|
Stumbras
AB Stumbras is the oldest and largest producer of strong alcoholic drinks in Kaunas, Lithuania. The company began operations in 1906. It is also the largest exporter of strong alcoholic beverages and one of the biggest taxpayers in Lithuania. The company's most famous brands include "Lithuanian vodka" (vodka), "999" (bitter), "Gloria" (brandy), "Stumbro Starka" (bitter), "Krupnikas" (liqueur) and "Poema" (liqueur). The company name translates as Wisent. History Tsarist Russia The origins of "Stumbras" lie in an 1894 law on monopolizing alcohol production by state-owned enterprises in the Russian Empire. The law was expected to increase budget revenues and to improve the quality of produced vodka. The government of Kaunas acquired a suitable plot of land in 1903 for a high price of 52,200 Russian rubles. The buildings were finished and production started at the end of 1906. The official name of the company was "Kazionyj Nr.1 vinyj očistnyj sklad" (State wine warehouse No. 1). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šilutė
Šilutė (, previously ''Šilokarčiama'', german: link=no, Heydekrug), is a city in the south of the Klaipėda County, Lithuania. The city was part of the Klaipėda Region and ethnographic Lithuania Minor. Šilutė was the interwar capital of Šilutė County and is currently the capital of Šilutė District Municipality. Name Šilutė's origin dates to an inn (Krug, locally ''karčema'') catering to travelers and their horses which was located halfway between Memel (Klaipėda) and Tilsit (Tilžė). The German name of ''Heydekrug'' referred to a ''Krug'' (an archaic word for inn) in the ''Heide'' (heathland). The inn was known for being in the region where most people spoke the Memelland-Samogitian dialect ''Šilokarčema''. History A famous fish market was opened in Šilutė almost 500 years ago, when Georg Tallat purchased the inn together with the land and fishing rights in 1511. The town was a gathering place for peasants from nearby Samogitia and Curonian and Prussian fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaunas
Kaunas (; ; also see other names) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Trakai of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Trakai Palatinate since 1413. In the Russian Empire, it was the capital of the Kaunas Governorate from 1843 to 1915. During the interwar period, it served as the temporary capital of Lithuania, when Vilnius was seized and controlled by Poland between 1920 and 1939. During that period Kaunas was celebrated for its rich cultural and academic life, fashion, construction of countless Art Deco and Lithuanian National Romanticism architectural-style buildings as well as popular furniture, the interior design of the time, and a widespread café culture. The city interwar architecture is regarded as among the finest examples of European Art Deco and has received the European Heritage Label. It contributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Bathing
Public baths originated when most people in population centers did not have access to private bathing facilities. Though termed "public", they have often been restricted according to gender, religious affiliation, personal membership, and other criteria. In addition to their hygienic function, public baths have also been social meeting places. They have included saunas, massages, and other relaxation therapies, as are found in modern day spas. As the percentage of dwellings containing private bathrooms has increased in some societies, the need for public baths has diminished, and they are now almost exclusively used recreationally. History Public facilities for bathing were constructed, as excavations have provided evidence for, in the 3rd millennium BC, as with the Great Bath, Mohenjo-daro. Ancient Greece In Greece by the sixth century BC men and women washed in basins near places of physical and intellectual exercise. Later gymnasia had indoor basins set overhead, the open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
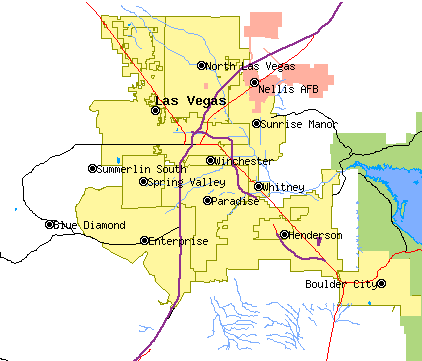
Las Vegas Valley
The Las Vegas Valley is a major metropolitan area in the Southern Nevada, southern part of the U.S. state of Nevada, and the second largest in the Southwestern United States. The state's largest urban agglomeration, the Las Vegas Metropolitan Statistical Area is coextensive since 2003 with Clark County, Nevada, Clark County, Nevada. The Valley is largely defined by the Las Vegas Valley landform, a Depression (geology), basin area surrounded by mountains to the north, south, east and west of the metropolitan area. The Valley is home to the three largest incorporated cities in Nevada: Las Vegas, Henderson, Nevada, Henderson and North Las Vegas, Nevada, North Las Vegas. Eleven unincorporated towns governed by the Clark County government are part of the Las Vegas Township and constitute the largest community in the state of Nevada. The names Las Vegas and Vegas are interchangeably used to indicate the Valley, Las Vegas Strip, the Strip, and the city, and as a brand by the Las Vegas Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), who did not participate in the battle himself, and Grand Duke Vytautas, decisively defeated the German Teutonic Order, led by Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen. Most of the Teutonic Order's leadership were killed or taken prisoner. Although defeated, the Teutonic Order withstood the subsequent siege of the Malbork Castle and suffered minimal territorial losses at the Peace of Thorn (1411), with other territorial disputes continuing until the Treaty of Melno in 1422. The order, however, never recovered their former power, and the financial burden of war reparations caused internal conflicts and an economic downturn in the lands controlled by them. The battle shifted the balance of pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litas
The Lithuanian litas (ISO currency code LTL, symbolized as Lt; plural ''litai'' (nominative) or ''litų'' (genitive) was the currency of Lithuania, until 1 January 2015, when it was replaced by the euro. It was divided into 100 centų (genitive case; singular ''centas'', nominative plural ''centai''). The litas was first introduced on 2 October 1922 after World War I, when Lithuania declared independence and was reintroduced on 25 June 1993, following a period of currency exchange from the rouble to the litas with the temporary talonas then in place. The name was modeled after the name of the country (similar to Latvia and its lats). From 1994 to 2002, the litas was pegged to the U.S. dollar at the rate of 4 to 1. The litas was pegged to the euro at the rate of 3.4528 to 1 since 2002. The euro was expected to replace the litas by 1 January 2007, but persistent high inflation and the economic crisis delayed the switch. On 1 January 2015 the litas was switched to the euro at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compound In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privatisation
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when a heavily regulated private company or industry becomes less regulated. Government functions and services may also be privatised (which may also be known as "franchising" or "out-sourcing"); in this case, private entities are tasked with the implementation of government programs or performance of government services that had previously been the purview of state-run agencies. Some examples include revenue collection, law enforcement, water supply, and prison management. Another definition is that privatization is the sale of a state-owned enterprise or municipally owned corporation to private investors; in this case shares may be traded in the public market for the first time, or for the first time since an enterprise's previous nationaliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shares
In financial markets, a share is a unit of equity ownership in the capital stock of a corporation, and can refer to units of mutual funds, limited partnerships, and real estate investment trusts. Share capital refers to all of the shares of an enterprise. The owner of shares in a company is a shareholder (or stockholder) of the corporation. A share is an indivisible unit of capital, expressing the ownership relationship between the company and the shareholder. The denominated value of a share is its face value, and the total of the face value of issued shares represent the capital of a company, which may not reflect the market value of those shares. The income received from the ownership of shares is a dividend. There are different types of shares such as equity shares, preference shares, deferred shares, redeemable shares, bonus shares, right shares, and employee stock option plan shares. Valuation Shares are valued according to the various principles in different markets, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holding Company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own shares of other companies to form a corporate group. In some jurisdictions around the world, holding companies are called parent companies, which, besides holding stock in other companies, can conduct trade and other business activities themselves. Holding companies reduce risk for the shareholders, and can permit the ownership and control of a number of different companies. ''The New York Times'' also refers to the term as ''parent holding company.'' Holding companies are also created to hold assets such as intellectual property or trade secrets, that are protected from the operating company. That creates a smaller risk when it comes to Lawsuit, litigation. In the United States, 80% of stock, in voting and value, must be owned before tax consolidation benefits s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian SSR
The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (Lithuanian SSR; lt, Lietuvos Tarybų Socialistinė Respublika; russian: Литовская Советская Социалистическая Республика, Litovskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Respublika), also known as Soviet Lithuania or simply Lithuania, was ''de facto'' one of the constituent republics of the USSR between 1940–1941 and 1944–1990. After 1946, its territory and borders mirrored those of today's Republic of Lithuania, with the exception of minor adjustments of the border with Belarus. During World War II, the previously independent Republic of Lithuania was occupied by the Soviet army on 16 June 1940, in conformity with the terms of the 23 August 1939 Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, and established as a puppet state on 21 July. Between 1941 and 1944, the German invasion of the Soviet Union caused its ''de facto'' dissolution. However, with the retreat of the Germans in 1944–1945, Soviet hegemony was re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |