|
Stuart Dreyfus
A native of Terre Haute, Indiana, Stuart E. Dreyfus is professor emeritus at University of California, Berkeley in the Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Department. While at the Rand Corporation he was a programmer of the JOHNNIAC computer. While at Rand he coauthored ''Applied Dynamic Programming'' with Richard Bellman. Following that work, he was encouraged to pursue a Ph.D. which he completed in applied mathematics at Harvard University in 1964, on the calculus of variations. In 1962, Dreyfus simplified the Dynamic Programming-based derivation of backpropagation (due to Henry J. Kelley and Arthur E. Bryson) using only the chain rule.Stuart Dreyfus (1990). Artificial Neural Networks, Back Propagation and the Kelley-Bryson Gradient Procedure. J. Guidance, Control and Dynamics, 1990.Eiji Mizutani , Stuart Dreyfus, Kenichi Nishio (2000). On derivation of MLP backpropagation from the Kelley-Bryson optimal-control gradient formula and its application. Proceedings of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terre Haute, Indiana
Terre Haute ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Vigo County, Indiana, United States, about 5 miles east of the state's western border with Illinois. As of the 2010 census, the city had a population of 60,785 and its metropolitan area had a population of 170,943. Located along the Wabash River, Terre Haute is one of the largest cities in the Wabash Valley and is known as the Queen City of the Wabash. The city is home to multiple higher-education institutions, including Indiana State University, Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology, and Ivy Tech Community College of Indiana. History Terre Haute's name is derived from the French phrase ''terre haute'' (pronounced in French), meaning "highland". It was named by French-Canadian explorers and fur trappers to the area in the early 18th century to describe the unique location above the Wabash River (see French colonization of the Americas). At the time, the area was claimed by the French and British and these highlands were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry J
The Henry J is an American automobile built by the Kaiser-Frazer Corporation and named after its chairman, Henry J. Kaiser. Production of six-cylinder models began in their Willow Run factory in Michigan on July 1950, and four-cylinder production started shortly after Labor Day, 1950. The official public introduction was on September 28, 1950. The car was marketed through 1954. Development The Henry J was the idea of Henry J. Kaiser, who sought to increase sales of his Kaiser automotive line by adding a car that could be built inexpensively and thus affordable for the average American in the same vein that Henry Ford produced the Model T. The goal was to attract "less affluent buyers who could only afford a used car" and the attempt became a pioneering American compact car. To finance the project, the Kaiser-Frazer Corporation received a federal government loan in 1949. This financing specified various particulars of the vehicle. Kaiser-Frazer would commit to design a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Operations Researchers
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing (living People)
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubert Dreyfus
Hubert Lederer Dreyfus (; October 15, 1929 – April 22, 2017) was an American philosopher and professor of philosophy at the University of California, Berkeley. His main interests included phenomenology, existentialism and the philosophy of both psychology and literature, as well as the philosophical implications of artificial intelligence. He was widely known for his exegesis of Martin Heidegger, which critics labeled "Dreydegger". Dreyfus was featured in Tao Ruspoli's film '' Being in the World'' (2010)'','' and was among the philosophers interviewed by Bryan Magee for the BBC Television series '' The Great Philosophers'' (1987)''.'' The '' Futurama'' character Professor ''Hubert'' Farnsworth is partly named after him, writer Eric Kaplan having been a former student. Life and career Dreyfus was born on 15 October 1929, in Terre Haute, Indiana, to Stanley S. and Irene (Lederer) Dreyfus.Don Quijote" would appear in print. After acting as an instructor in philosophy at Brand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
What Computers Can't Do
Hubert Dreyfus was a critic of artificial intelligence research. In a series of papers and books, including ''Alchemy and AI'' (1965), ''What Computers Can't Do'' (1972; 1979; 1992) and ''Mind over Machine'' (1986), he presented a pessimistic assessment of AI's progress and a critique of the philosophical foundations of the field. Dreyfus' objections are discussed in most introductions to the philosophy of artificial intelligence, including , the standard AI textbook, and in , a survey of contemporary philosophy. Dreyfus argued that human intelligence and expertise depend primarily on unconscious processes rather than conscious symbolic manipulation, and that these unconscious skills can never be fully captured in formal rules. His critique was based on the insights of modern continental philosophers such as Merleau-Ponty and Heidegger, and was directed at the first wave of AI research which used high level formal symbols to represent reality and tried to reduce intelligence t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jürgen Schmidhuber
Jürgen Schmidhuber (born 17 January 1963) is a German computer scientist most noted for his work in the field of artificial intelligence, deep learning and artificial neural networks. He is a co-director of the Dalle Molle Institute for Artificial Intelligence Research in Lugano, in Ticino in southern Switzerland. Following Google Scholar, from 2016 to 2021 he has received more than 100,000 scientific citations. He has been referred to as "father of modern AI," "father of AI," "dad of mature AI," "Papa" of famous AI products, "Godfather," and "father of deep learning." (Schmidhuber himself, however, has called Alexey Grigorevich Ivakhnenko the "father of deep learning.") Schmidhuber completed his undergraduate (1987) and PhD (1991) studies at the Technical University of Munich in Munich, Germany. His PhD advisors were Wilfried Brauer and Klaus Schulten. He taught there from 2004 until 2009 when he became a professor of artificial intelligence at the Università della ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Rule
In calculus, the chain rule is a formula that expresses the derivative of the Function composition, composition of two differentiable functions and in terms of the derivatives of and . More precisely, if h=f\circ g is the function such that h(x)=f(g(x)) for every , then the chain rule is, in Lagrange's notation, :h'(x) = f'(g(x)) g'(x). or, equivalently, :h'=(f\circ g)'=(f'\circ g)\cdot g'. The chain rule may also be expressed in Leibniz's notation. If a variable depends on the variable , which itself depends on the variable (that is, and are dependent variables), then depends on as well, via the intermediate variable . In this case, the chain rule is expressed as :\frac = \frac \cdot \frac, and : \left.\frac\_ = \left.\frac\_ \cdot \left. \frac\_ , for indicating at which points the derivatives have to be evaluated. In integral, integration, the counterpart to the chain rule is the substitution rule. Intuitive explanation Intuitively, the chain rule states that knowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur E
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning “Bear”. Another theory, more widely believed, is that the name is derived from the Roman clan '' Artorius'' who lived in Roman Britain for centuries. A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Italian it is Arturo. Etymology The earliest datable attestation of the name Arthur is in the early 9th century Welsh-Latin text ''Historia Brittonum'', where it refers to a circa 5th to 6th-century Briton general who fought against the invading Saxons, and who later gave rise to the famous King Arthur of medieval legend and literature. A possible earlier mention of the same man is to be found in the epic Welsh poem ''Y Gododdin'' by Aneirin, which some scholars assign to the late 6th century, though this is still a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
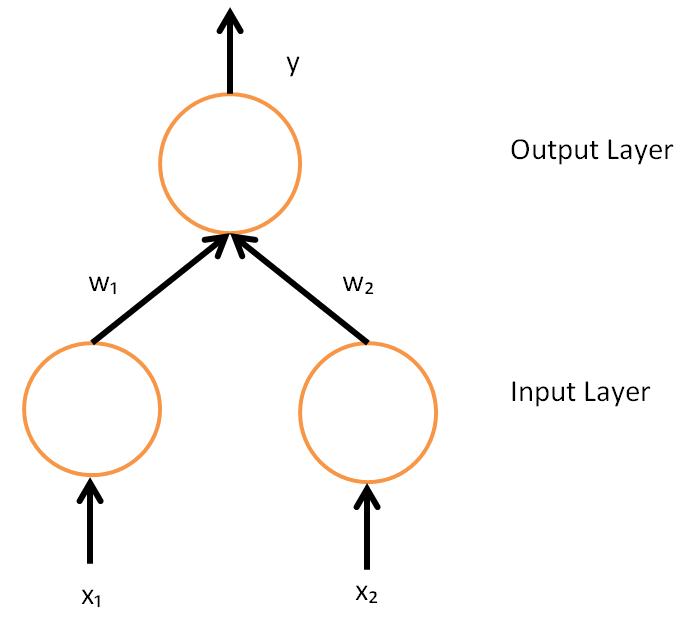
Backpropagation
In machine learning, backpropagation (backprop, BP) is a widely used algorithm for training feedforward artificial neural networks. Generalizations of backpropagation exist for other artificial neural networks (ANNs), and for functions generally. These classes of algorithms are all referred to generically as "backpropagation". In fitting a neural network, backpropagation computes the gradient of the loss function with respect to the weights of the network for a single input–output example, and does so efficiently, unlike a naive direct computation of the gradient with respect to each weight individually. This efficiency makes it feasible to use gradient methods for training multilayer networks, updating weights to minimize loss; gradient descent, or variants such as stochastic gradient descent, are commonly used. The backpropagation algorithm works by computing the gradient of the loss function with respect to each weight by the chain rule, computing the gradient one laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)