|
Subinvolution
{{Short description, Medical condition after childbirthSubinvolution is a medical condition in which after childbirth, the uterus does not return to its normal size. Presentation Symptoms The condition may be asymptomatic. The predominant symptoms are: * Abnormal lochial discharge either excessive or prolonged * Irregular or at times excessive uterine bleeding * Irregular cramp like pain is cases of retained products or rise of temperature in sepsis Signs # The uterine height is greater than the normal for the particular day of puerperium. Normal puerperal uterus may be displaced by a full bladder or a loaded rectum. It feels boggy and softer upon palpation. # Presence of features responsible for subinvolution may be evident. Causes Predisposing factors # Grand multiparity # Overdistension of uterus as in twins and hydramnios # Ill maternal health # Caesarean section # Uterine prolapse # Retroversion after the uterus becomes pelvic organ # Uterine fibroid Aggravating factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Involution (medicine)
Involution is the shrinking or return of an organ to a former size. At a cellular level, involution is characterized by the process of proteolysis of the basement membrane (basal lamina), leading to epithelial regression and apoptosis, with accompanying stromal fibrosis. The consequent reduction in cell number and reorganization of stromal tissue leads to the reduction in the size of the organ. Examples Thymus The thymus continues to grow between birth and puberty and then begins to atrophy, a process directed by the high levels of circulating sex hormones. Proportional to thymic size, thymic activity (T cell output) is most active before puberty. Upon atrophy, the size and activity are dramatically reduced, and the organ is primarily replaced with fat. The atrophy is due to the increased circulating level of sex hormones, and chemical or physical castration of an adult results in the thymus increasing in size and activity. Uterus Involution is the process by which the uterus is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the shortening and opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the postpartum. The first stage is characterized by abdominal cramping or back pain that typically lasts half a minute and occurs every 10 to 30 minutes. Contractions gradually becomes stronger and closer together. Since the pain of childbirth correlates with contractions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
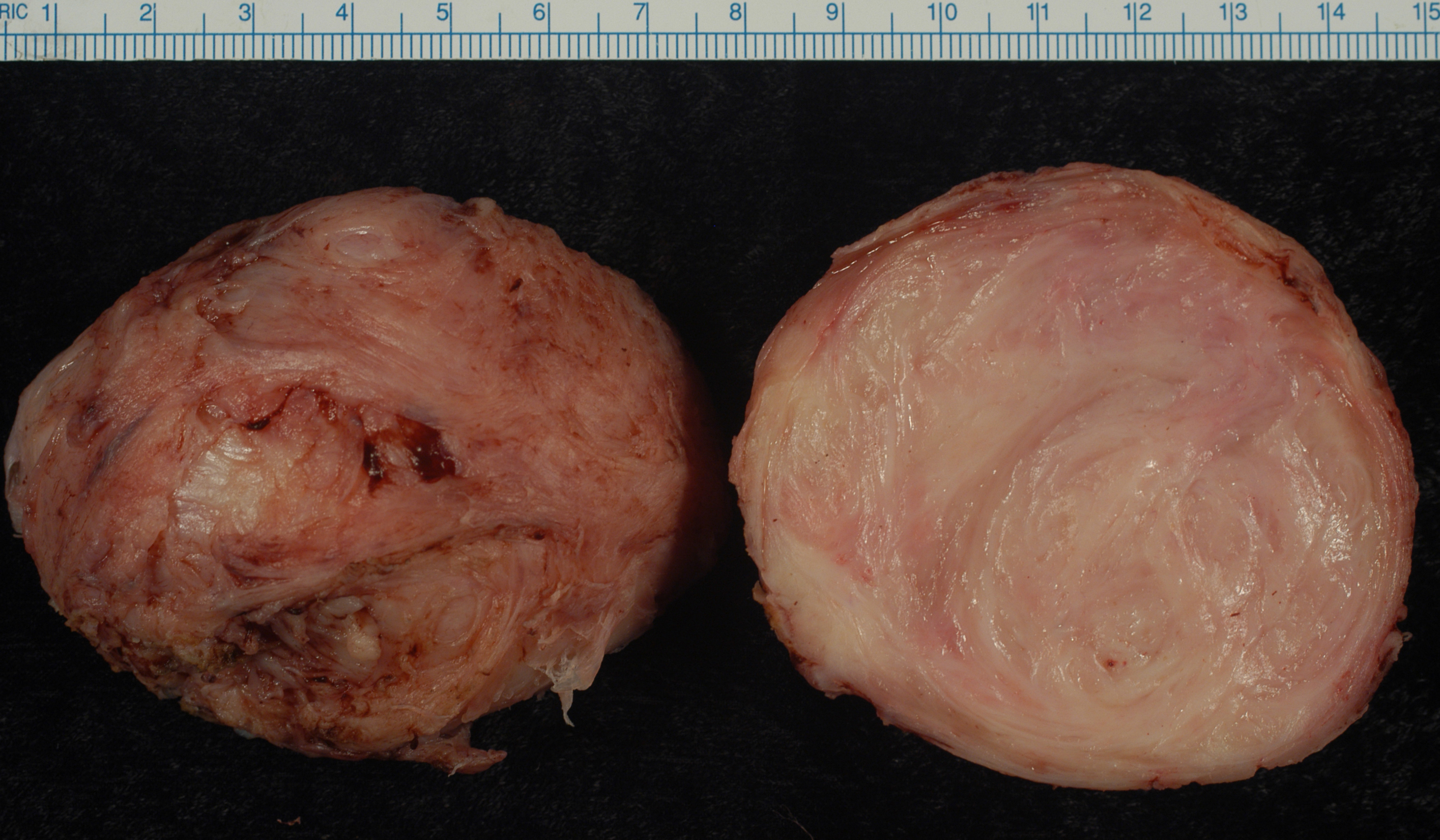
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, is a narrow part known as the isthmus that connects to the cervix, leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes, at the uterine horns, and the rounded part above the openings to the fallopian tubes is the fundus. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the uterotubal junction. The fertilized egg is carried to the uterus along the fallopian tube. It will have divided on its journey to form a blastocyst that will implant itself into the lining of the uterus – the endometrium, where it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochia
In the field of obstetrics, lochia is the vaginal discharge after giving birth, containing blood, mucus, and uterine tissue. Lochia discharge typically continues for four to eight weeks after childbirth, a time known as the postpartum period or puerperium. A 2016 review ties this "lochial period" to worldwide customs of postpartum confinement, a time for the new mother and baby to bond. Lochia is sterile for the first two days, but not so by the third or fourth day, as the uterus begins to be colonized by vaginal commensals such as non-hemolytic streptococci and '' E. coli''. Stages It progresses through three stages: #Lochia rubra (or cruenta) is the first discharge, composed of blood, shreds of fetal membranes, decidua, vernix caseosa, lanugo and membranes. It is red in color because of the large amount of blood it contains. It lasts 1 to 4 days after birth, before easing to light "spotting". #Lochia serosa is the term for lochia that has thinned and turned brownish or pink in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerperium
The postpartum (or postnatal) period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to end within 6 weeks as the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, returns to a non-pregnant state. The terms puerperium, puerperal period, or immediate postpartum period are commonly used to refer to the first six weeks following childbirth. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes the postnatal period as the most critical and yet the most neglected phase in the lives of mothers and babies; most maternal and infant mortality, newborn deaths occur during this period. In scientific literature, the term is commonly abbreviated to P''x'', where ''x'' is a number; for example, "day P5" should be read as "the fifth day after birth". This is not to be confused with the medical nomenclature that uses G P to stand for number and outcomes of pregnancy (gravidity and parity). A female giving birth in a hospital may leave as soon as they are medically stable, which can be as ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parity (biology)
In biology and human medicine, gravidity and parity are the number of times a woman is or has been pregnant (gravidity) and carried the pregnancies to a viable gestational age (parity). These terms are usually coupled, sometimes with additional terms, to indicate more details of the woman's obstetric history. When using these terms: * Gravida indicates the number of times a woman is or has been pregnant, regardless of the pregnancy outcome. A current pregnancy, if any, is included in this count. A multiple pregnancy (e.g., twins, triplets, etc.) is counted as 1. * Parity, or "para", indicates the number of births (including live births and stillbirths) where pregnancies reached viable gestational age. A multiple pregnancy (e.g., twins, triplets, etc.) carried to viable gestational age is still counted as 1. * Abortus is the number of pregnancies that were lost prior to viable gestational age for any reason, including induced abortions or miscarriages but not stillbirths. The abort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesarean Section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk. Reasons for the operation include obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, breech birth, and problems with the placenta or umbilical cord. A caesarean delivery may be performed based upon the shape of the mother's pelvis or history of a previous C-section. A trial of vaginal birth after C-section may be possible. The World Health Organization recommends that caesarean section be performed only when medically necessary. Most C-sections are performed without a medical reason, upon request by someone, usually the mother. A C-section typically takes 45 minutes to an hour. It may be done with a spinal block, where the woman is awake, or under general anesthesia. A urinary catheter is used to drain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse is when the uterus descends towards or through the opening of the vagina. Symptoms may include vaginal fullness, pain with sex, trouble urinating, urinary incontinence, and constipation. Often it gets worse over time. Low back pain and vaginal bleeding may also occur. Risk factors include pregnancy, childbirth, obesity, constipation, and chronic coughing. Diagnosis is based on examination. It is a form of pelvic organ prolapse, together with bladder prolapse, large bowel prolapse, and small bowel prolapse. Preventive efforts include managing chronic breathing problems, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. Mild cases may be treated with a pessary together with hormone replacement therapy. More severe cases may require surgery such as a vaginal hysterectomy. About 14% of women are affected. It occurs most commonly after menopause. Causes The most common cause of uterine prolapse is trauma during childbirth, in particular multiple or difficult bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroversion
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Fibroid
Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas or fibroids, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Most women with fibroids have no symptoms while others may have painful or heavy periods. If large enough, they may push on the bladder, causing a frequent need to urinate. They may also cause pain during penetrative sex or lower back pain. A woman can have one uterine fibroid or many. Occasionally, fibroids may make it difficult to become pregnant, although this is uncommon. The exact cause of uterine fibroids is unclear. However, fibroids run in families and appear to be partly determined by hormone levels. Risk factors include obesity and eating red meat. Diagnosis can be performed by pelvic examination or medical imaging. Treatment is typically not needed if there are no symptoms. NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, may help with pain and bleeding while paracetamol (acetaminophen) may help with pain. Iron supplements may be needed in those with heavy periods. Medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |