|
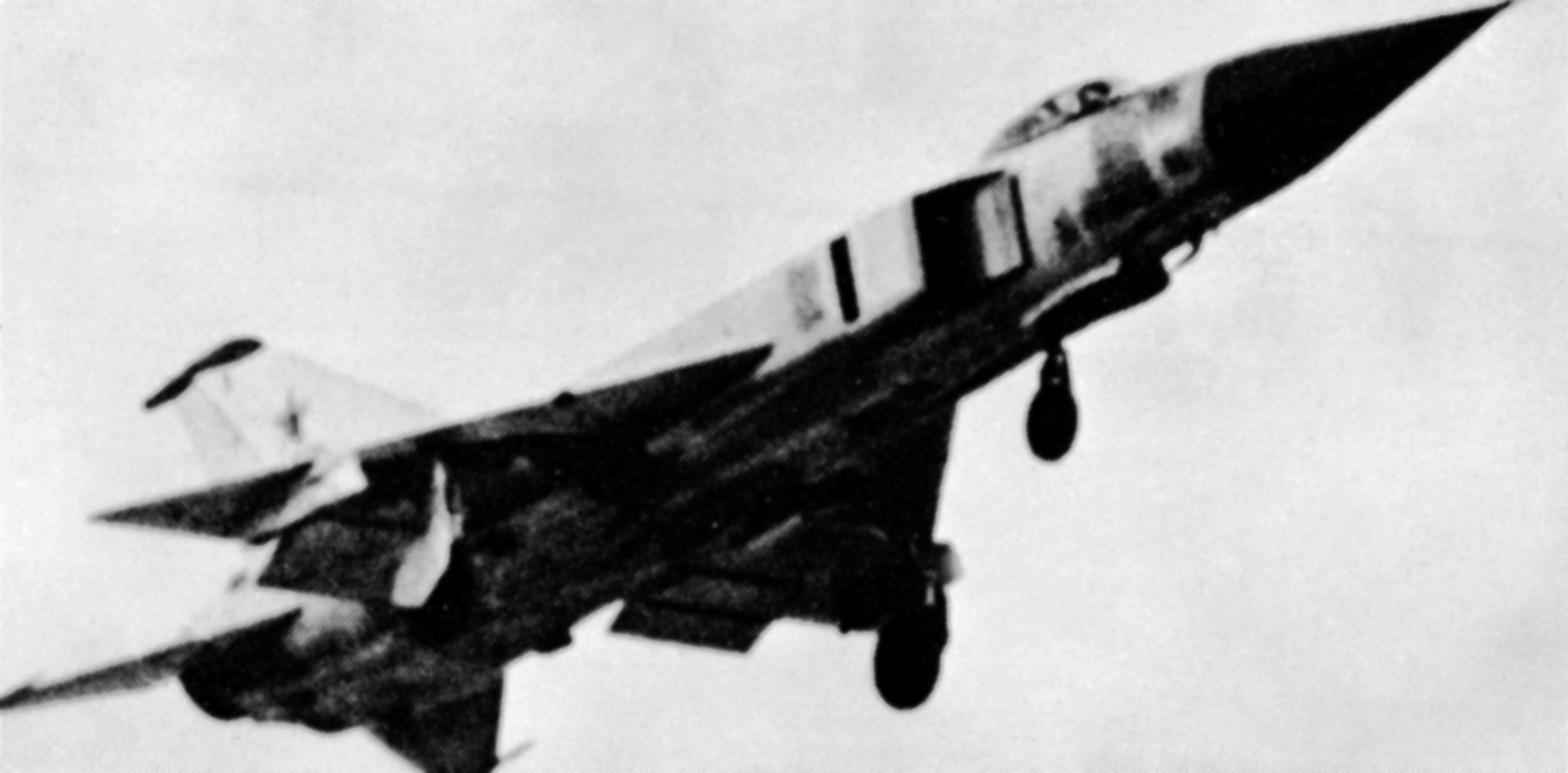
Su-11
The Sukhoi Su-11 (NATO reporting name: Fishpot-C) was an interceptor aircraft used by the Soviet Union in the 1960s. Design and development The Su-11 was an upgraded version of the Sukhoi Su-9 ('Fishpot') interceptor, which had been developed in parallel with the OKB's swept wing Su-7 fighter bomber. Recognizing the Su-9's fundamental limitations, Sukhoi began work on the Su-11, which first flew in 1961 as the T-47 prototype. The Su-11 shared the Su-9's delta wing, swept tailplanes and cigar-shaped fuselage, as well as the circular nose intake, but had a longer nose to accommodate the more powerful 'Oryol' (''Eagle''; NATO reporting name 'Skip Spin') radar set. A more powerful Lyulka AL-7F-1 turbojet was installed, providing 9.8 kN (2,210 lbf) more afterburning thrust for improved climb rate and high-altitude performance (and to compensate for increased weight). The Su-11 can be distinguished from the Su-9 by the external fuel pipes atop the fuselage, aft of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-9
The Sukhoi Su-9 ( NATO reporting name: Fishpot) was a single-engine, all-weather, missile-armed interceptor aircraft developed by the Soviet Union. Development The Su-9 emerged from aerodynamic studies by TsAGI, the Soviet aerodynamic center, during the Korean War, which devised several optimum aerodynamic configurations for jet fighters. The design first flew in 1956 as the T-405 prototype. The Su-9 was developed at the same time as the Su-7 "Fitter", and both were first seen by the West at the Tushino Aviation Day on 24 June 1956, where the Su-9 was dubbed Fitter-B. It entered service in 1959. Total production of the Su-9 was about 1,100 aircraft. It is believed that at least some Su-9s were upgraded to Su-11 "Fishpot-C" form. None were exported to any of the USSR's client states nor to the Warsaw Pact nations. Remaining Su-9s and later Su-11s were retired during the 1970s. Some were retained as test vehicles or converted to remote-piloted vehicles for use as unmanned aer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Su-15
The Sukhoi Su-15 ( NATO reporting name: Flagon) is a twinjet supersonic interceptor aircraft developed by the Soviet Union. It entered service in 1965 and remained one of the front-line designs into the 1990s. The Su-15 was designed to replace the Sukhoi Su-11 and Sukhoi Su-9, which were becoming obsolete as NATO introduced newer and more capable strategic bombers. Development Recognizing the limitations of the earlier Su-9 and Su-11 in intercepting the new Boeing B-52 Stratofortress, particularly in terms of radar and aircraft performance, the Sukhoi OKB quickly began the development of a heavily revised and more capable aircraft. A variety of development aircraft evolved, including the Sukhoi T-49, which shared the fuselage of the Su-9 (including its single engine), but used cheek-mounted intakes to leave the nose clear for a large radome for the RP-22 Oryol-D ("Eagle") radar (NATO "Skip Spin"), and the T-5, essentially a heavily modified Su-11 with a widened rear fuselage c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-8 (missile)
The Kaliningrad K-8 (R-8) ( NATO reporting name AA-3 ' Anab') was a medium-range air-to-air missile developed by the Soviet Union for interceptor aircraft use.Gordon, Yefim. ''Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons''. Midland. 2004. The missile was developed by OKB-339/NII-339 (currently Phazotron NIIR). The infrared seeker was developed by TsKB-589 GKOT (currently TsKB Geofizika), who also developed the seeker for 9M31 missile of 9K31 Strela-1. History The K-8's development began in 1955, known as R-8 in service. Like most Soviet air-to-air missiles, it was made with a choice of semi-active radar homing or infrared seeker heads. The original missile was compatible with the Uragan-5B radar used on the Sukhoi Su-11 and several developmental aircraft from Mikoyan-Gurevich. It was upgraded to R-8M (better known as R-98) standard in 1961, giving the SARH weapon the capability for head-on intercepts. In 1963 it was further upgraded to the R-8M1, making it compatible with the RP-11 Oriol- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyulka AL-7
The Lyulka AL-7 was a turbojet designed by Arkhip Mikhailovich Lyulka and produced by his Lyulka design bureau. The engine was produced between 1954 and 1970.Gunston 1989, p.100. Design and development The AL-7 had supersonic airflow through the first stage of the compressor. TR-7 prototype, developing 6,500 kgf (14,330 lbf, 63.7 kN) of thrust, was tested in 1952, and the engine was initially intended for Ilyushin's Il-54 bomber. The afterburning AL-7F version was created in 1953. In April 1956, the Sukhoi S-1 prototype, equipped with the AL-7F, exceeded Mach 2 at 18,000 m (70,900 ft), which led to the production of the Su-7 'Fitter' and Su-9 'Fishpot', equipped with this engine.Green, William and Gordon Swanborough. ''The Great Book of Fighters.'' St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing, 2001. . Later, the engine was adopted for the Tu-128 'Fiddler' in 1960, and for the AS-3 'Kangaroo' cruise missile. The Beriev Be-10 jet flying boat used a non-afterburning AL-7PB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaliningrad K-8
The Kaliningrad K-8 (R-8) ( NATO reporting name AA-3 ' Anab') was a medium-range air-to-air missile developed by the Soviet Union for interceptor aircraft use.Gordon, Yefim. ''Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons''. Midland. 2004. The missile was developed by OKB-339/NII-339 (currently Phazotron NIIR). The infrared seeker was developed by TsKB-589 GKOT (currently TsKB Geofizika), who also developed the seeker for 9M31 missile of 9K31 Strela-1. History The K-8's development began in 1955, known as R-8 in service. Like most Soviet air-to-air missiles, it was made with a choice of semi-active radar homing or infrared seeker heads. The original missile was compatible with the Uragan-5B radar used on the Sukhoi Su-11 and several developmental aircraft from Mikoyan-Gurevich. It was upgraded to R-8M (better known as R-98) standard in 1961, giving the SARH weapon the capability for head-on intercepts. In 1963 it was further upgraded to the R-8M1, making it compatible with the RP-11 Oriol-D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Air Defence Forces
The Soviet Air Defence Forces (russian: войска ПВО, ''voyska protivovozdushnoy oborony'', ''voyska PVO'', ''V-PVO'', lit. ''Anti-Air Defence Troops''; and formerly ''protivovozdushnaya oborona strany'', ''PVO strany'', lit. ''Anti-Air Defence of the Country'') was the air defence branch of the Soviet Armed Forces. Formed in 1941, it continued being a service branch of the Russian Armed Forces after 1991 until it was merged into the Air Force in 1998. Unlike Western air defence forces, V-PVO was a branch of the military unto itself, separate from the Soviet Air Force (VVS) and Air Defence Troops of Ground Forces. During the Soviet period it was generally ranked third in importance of the Soviet services, behind the Strategic Rocket Forces and the Ground Forces. History Service during Second World War Preparations for creation of the air defence forces started in 1932, and by the beginning of Operation Barbarossa, June 1941, there were 13 PVO zones within the military di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1964 In Aviation
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1964: Events * Chilean President Jorge Alessandri grants the Chilean Navy the authority to operate all types of aircraft without restriction. It is the first time that the navy has administrative control of all naval aircraft since 1930. January * January 13 – A United States Air Force B-52D Stratofortress carrying two Mark 53 nuclear bombs loses its vertical stabilizer in turbulence during a winter storm and crashes on Savage Mountain near Barton, Maryland. Only two of the five crewmen survive. The bombs are recovered two days later. * January 22 – In its first public violation of the 1959 requirement for all aircraft operating from the aircraft carrier ''Minas Gerais'' to belong to the Brazilian Air Force, the Brazilian Navy steams ''Minas Gerais'' into Guanabara Bay at Rio de Janeiro with four navy T-28 Trojan trainers on her flight deck.Scheina, Robert L., ''Latin America: A Naval History 1810-1987'', Annapolis, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi
The JSC Sukhoi Company (russian: ПАО «Компания „Сухой“», ) is a Russian aircraft manufacturer (formerly Soviet Union, Soviet), headquartered in Begovoy District, Northern Administrative Okrug, Moscow, that designs both civilian and military aircraft. It was founded in the Soviet Union by Pavel Sukhoi in 1939 as the Sukhoi Design Bureau (OKB-51, OKB, design office prefix Su). During February 2006, the Russian government merged Sukhoi with Mikoyan, Ilyushin, Irkut (aircraft manufacturer), Irkut, Tupolev, and Yakovlev as a new company named United Aircraft Corporation.Russian Aircraft Industry Seeks Revival Through Merger ." ''The New York Times.'' February 22, 2006. History [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-7
The Sukhoi Su-7 ( NATO designation name: Fitter-A) is a swept wing, supersonic fighter aircraft developed by the Soviet Union in 1955. Originally, it was designed as a tactical, low-level dogfighter, but was not successful in this role. On the other hand, the soon-introduced Su-7B series became the main Soviet fighter-bomber and ground-attack aircraft of the 1960s. The Su-7 was rugged in its simplicity, but its Lyulka AL-7 engine had such high fuel consumption that it seriously limited the aircraft's payload, as even short-range missions required that at least two hardpoints be used to carry drop tanks rather than ordnance. Design and development Original Su-7 fighters On 14 May 1953, after Joseph Stalin's death, the Sukhoi OKB was reopened"Sukhoi Su-7." ''Sukhoi Company Museum.'' Retrieved: 28 January 2011 and by the summer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1983 In Aviation
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1983: Events January * France agrees to supply Iraq with five Dassault-Breguet Super Étendard strike fighters capable of firing the Exocet anti-ship missile.Cordesman, Anthony H., and Abraham R. Wagner, ''The Lessons of Modern War, Volume II: The Iran–Iraq War'', Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press, 1990, , p. 171. * January 1 – Eastern Air Lines makes its first Boeing 757 revenue flight. * January 2 – In the Iran–Iraq War, Iraqi Air Force aircraft in the Persian Gulf attack a convoy of merchant ships from the Iranian port of Bandar-e Emam Khomeyni, setting fire to the Singaporean cargo ship ''Eastern'' and the Liberian cargo ship ''Orient Horizon'', forcing them both to run aground.Cordesman and Wagner, p. 534. * January 5 – United Airlines begins the first scheduled nonstop service between the continental United States and Maui. *January 16 – The Turkish Airlines Boeing 727-2F2 ''Afyon'', operating as Flight 158, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Control Interception
Ground-controlled interception (GCI) is an air defence tactic whereby one or more radar stations or other observational stations are linked to a command communications centre which guides interceptor aircraft to an airborne target. This tactic was pioneered during World War I by the London Air Defence Area organization, which became the Royal Air Force's Dowding system in World War II, the first national-scale system. The ''Luftwaffe'' introduced similar systems during the war, but most other combatants did not suffer the same threat of air attack and did not develop complex systems like these until the Cold War era. Today the term GCI refers to the style of battle direction, but during WWII it also referred to the radars themselves. Specifically, the term was used to describe a new generation of radars that spun on their vertical axis in order to provide a complete 360 degree view of the sky around the station. Previous systems, notably Chain Home (CH), could only be directed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Air Force
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces were formed from components of the Imperial Russian Air Service in 1917, and faced their greatest test during World War II. The groups were also involved in the Korean War, and dissolved along with the Soviet Union itself in 1991–92. Former Soviet Air Forces' assets were subsequently divided into several air forces of former Soviet republics, including the new Russian Air Force. "March of the Pilots" was its song. Origins The ''All-Russia Collegium for Direction of the Air Forces of the Old Army'' (translation is uncertain) was formed on 20 December 1917. This was a Bolshevik aerial headquarters initially led by Konstantin Akashev. Along with a general postwar military reorganisation, the collegium was reconstituted as the "Workers' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)