|
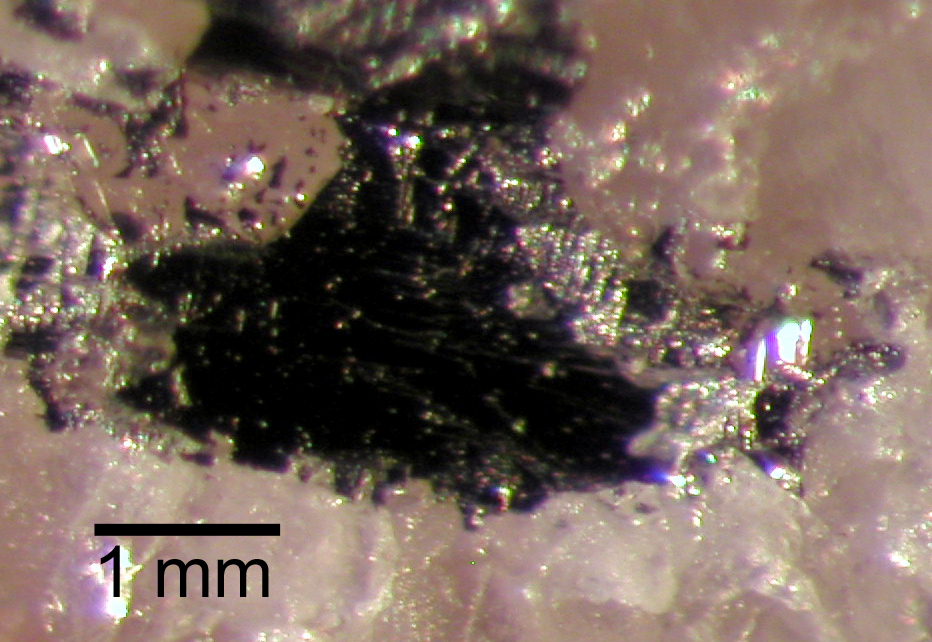
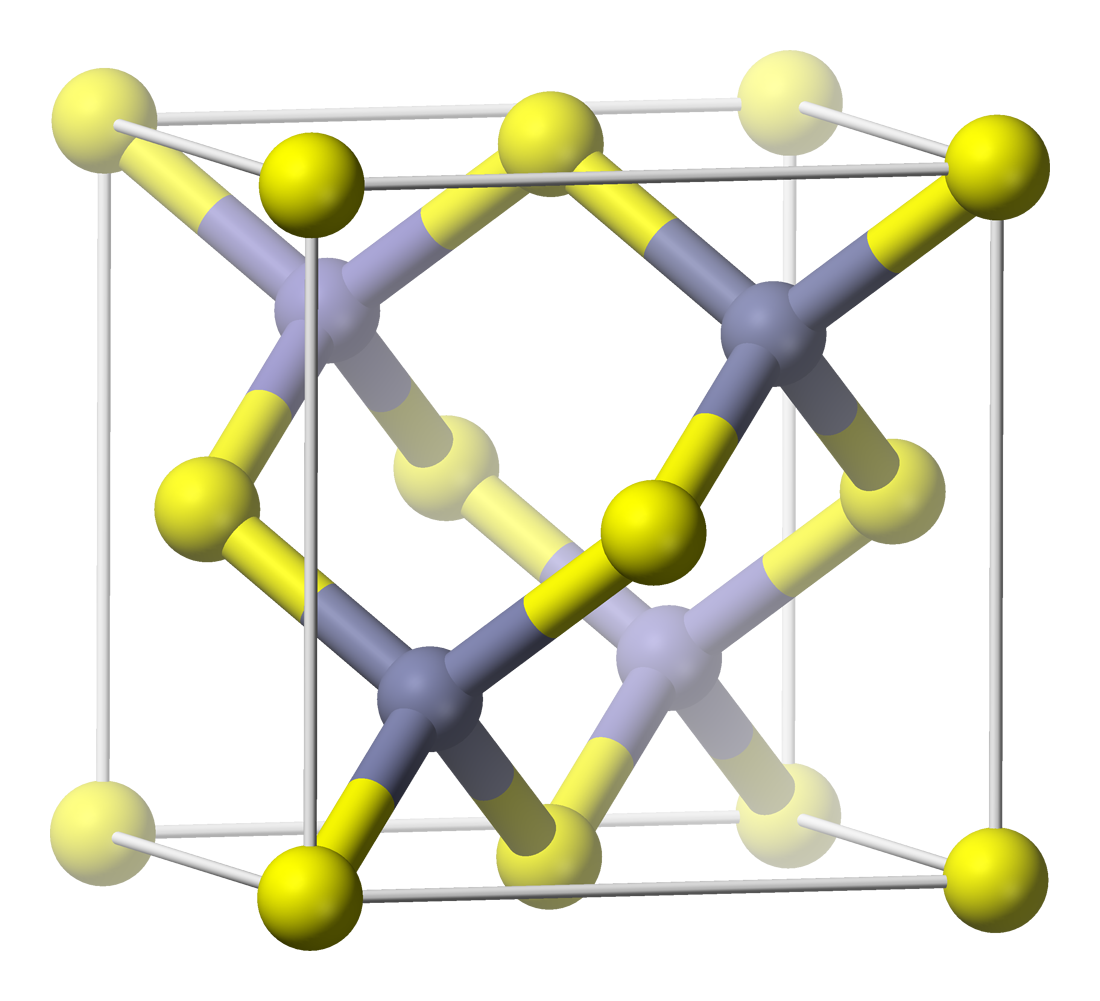
Stützite
Stützite or stuetzite is a silver telluride mineral with formula: Ag5−xTe3 (with x = 0.24 to 0.36) or Ag7Te4. It was first described in 1951 from a museum specimen from Sacarimb, Romania. It was named for Austrian mineralogist Xavier Stütz (1747–1806). It occurs with other sulfide and telluride minerals in hydrothermal ore occurrences. Associated minerals include sylvanite, hessite, altaite, petzite, empressite, native tellurium, native gold, galena, sphalerite, colusite, tennantite and pyrite The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust .... References Telluride minerals Silver minerals Hexagonal minerals Minerals in space group 191 {{mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hessite
Hessite is a mineral form of disilver telluride (Ag2Te). It is a soft, dark grey telluride mineral which forms monoclinic crystals. It is named after Germain Henri Hess (1802–1850). Hessite is found in the US in Eagle County, Colorado and in Calaveras County, California and in many other locations. Stützite Stützite or stuetzite is a silver telluride mineral with formula: Ag5−xTe3 (with x = 0.24 to 0.36) or Ag7Te4. It was first described in 1951 from a museum specimen from Sacarimb, Romania. It was named for Austrian mineralogist Xavier Stütz ... (Ag7Te4) and empressite (AgTe) are related silver telluride minerals. References Silver minerals Telluride minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14 Minerals described in 1843 {{Mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telluride Mineral
A telluride mineral is a mineral that has the telluride anion as a main component. Tellurides are similar to sulfides and are grouped with them in both the Dana and Strunz mineral classification systems.http://webmineral.com/strunz/II.shtml Webmineral Strunz Examples include: * altaite * calaverite * coloradoite * empressite * hessite * kostovite * krennerite * melonite * merenskyite * petzite * rickardite * stützite * sylvanite * tellurobismuthite * temagamite * tetradymite * vulcanite See also * Cripple Creek & Victor Gold Mine The Cripple Creek & Victor Gold Mine, formerly and historically the Cresson Mine, is an active gold mine located near the town of Victor, in the Cripple Creek mining district in the US state of Colorado. The richest gold mine in Colorado history ... References * {{Mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petzite
The mineral petzite, Ag3 Au Te2, is a soft, steel-gray telluride mineral generally deposited by hydrothermal activity. It forms isometric crystals, and is usually associated with rare tellurium and gold minerals, often with silver, mercury, and copper. The name comes from chemist W. Petz, who first analyzed the mineral from the type locality in Săcărâmb, Transylvania, Romania in 1845. It was described by Wilhelm Karl Ritter von Haidinger in 1845 and dedicated to W. Petz who had carried out the first analyses. It occurs with other tellurides in vein gold deposits. It is commonly associated with native gold, hessite, sylvanite, krennerite, calaverite, altaite, montbrayite, melonite, frohbergite, tetradymite, rickardite, vulcanite and pyrite. Petzite forms together with uytenbogaardtite (Ag3AuS2) and fischesserite (Ag3AuSe2) the uytenbogaardtite group. See also *List of minerals *List of minerals named after people This is a list of minerals named after people. The chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Minerals
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telluride Minerals
Telluride may refer to: *Telluride, Colorado, the county seat of San Miguel County in southwest Colorado *Telluride Ski Resort, a ski resort located in Mountain Village, Colorado *Telluride Film Festival, a film festival that takes place in Telluride, Colorado *Telluride (chemistry), the tellurium anion and its derivatives *Telluride mineral, any mineral that has the telluride ion as its main component *Telluride Association, an educational non-profit organization in the United States *Telluride House, a Cornell University residential society and one of the Telluride Association's programs * "Telluride" (song), by Tim McGraw, 2001; covered by Josh Gracin, 2008 *Kia Telluride The Kia Telluride is a mid-size crossover SUV with three-row seating manufactured and marketed by Kia since 2019. Positioned above the smaller Sorento, the Telluride was previewed as a concept car in 2016, with the production model debuting in th ..., a mid-size crossover SUV made by Kia Motors See also * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''Brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what we now call pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the pyrite group, sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tennantite
Tennantite is a copper arsenic sulfosalt mineral with an ideal formula . Due to variable substitution of the copper by iron and zinc the formula is . It is gray-black, steel-gray, iron-gray or black in color. A closely related mineral, tetrahedrite ) has antimony substituting for arsenic and the two form a solid solution series. The two have very similar properties and is often difficult to distinguish between tennantite and tetrahedrite. Iron, zinc, and silver substitute up to about 15% for the copper site. The mineral was first described for an occurrence in Cornwall, England in 1819, where it occurs as small crystals of cubic or dodecahedral form, and was named after the English chemist Smithson Tennant (1761–1815). It is found in hydrothermal veins and contact metamorphic deposits in association with other Cu–Pb–Zn–Ag sulfides and sulfosalts, pyrite, calcite, dolomite, siderite, barite, fluorite and quartz. The arsenic component of tennantite causes the metal smelte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits, Mississippi-Valley type, and Volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposit, volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfide mineral, sulfides), calcite, dolomite (mineral), dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver. Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system often showing octahedral forms. It is often associated with the minerals sphalerite, calcite and fluorite. Occurrence Galena is the main ore of lead, used since ancient times, since lead can be smelted from galena in an ordinary wood fire. Galena typically is found in hydrothermal veins in association with sphalerite, marcasite, chalcopyrite, cerussite, anglesite, dolomite, calcite, quartz, barite, and fluorite. It is also found in association with sphalerite in low-temperature lead-zinc deposits within limestone beds. Minor amounts are found in contact metamorphic zones, in pegmatites, and disseminated in sedimentary rock. In some deposits the galena contains up to 0.5% silver, a byproduct that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellurium
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally found in native form as elemental crystals. Tellurium is far more common in the Universe as a whole than on Earth. Its extreme rarity in the Earth's crust, comparable to that of platinum, is due partly to its formation of a volatile hydride that caused tellurium to be lost to space as a gas during the hot nebular formation of Earth.Anderson, Don L.; "Chemical Composition of the Mantle" in ''Theory of the Earth'', pp. 147-175 Tellurium-bearing compounds were first discovered in 1782 in a gold mine in Kleinschlatten, Transylvania (now Zlatna, Romania) by Austrian mineralogist Franz-Joseph Müller von Reichenstein, although it was Martin Heinrich Klaproth who named the new element in 1798 after the Latin 'earth'. Gold telluride minerals ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |