|
Subdominant Key
In music, the subdominant is the fourth tonal degree () of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance ''below'' the tonic as the dominant is ''above'' the tonicin other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdominant. It also happens to be the note one step below the dominant. In the movable do solfège system, the subdominant note is sung as ''fa''. The triad built on the subdominant note is called the subdominant chord. In Roman numeral analysis, the subdominant chord is typically symbolized by the Roman numeral "IV" in a major key, indicating that the chord is a major triad. In a minor key, it is symbolized by "iv", indicating that the chord is a minor triad. These chords may also appear as seventh chords: in major, as IVM7, or in minor as iv7 or sometimes IV7: A cadential subdominant chord followed by a tonic chord produces the so-called plagal cadence. As with other chords which often precede the dominant, subdominant chords typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music
Music is generally defined as the The arts, art of arranging sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Exact definition of music, definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect of all human societies, a cultural universal. While scholars agree that music is defined by a elements of music, few specific elements, there is Elements of music#Selection of elements, no consensus on their precise definitions. The creation of music is commonly divided into musical composition, musical improvisation, and musical performance, though the topic itself extends into #Academic study, academic disciplines, Music journalism, criticism, Philosophy of music, philosophy, and Music psychology, psychology. Music may be performed or improvised using a vast range of musical instrument, instruments, including the human voice. In some musical contexts, a performance or composi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Chord
In music theory, a minor chord is a chord that has a root, a minor third, and a perfect fifth. When a chord comprises only these three notes, it is called a minor triad. For example, the minor triad built on C, called a C minor triad, has pitches C–E–G: In harmonic analysis and on lead sheets, a C minor chord can be notated as Cm, C−, Cmin, or simply the lowercase "c". A minor triad is represented by the integer notation . A minor triad can also be described by its intervals: the interval between the bottom and middle notes is a minor third, and the interval between the middle and top notes is a major third. By contrast, a major triad has a major third on the bottom and minor third on top. They both contain fifths, because a minor third (three semitones) plus a major third (four semitones) equals a perfect fifth (seven semitones). Chords that are constructed of consecutive (or "stacked") thirds are called '' tertian.'' In Western classical music from 1600 to 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
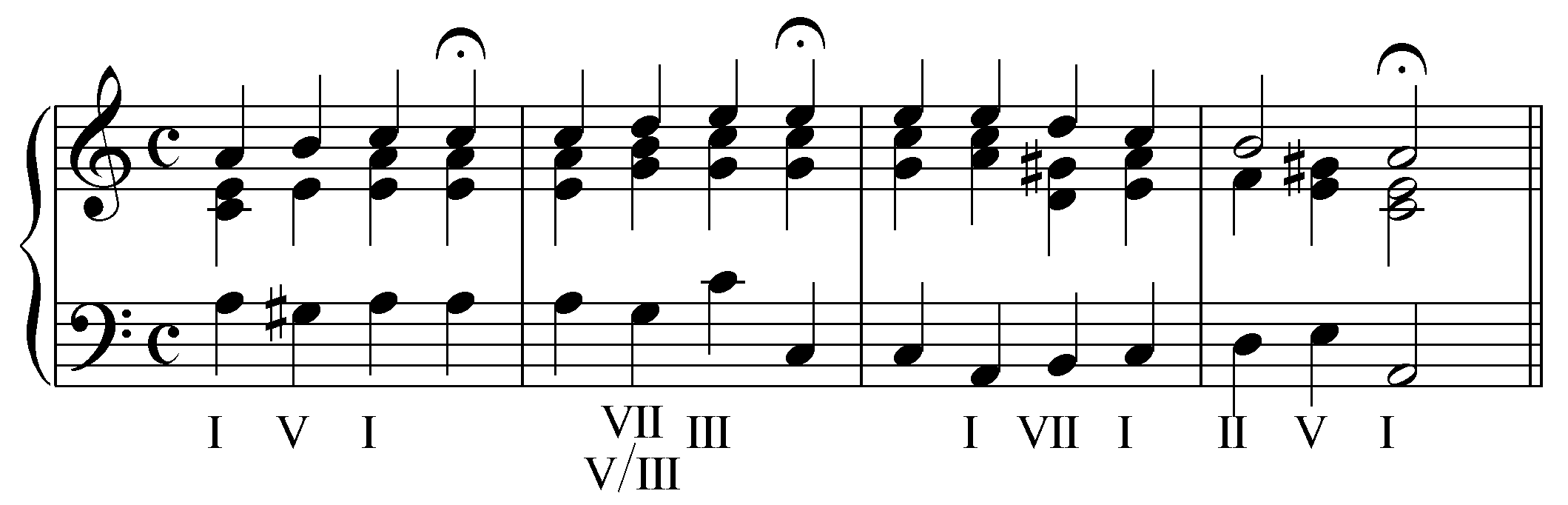
Subtonic
In music, the subtonic is the degree of a musical scale which is a whole step below the tonic note. In a major key, it is a lowered, or flattened, seventh scale degree (). It appears as the seventh scale degree in the natural minor and descending melodic minor scales but not in the major scale. In major keys, the subtonic sometimes appears in borrowed chords. In the movable do solfège system, the subtonic note is sung as ''te'' (or ''ta''). The subtonic can be contrasted with the leading note, which is a ''half step'' below the tonic. The distinction between leading note and subtonic has been made by theorists since at least the second quarter of the 20th century. Before that, the term ''subtonic'' often referred to the leading tone triad, for example. The word ''subtonic'' is also used as an English translation of ''subtonium'', the Latin term used in Gregorian chant theory for the similar usage of a tone one whole step below the mode final in the Dorian, Phrygian, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitone
A semitone, also called a half step or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically. It is defined as the interval between two adjacent notes in a 12-tone scale. For example, C is adjacent to C; the interval between them is a semitone. In a 12-note approximately equally divided scale, any interval can be defined in terms of an appropriate number of semitones (e.g. a whole tone or major second is 2 semitones wide, a major third 4 semitones, and a perfect fifth 7 semitones. In music theory, a distinction is made between a diatonic semitone, or minor second (an interval encompassing two different staff positions, e.g. from C to D) and a chromatic semitone or augmented unison (an interval between two notes at the same staff position, e.g. from C to C). These are enharmonically equivalent when twelve-tone equal temperament is used, but are not the same thing in meantone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Tone
In music theory, a leading-tone (also called a subsemitone, and a leading-note in the UK) is a note or pitch which resolves or "leads" to a note one semitone higher or lower, being a lower and upper leading-tone, respectively. Typically, ''the'' leading tone refers to the seventh scale degree of a major scale (), a major seventh above the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the leading-tone is sung as ''ti''. A leading-tone triad is a triad built on the seventh scale degree in a major key (vii in Roman numeral analysis), while a leading-tone seventh chord is a seventh chord built on the seventh scale degree (vii7). Walter Piston considers and notates vii as V, an incomplete dominant seventh chord. (For the Roman numeral notation of these chords, see Roman numeral analysis.) Note Seventh scale degree (or lower leading tone) Typically, when people speak of ''the'' leading tone, they mean the seventh scale degree () of the major scale, which has a strong affinity fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulation (music)
In music, modulation is the change from one tonality ( tonic, or tonal center) to another. This may or may not be accompanied by a change in key signature (a key change). Modulations articulate or create the structure or form of many pieces, as well as add interest. Treatment of a chord as the tonic for less than a phrase is considered tonicization. Requirements * Harmonic: quasi- tonic, modulating dominant, pivot chordForte (1979), p. 267. * Melodic: recognizable segment of the scale of the quasi-tonic or strategically placed leading-tone * Metric and rhythmic: quasi-tonic and modulating dominant on metrically accented beats, prominent pivot chord The quasi-tonic is the tonic of the new key established by the modulation was semi. The modulating dominant is the dominant of the quasi-tonic. The pivot chord is a predominant to the modulating dominant and a chord common to both the keys of the tonic and the quasi-tonic. For example, in a modulation to the dominant, ii/V– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riemannian Theory
"Riemannian theory" in general refers to the musical theories of German theorist Hugo Riemann (1849–1919). His theoretical writings cover many topics, including musical logic, notation, harmony, melody, phraseology, the history of music theory,''Geschichte der Musiktheorie im IX.-XIX. Jahrhundert'', Berlin, 1898. etc. More particularly, the term ''Riemannian theory'' often refers to his theory of harmony, characterized mainly by its dualism and by a concept of harmonic functions. Dualism Riemann's "dualist" system for relating triads was adapted from earlier 19th-century harmonic theorists. The term "dualism" refers to the emphasis on the inversional relationship between major and minor, with minor triads being considered "upside down" versions of major triads; this "harmonic dualism" (harmonic polarity) is what produces the change-in-direction described above. See also the related term Utonality.Klumpenhouwer, Henry, ''Some Remarks on the Use of Riemann Transformations,'' M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predominant Chord
In music theory, a predominant chord (also pre-dominant) is any chord which normally resolves to a dominant chord.Benward & Saker (2009). ''Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II'', Glossary, p.359. Eighth Edition. . "Any chord in functional harmony that normally resolves to the dominant chord." Examples of predominant chords are the subdominant (IV, iv), supertonic (ii, ii°), Neapolitan sixth and German sixth. Other examples are the secondary dominant (V/V) and secondary leading tone chord. Predominant chords may lead to secondary dominants. Predominant chords both expand away from the tonic ''and'' lead to the dominant, affirming the dominant's pull to the tonic.Cleland, Kent D. and Dobrea-Grindahl, Mary (2013). ''Developing Musicianship Through Aural Skills: A Holistic Approach to Sight Singing and Ear Training'', p.255. Routledge. . Thus they lack the stability of the tonic and the drive towards resolution of the dominant. The predominant harmonic function is part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadence
In Western musical theory, a cadence (Latin ''cadentia'', "a falling") is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards. Don Michael Randel (1999). ''The Harvard Concise Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', pp. 105-106. . A harmonic cadence is a progression of two or more chords that concludes a phrase, section, or piece of music. A rhythmic cadence is a characteristic rhythmic pattern that indicates the end of a phrase. A cadence can be labeled "weak" or "strong" depending on the impression of finality it gives. While cadences are usually classified by specific chord or melodic progressions, the use of such progressions does not necessarily constitute a cadence—there must be a sense of closure, as at the end of a phrase. Harmonic rhythm plays an important part in determining where a cadence occurs. Cadences are strong indicators of the tonic or central pitch of a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Chord
A seventh chord is a chord consisting of a triad plus a note forming an interval of a seventh above the chord's root. When not otherwise specified, a "seventh chord" usually means a dominant seventh chord: a major triad together with a minor seventh. However, a variety of sevenths may be added to a variety of triads, resulting in many different types of seventh chords. In its earliest usage, the seventh was introduced solely as an embellishing or nonchord tone. The seventh destabilized the triad, and allowed the composer to emphasize movement in a given direction. As time passed and the collective ear of the western world became more accustomed to dissonance, the seventh was allowed to become a part of the chord itself, and in some modern music, jazz in particular, nearly every chord is a seventh chord. Additionally, the general acceptance of equal temperament during the 19th century reduced the dissonance of some earlier forms of sevenths. Classification Most textbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallace Berry
Wallace Berry (10 January 1928 – 16 November 1991) was an American music theorist and composer who taught at the University of Michigan and later at the University of British Columbia. Mid-way through his career, Berry shifted focus from music composition, and became a leading figure in the research and teaching of music theory. Life and career Berry was born in La Crosse, Wisconsin. Berry was educated at the University of Southern California (BMus 1949, PhD 1956), where he studied with Halsey Stevens. His composition ''Spoon River'', on texts by Edgar Lee Masters (1952), won him national recognition. In 1953-54, he studied under Nadia Boulanger in Paris. He taught at the University of Michigan (1957–77), becoming chair of music theory in 1968. He was chair of the music department in the University of British Columbia from 1978–84, and thereafter taught theory. Berry was the founding Vice President of the Society for Music Theory from 1977-1982, and then became the socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Triad
In music, a primary triad is one of the three triads, or three-note chords built from major or minor thirds, most important in tonal and diatonic music, as opposed to an auxiliary triad or secondary triad. Each triad found in a diatonic key corresponds to a particular diatonic function. Functional harmony tends to rely heavily on the primary triads: triads built on the tonic, subdominant, and dominant degrees.Harrison, Daniel (1994). ''Harmonic Function in Chromatic Music: A Renewed Dualist Theory and an Account of its Precedents'', p.45. . Cited in Deborah Rifkin. "A Theory of Motives for Prokofiev's Music", p.274, ''Music Theory Spectrum'', Vol. 26, No. 2 (Autumn, 2004), pp. 265-289. University of California Press on behalf of the Society for Music Theory The roots of these triads begin on the first, fourth, and fifth degrees (respectively) of the diatonic scale, otherwise symbolized: I, IV, and V (again, respectively). Primary triads, "express function clearly and unam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |