|
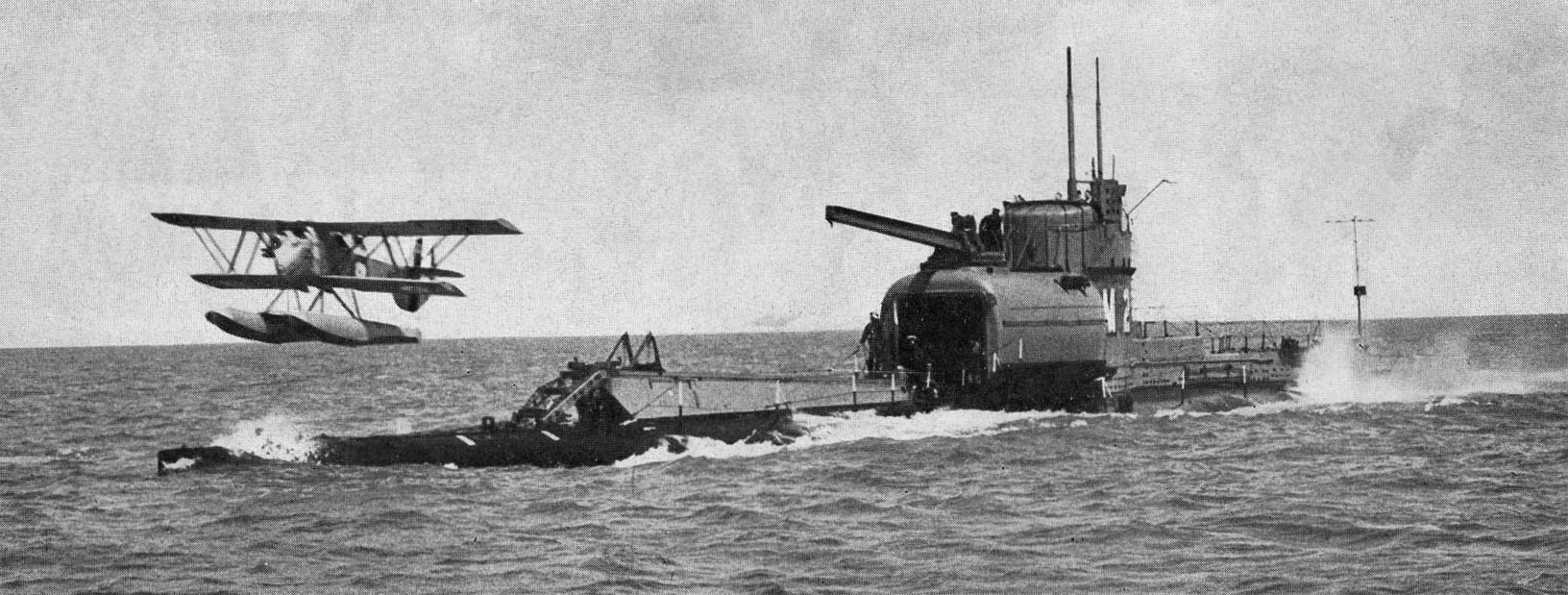
Submarine Aircraft Carriers
A submarine aircraft carrier is a submarine equipped with aircraft for observation or attack missions. These submarines saw their most extensive use during World War II, although their operational significance remained rather small. The most famous of them were the Japanese s and the , although small numbers of similar craft were built for other nations' navies as well. Most operational submarine aircraft carriers, with the exception of the ''I-400'' and AM classes, used their aircraft for reconnaissance and observation. This is in contrast to the typical surface aircraft carrier, whose main function is serving as a base for offensive aircraft. Early history (World War I) Germany was the first nation to experiment with submarine aircraft carriers, initiated by the Imperial German Naval Air Service commander Oberleutnant zur See Friedrich von Arnauld de la Perière who commanded a unit of two Friedrichshafen FF.29 reconnaissance seaplanes in Zeebrugge. One of the first U-boa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Submarine HMS M2
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Briton (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walther Forstmann
Walther Forstmann (9 March 1883 – 2 November 1973) was one of the most highly decorated U-boat commanders in the ''Kaiserliche Marine'' during World War I. He also served in the ''Kriegsmarine'' during World War II in different staff positions. In his time as commander of and in World War I, he conducted 47 patrols and succeeded in sinking 148 ships for a total tonnage of . As such, he is the second most successful submarine commander ever (by tonnage sunk), after de la Perière. World War I On 12 August 1916 ''Kapitänleutnant'' Forstmann of ''U-39'' was awarded the Pour le Mérite for his achievements so far in the First World War. In 1917 Forstmann, in command of ''U-39'', sank five valuable steamers within only two days in the Straits of Gibraltar with over , the (3,862 tonnes), (3,847 tonnes), (4,385 tonnes), (4,702 tonnes) and the Japanese steamer (3,555 tonnes). The ships carried a total load of 31,500 tonnes of coal, of which more than 26,000 tonnes were meant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles. The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hundred years, has changed its meaning over time. During the Age of Sail, the term ''cruising'' referred to certain kinds of missions—independent scouting, commerce protection, or raiding—fulfilled by frigates or sloops-of-war, which functioned as the ''cruising warships'' of a fleet. In the middle of the 19th century, ''cruiser'' came to be a classification of the ships intended for cruising distant waters, for commerce raiding, and for scouting for the battle fleet. Cruisers came in a wide variety of sizes, from the medium-sized protected cruiser to large armored cruisers that were nearly as big (although not as powerful or as well-armored) as a pre-dreadnought battleship. With the advent of the dreadnought battleship before World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Commissioning
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in active duty with its country's military forces. The ceremonies involved are often rooted in centuries-old naval tradition. Ship naming and launching endow a ship hull with her identity, but many milestones remain before she is completed and considered ready to be designated a commissioned ship. The engineering plant, weapon and electronic systems, galley, and other equipment required to transform the new hull into an operating and habitable warship are installed and tested. The prospective commanding officer, ship's officers, the petty officers, and seamen who will form the crew report for training and familiarization with their new ship. Before commissioning, the new ship undergoes sea trials to identify any deficiencies needing corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
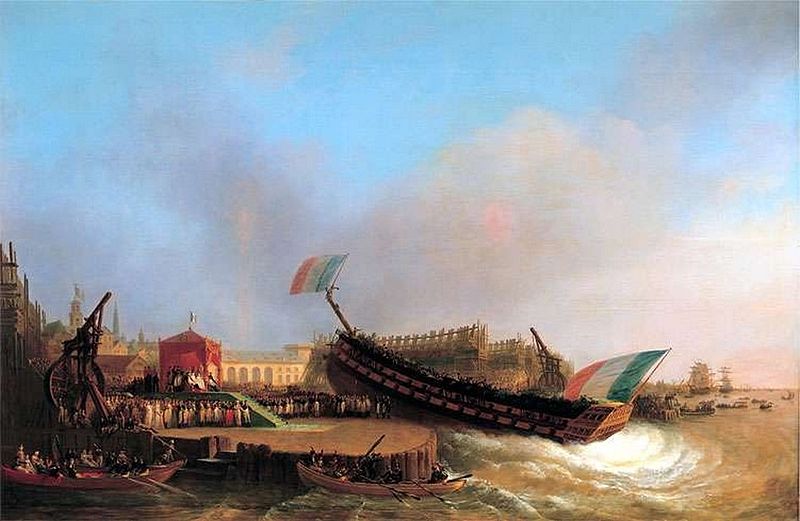
Ship Naming And Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performance of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back thousands of years, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and, in addition to the size and weight of the vessel, represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The oldest, most familiar, and most widely used is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surcouf FRA
Surcouf may refer to: __NOTOC__ People * Édouard Surcouf (1862–1938), French engineer, dirigible designer and pilot, and industrialist * Jacques Surcouf (1873–1934), French entomologist * Marie Surcouf (1863–1928), French balloonist and feminist * Nicolas Surcouf (1770–1848), French privateer and shipowner, brother of Robert Surcouf * Robert Surcouf (1773–1827), French privateer, slave trader and shipowner Ships * French ship ''Surcouf'', five ships named after Robert Surcouf Works about Robert Surcouf * ''Surcouf'' (film), a 1924 French silent film serial * ''Surcouf'' (opéra comique), an 1887 French opéra comique * ''The Sea Pirate'', original title ''Surcouf, le tigre des sept mers'', a 1966 French-Italian-Spanish adventure film See also * * * Robert Surcouf de Maisonneuve Robert Surcouf de Maisonneuve (4 January 1671Cunat, p. 145 – c. 1720Cunat, p. 152) was a Breton privateer. Career Born in Saint-Malo, Surcouf de Maisonneuve captained the private ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floatplane
A floatplane is a type of seaplane with one or more slender floats mounted under the fuselage to provide buoyancy. By contrast, a flying boat uses its fuselage for buoyancy. Either type of seaplane may also have landing gear suitable for land, making the vehicle an amphibious aircraft. British usage is to call "floatplanes" "seaplanes" rather than use the term "seaplane" to refer to both floatplanes and flying boats. Use Since World War II and the advent of helicopters, advanced aircraft carriers and land-based aircraft, military seaplanes have stopped being used. This, coupled with the increased availability of civilian airstrips, have greatly reduced the number of flying boats being built. However, numerous modern civilian aircraft have floatplane variants, most of these are offered as third-party modifications under a supplemental type certificate (STC), although there are several aircraft manufacturers that build floatplanes from scratch. These floatplanes have found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sopwith Tabloid
The Sopwith Tabloid and Sopwith Schneider (floatplane) were British biplanes, originally designed as sports aircraft and later adapted for military use. They were among the first successful types to be built by the Sopwith Aviation Company. The " Tabloid", so named because of its small size, caused a sensation when it made its first public appearance. A floatplane variant was prepared in under a month and entered for the 1914 Schneider Trophy race where it was piloted by Howard Pixton. This aircraft won the competition against minimal opposition.Bruce, 1996, p.1 Production orders for both types were placed by the military, and although a few Gnome Lambda-powered Tabloids saw limited service in the early war years, some Schneiders were still in Naval service four years later, at the end of the First World War. Design and development The original Tabloid, which was first flown by Harry Hawker on 27 November 1913, was a two-seat single-bay biplane with a side-by-side seating, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoplane
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple planes. A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing configuration and is the simplest to build. However, during the early years of flight, these advantages were offset by its greater weight and lower manoeuvrability, making it relatively rare until the 1930s. Since then, the monoplane has been the most common form for a fixed-wing aircraft. Characteristics Support and weight The inherent efficiency of the monoplane is best achieved in the cantilever wing, which carries all structural forces internally. However, to fly at practical speeds the wing must be made thin, which requires a heavy structure to make it strong and stiff enough. External bracing can be used to improve structural efficiency, reducing weight and cost. For a wing of a given size, the weight reduction allows it to fly slower a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LFG Stralsund V 19 Putbus
The LFG Stralsund V 19 Putbus was a submarine-borne floatplane scout designed and built by LFG Roland in the latter stages of World War I. Design The V 19 Putbus was a single-seat long-wing monoplane made from aluminum. The fuselage was tube-shaped, made from flat wrapped duraluminum, and the fuel was stored in the wings, which had automatic shut-off valves that allowed the wings to be removed without draining the fuel tanks. Developmental history The LFG Stralsund V 19 Putbus was completed in September 1918 and conducted flight tests on behalf of the Imperial German Navy until the Armistice. Three production V 19s were ordered, but none were built by the time the Armistice was signed in November 1918. Interestingly, the Putbus was spared from demolition and scrapping under the terms of the Inter-Allied Disarmament Commission and continued to fly until 1923, when it was eventually scrapped after failing to find a commercial role. Specifications References Further reading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hansa-Brandenburg W
The Hansa-Brandenburg W was a reconnaissance floatplane produced in Germany in 1914 to equip the Imperial German Navy. Similar in general layout to the Hansa-Brandenburg B.I landplane, the W was a conventional three-bay biplane with unstaggered wings of equal span. The pilot and observer sat in tandem, open cockpits, and the undercarriage consisted of twin pontoons. The NW and GNW of 1915 were a revised versions powered by a more powerful engine. Variants * W - initial production version with Benz Bz.II engine (27 built) * NW - revised version with Mercedes D.III engine * GNW - revised version with Mercedes D.III engine Operators ; *Kaiserliche Marine ; *Ottoman Air Force The Aviation Squadrons of the Ottoman Empire were military aviation units of the Ottoman Army and Navy.Edward J. Erickson, ''Ordered To Die: A History of the Ottoman Army in the First World War'', "Appendix D The Ottoman Aviation Inspectorate an ... Specifications (NW) References * * {{Han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biplane
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While a biplane wing structure has a structural advantage over a monoplane, it produces more drag than a monoplane wing. Improved structural techniques, better materials and higher speeds made the biplane configuration obsolete for most purposes by the late 1930s. Biplanes offer several advantages over conventional cantilever monoplane designs: they permit lighter wing structures, low wing loading and smaller span for a given wing area. However, interference between the airflow over each wing increases drag substantially, and biplanes generally need extensive bracing, which causes additional drag. Biplanes are distinguished from tandem wing arrangements, where the wings are placed forward and aft, instead of above and below. The term is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_underway_2009.jpg)

.jpg)


.jpg)