QOL and its relationship with health. Engaged theory One approach, called engaged theory, outlined in the journal of ''Applied Research in the Quality of Life'', posits four domains in assessing quality of life: ecology, economics, politics and culture. In the domain of culture, for example, it includes the following subdomains of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. Indicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisapride
Cisapride is a gastroprokinetic agent, a drug that increases motility in the upper gastrointestinal tract. It acts directly as a serotonin 5-HT4 receptor agonist and indirectly as a parasympathomimetic. Stimulation of the serotonin receptors increases acetylcholine release in the enteric nervous system. It has been sold under the trade names Prepulsid (Janssen-Ortho) and Propulsid (in the United States). It was discovered by Janssen Pharmaceuticals in 1980. In many countries, it has been either withdrawn from the market or had its indications limited due to incidence of serious cardiac side-effects. Propulsid was linked to children's deaths. The commercial preparations of this drug are the racemic mixture of both enantiomers of the compound. The (+) enantiomer itself has the major pharmacologic effects and does not induce many of the detrimental side-effects of the mixture. Medical uses Cisapride has been used for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). There i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |