|
Stylonuridae
Stylonuridae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Stylonuroidea (along with Parastylonuridae), which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Stylonuridae, which lived from Early Silurian to the Late Devonian, were small to very large forms with scales developing into tubercules and knobs. The prosoma (head) exhibited variable shape, with arcuate compound eyes located subcentrally, or anteriorly. Their abdomens were slender. Their walking legs were long and powerful, sometimes characterized by spines. Most genera did not have swimming legs. 1955. Merostomata. ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, Part P Arthropoda 2, Chelicerata'', P: 36. Description Stylonurids are stylonuroids with undifferentiated opisthosoma with appendages II-IV being spiniferous akin to the genus '' Ctenopterus'', whilst append ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parastylonuridae
The Parastylonuridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Stylonuroidea (along with Stylonuridae), which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Description Parastylonurids are stylonuroids with a posterior second order opisthosomal differentiation and with spiniferous appendages II-IV akin to the genus '' Hughmilleria'' and non-spiniferous appendages V-VI akin to the genus '' Parastylonurus'' or '' Pagea''. Unlike the close relatives in the Stylonuridae, there are no adaptations towards sweep-feeding within the Parastylonuridae. They retain primitive ''Hughmilleria''-like prosomal appendages II-IV unsuited for such a lifestyle, and they were likely scavengers instead of sweep-feeders. Systematics and genera The Stylonuridae is classified within the superfamily Stylonuroidea within the Stylonur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenopterus
''Ctenopterus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Stylonuridae. It contains only one species, ''Ctenopterus cestrotus'' from the Early Silurian of Otisville, New York.Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 16.0 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils16.0.pdf (PDF). Description Stylonurids, which lived from the Ordovician to Lower Permian periods, were small to very large forms with scales developing into tubercules and knobs. The prosoma (head) exhibited variable shape, with arcuate compound eyes located subcentrally, or anteriorly. Their abdomens were slender. Their walking legs were long and powerful, sometimes characterized by spines. Most genera did not have swimming legs. 1955. Merostomata. ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, Part P Arthropoda 2, Chelicerata'', P36. ''Ctenopterus'' is dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylonurina
Stylonurina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, a group of extinct arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Members of the suborder are collectively and informally known as "stylonurine eurypterids" or "stylonurines". They are known from deposits primarily in Europe and North America, but also in Siberia. Compared to the other suborder, Eurypterina, the stylonurines were comparatively rare and retained their posterior prosomal appendages for walking. Despite their rarity, the stylonurines have the longest temporal range of the two suborders. The suborder contains some of the oldest known eurypterids, such as ''Brachyopterus'', from the Middle Ordovician as well as the youngest known eurypterids, from the Late Permian. They remained rare throughout the Ordovician and Silurian, though the radiation of the mycteropoids (a group of large sweep-feeding forms) in the Late Devonian and Carboniferous is the last major radiation of the eurypterids before their extinction in the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylonuroidea
Stylonuroidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Stylonuroidea, which lived from the Early Silurian to the Late Devonian, were characterized by their last pair of prosomal (head) appendages, which were developed as walking legs, or less commonly developed as swimming legs with paddles formed by the expansion of the two or three penultimate joints. 1955. Merostomata. ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, Part P Arthropoda 2, Chelicerata'', P36. as Stylonuracea Description Stylonuroids are designated as stylonurines with flattened or truncated posterior metastomata margins. Of the four stylonurine superfamilies, the Stylonuroidea is the most poorly known. Whilst the topology of most stylonurine clades fit well with the stratigraphic record, Stylonuroidea is an exception in that the earliest record of the most der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylonurus
''Stylonurus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Stylonuridae. The genus contains three species: ''Stylonurus powriensis'' from the Devonian of Scotland, ''Stylonurus shaffneri'' from the Devonian of Pennsylvania and ''Stylonurus perspicillum'' from the Devonian of Germany.Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 16.0 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils16.0.pdf (PDF). The assignment of ''S. perspicillum'' and ''S. shaffneri'' to the genus is doubtful. A previously assigned species, ''S. ensiformis'', is today regarded as synonymous with ''S. powriensis''. Description Stylonurids, which lived from the Ordovician to Lower Permian periods, were small to very large forms with scales developing into tubercules and knobs. The prosoma (head) exhibited variable shape, with arcuate compound eyes located subcen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagea
''Pagea'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid classified as part of the family Stylonuridae. It contains three species, all from the Devonian (Lochkovian to Pragian); ''P. plotnicki'' from Nunavut, Canada and ''P. sturrocki'' and ''P. symondsii'' from the Old Red Sandstone of the United Kingdom.Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 16.0 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils16.0.pdf (PDF). The genus is named in honor of David Page, an early worker on the fauna of the Old Red Sandstone and describer of the first Stylonurine eurypterid. Description ''Pagea'' was a large stylonurid eurypterid. The third and fourth prosomal appendages bore double rows of flat spines. The prosoma was subrectangularly shaped, with the eyes located on the anterior half. The metastoma was narrow in relation to the width of the prosoma, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurieipterus
''Laurieipterus'' is a genus of a eurypterid classified as part of the family Stylonuridae. It contains one species, ''L. elegans'' from the Early Silurian of Scotland Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ....Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 16.0 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils16.0.pdf (PDF). References Silurian arthropods of Europe Silurian eurypterids Stylonuroidea Eurypterids of Europe {{eurypterid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
