|
Substrate Mapping
Substrate mapping (or wafer mapping) is a process in which the performance of semiconductor devices on a substrate is represented by a map showing the performance as a colour-coded grid. The map is a convenient representation of the variation in performance across the substrate, since the distribution of those variations may be a clue as to their cause. The concept also includes the package of data generated by modern wafer testing equipment which can be transmitted to equipment used for subsequent 'back-end' manufacturing operations. History The initial process supported by substrate maps was inkless binning. Each tested die is assigned a bin value, depending on the result of the test. For example, a pass die is assigned a bin value of 1 for a good bin, bin 10 for an open circuit, and bin 11 for a short circuit. In the very early days of wafer test, the dies were put in different bins or buckets, depending on the test results. Physical binning may no longer be used, but the ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Device Fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are present in everyday electrical and electronics, electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of Photolithography, photolithographic and chemical processing steps (such as surface passivation, thermal oxidation, planar process, planar diffusion and p–n junction isolation, junction isolation) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer (electronics), wafer made of pure semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. The entire manufacturing process takes time, from start to packaged chips ready for shipment, at least six to eight weeks (tape-out only, not including the circuit design) and is performed in highly specialized semiconduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
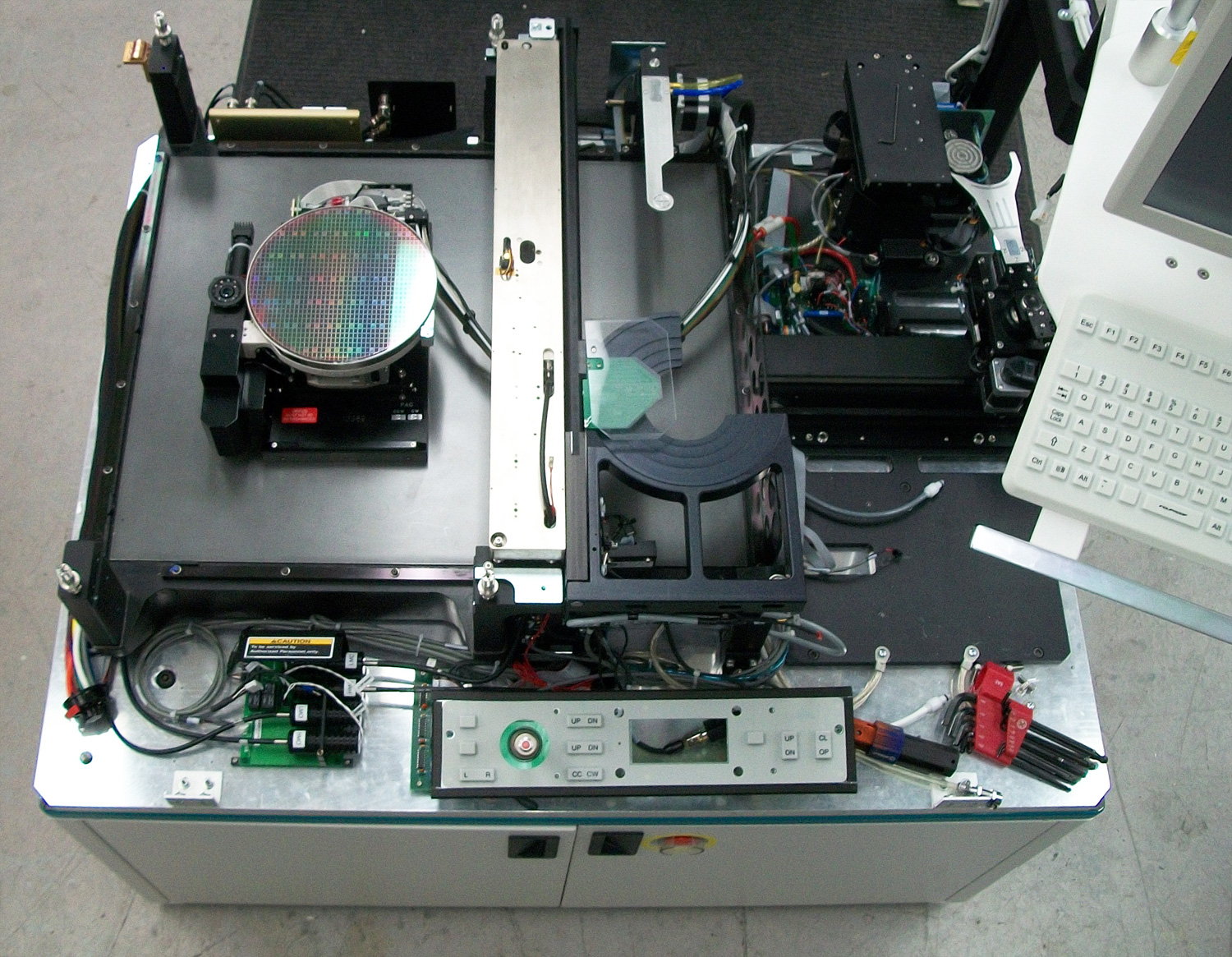
Wafer Testing
Wafer testing is a step performed during semiconductor device fabrication after BEOL process is finished. During this step, performed before a wafer is sent to die preparation, all individual integrated circuits that are present on the wafer are tested for functional defects by applying special test patterns to them. The wafer testing is performed by a piece of test equipment called a wafer prober. The process of wafer testing can be referred to in several ways: Wafer Final Test (WFT), Electronic Die Sort (EDS) and Circuit Probe (CP) are probably the most common. Wafer prober A wafer prober is a machine used for integrated circuits verification against designed functionality. It's either manual or automatic test equipment. For electrical testing a set of microscopic contacts or probes called a probe card are held in place whilst the wafer, vacuum-mounted on a wafer chuck, is moved into electrical contact. When a die (or array of dice) have been electrically tested the prober mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Attachment
In electronics manufacturing, integrated circuit packaging is the final stage of semiconductor device fabrication, in which the block of semiconductor material is encapsulated in a supporting case that prevents physical damage and corrosion. The case, known as a " package", supports the electrical contacts which connect the device to a circuit board. In the integrated circuit industry, the process is often referred to as packaging. Other names include semiconductor device assembly, assembly, encapsulation or sealing. The packaging stage is followed by testing of the integrated circuit. The term is sometimes confused with electronic packaging, which is the mounting and interconnecting of integrated circuits (and other components) onto printed-circuit boards. Design considerations Electrical The current-carrying traces that run out of the die, through the package, and into the printed circuit board (PCB) have very different electrical properties compared to on-chip signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer (electronics)
In electronics, a wafer (also called a slice or substrate) is a thin slice of semiconductor, such as a crystalline silicon Crystalline silicon or (c-Si) Is the crystalline forms of silicon, either polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si, consisting of small crystals), or monocrystalline silicon (mono-Si, a continuous crystal). Crystalline silicon is the dominant semiconduc ... (c-Si), used for the fabrication of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaics, to manufacture solar cells. The wafer serves as the substrate (materials science), substrate for microelectronic devices built in and upon the wafer. It undergoes many microfabrication processes, such as doping (semiconductor), doping, ion implantation, Etching (microfabrication), etching, thin-film deposition of various materials, and Photolithography, photolithographic patterning. Finally, the individual microcircuits are separated by wafer dicing and Integrated circuit packaging, packaged as an integrated circuit. History I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |