|
Subordination Trees 2
{{disambig ...
Subordination may refer to *Subordination in a hierarchy (in military, society, etc.) ** Insubordination, disobedience *Subordination (linguistics) *Subordination (finance) * Subordination agreement, a legal document used to deprecate the claim of one party in favor of another * Subordination (horse), a Thoroughbred racehorse In mathematics * Littlewood subordination theorem * Subordinate partition of unity in paracompact space In mathematics, a paracompact space is a topological space in which every open cover has an open refinement that is locally finite. These spaces were introduced by . Every compact space is paracompact. Every paracompact Hausdorff space is normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as architecture, philosophy, design, mathematics, computer science, organizational theory, systems theory, systematic biology, and the social sciences (especially political philosophy). A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's subordinates, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a path. All parts of the hierarchy that are not linked vertically to one ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insubordination
Insubordination is the act of willfully disobeying a lawful order of one's superior. It is generally a punishable offense in hierarchical organizations such as the armed forces, which depend on people lower in the chain of command obeying orders. Military Insubordination is when a service member willfully disobeys the lawful orders of a superior officer. If a military officer disobeys the lawful orders of their civilian superiors, this also counts. For example, the head of state in many countries, is also the most superior officer of the military as the Commander in Chief. Generally, however, an officer or soldier may disobey an unlawful order to the point of mutiny (see Nuremberg defense). In the U.S. military, insubordination is covered under Article 91 of the Uniform Code of Military Justice. It covers disobeying lawful orders as well as disrespectful language or even striking a superior. The article for insubordination should not be confused with the article for contempt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subordination (linguistics)
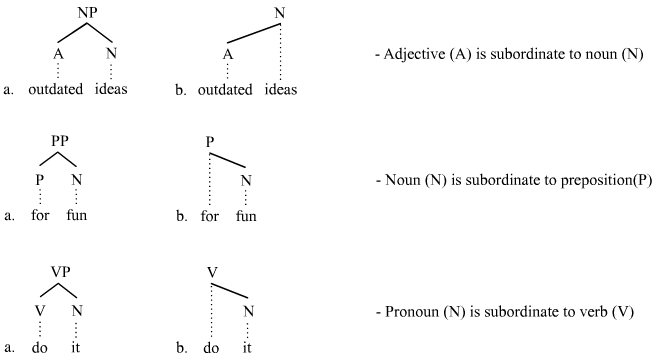
In linguistics, subordination (abbreviated variously , , or ) is a principle of the hierarchical organization of linguistic units. While the principle is applicable in semantics, morphology, and phonology, most work in linguistics employs the term "subordination" in the context of syntax, and that is the context in which it is considered here. The syntactic units of sentences are often either subordinate or coordinate to each other. Hence an understanding of subordination is promoted by an understanding of coordination, and vice versa. Subordinate clauses Subordination as a concept of syntactic organization is associated closely with the distinction between ''coordinate'' and ''subordinate'' clauses. One clause is subordinate to another if it depends on it. The dependent clause is called a ''subordinate clause'' and the independent clause is called the ''main clause'' (= matrix clause). Subordinate clauses are usually introduced by subordinators (= subordinate conjunctions) such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subordination (finance)
Subordination in banking and finance refers to the order of priorities in claims for ownership or interest in various assets. United States law Subordination of debt Subordination is the process by which a creditor is placed in a lower priority for the collection of its debt from its debtor's assets than the priority the creditor previously had, In common parlance, the debt is said to be subordinated but in reality, it is the right of the creditor to collect the debt that has been reduced in priority. The priority of right to collect the debt is important when a debtor owes more than one creditor but has assets of insufficient value to pay them all in full at the time of a default. Except in bankruptcy proceedings, the creditor with the first priority for collection will generally have the first claim on the debtor's assets for its debt and the creditors whose rights are subordinate will thus have fewer assets to satisfy their claims. Subordination can take place by operation of la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subordination Agreement
A subordination agreement is a legal document used to make the claim of one party junior to (or inferior to) a claim in favor of another. It is generally used to grant first lien status to a lienholder A lien ( or ) is a form of security interest granted over an item of property to secure the payment of a debt or performance of some other obligation. The owner of the property, who grants the lien, is referred to as the ''lienee'' and the pers ... who would otherwise be secondary to another party, with the approval of the party that would otherwise have first lien. Typically a subordination arises when there are two existing mortgages, a first mortgage and a second mortgage, and the mortgagor intends to refinance the first mortgage. If the holder of the second mortgage does not subordinate the lien of its mortgage to the new mortgage, the new lender will not refinance the first mortgage. However, the second mortgage holder does not want to release its mortgage and re-file, du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subordination (horse)
Subordination (foaled May 24, 1994) is an American millionaire Thoroughbred racehorse who won major Graded stakes races in 1997 and 1998. Owned by Seth Klarman's Klaravich Stables and trained by Gary Sciacca, Subordination won on both dirt and turf racing surfaces. Retired to stud, Subordination stands in at Montana Ranch in Uruguay Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ... References Subordination's pedigree and partial racing statsVideo at YouTube of Subordination winning the 1998 Belmont Breeders' Cup Handicap 1994 racehorse births Thoroughbred family 2-e Racehorses bred in Kentucky Racehorses trained in the United States {{Racehorse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littlewood Subordination Theorem
In mathematics, the Littlewood subordination theorem, proved by J. E. Littlewood in 1925, is a theorem in operator theory and complex analysis. It states that any Holomorphic function, holomorphic univalent function, univalent self-mapping of the unit disk in the complex numbers that fixes 0 induces a contraction operator, contractive composition operator on various function spaces of holomorphic functions on the disk. These spaces include the Hardy spaces, the Bergman spaces and Dirichlet space. Subordination theorem Let ''h'' be a holomorphic univalent mapping of the unit disk ''D'' into itself such that ''h''(0) = 0. Then the composition operator ''C''''h'' defined on holomorphic functions ''f'' on ''D'' by :C_h(f) = f\circ h defines a linear operator with operator norm less than 1 on the Hardy spaces H^p(D), the Bergman spaces A^p(D). (1 ≤ ''p'' < ∞) and the Dirichlet space . The norms on these spaces are defined by: : |