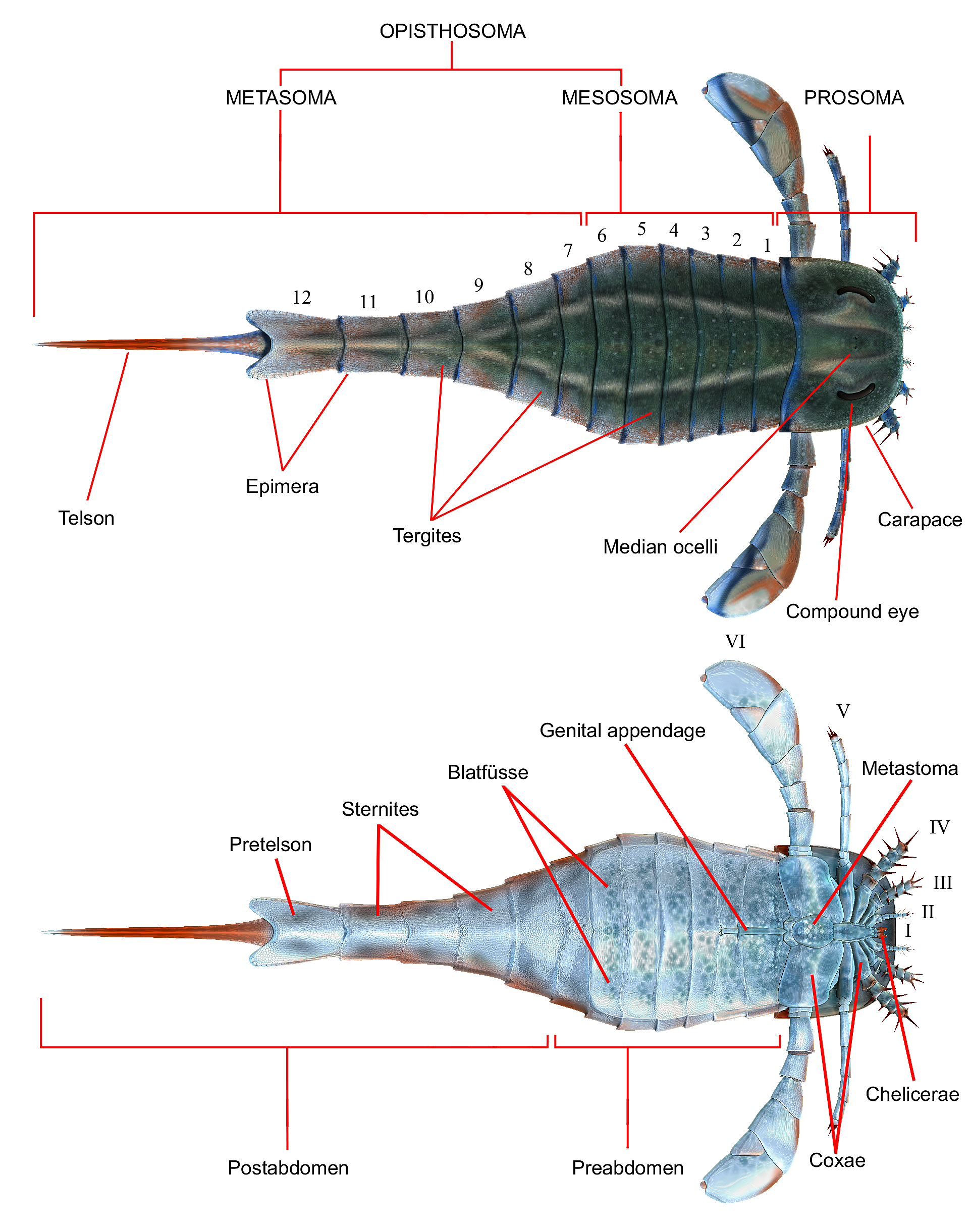
Eurypterid
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct arthropods that form the Order (biology), order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period 467.3 Myr, million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic Chelicerata, chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soligorskopterus
''Soligorskopterus'' is a genus of eurypterid, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods. Fossils of ''Soligorskopterus'' have been discovered in deposits from the Late Devonian. The genus contains two species: ''S. tchepeliensis'', the type species, from the Middle Famennian stage of Belarus, and ''S. shpinevi'', from the Lower Frasnian stage of Russia. Its name derives from Soligorsk, the closest city from the fossil site of the type species, and the Greek word πτερόν (''pteron''), which means wing. See also * List of eurypterid genera * Timeline of eurypterid research This timeline of eurypterid research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, and taxonomic revisions of eurypterids, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods closely related to modern arac ... References Devonian eurypterids Eurypterids of Europe Frasnian life Famennian life Fossils of Russia Fossil taxa described in 2018 Stylonuroidea [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerate
The subphylum Chelicerata (from New Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. It contains the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, ticks, and mites, among many others), as well as a number of extinct lineages, such as the eurypterids (sea scorpions) and chasmataspidids. The Chelicerata originated as marine animals in the Middle Cambrian period; the first confirmed chelicerate fossils, belonging to '' Sanctacaris'', date from 508 million years ago. The surviving marine species include the four species of xiphosurans (horseshoe crabs), and possibly the 1,300 species of pycnogonids (sea spiders), if the latter are indeed chelicerates. On the other hand, there are over 77,000 well-identified species of air-breathing chelicerates, and there may be about 500,000 unidentified species. Like all arthropods, chelicerates have segmented bodies with jointed limbs, all covered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhuddanian
In the geologic timescale, the Rhuddanian is the first age of the Silurian Period and of the Llandovery Epoch. The Silurian is in the Paleozoic Era of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Rhuddanian Age began 443.8 ± 1.5 Ma and ended 440.8 ± 1.2 Ma (million years ago). It succeeds the Himantian Age (the last age of the Ordovician Period) and precedes the Aeronian Age. GSSP The GSSP for the Silurian is located in a section at Dob's Linn, Scotland, in an artificial excavation created just north of the Linn Branch Stream. Two lithological units ( formations) occur near the boundary. The lower is the Hartfell Shale ( thick), consisting chiefly of pale gray mudstone with subordinate black shales and several interbedded meta-bentonites. Above this is the thick Birkhill Shale, which consist predominantly of black graptolitic shale with subordinate gray mudstones and meta-bentonites. See also * Ordovician-Silurian extinction events * Early Palaeozoic Icehouse The Andean-Saharan glaciatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |