|
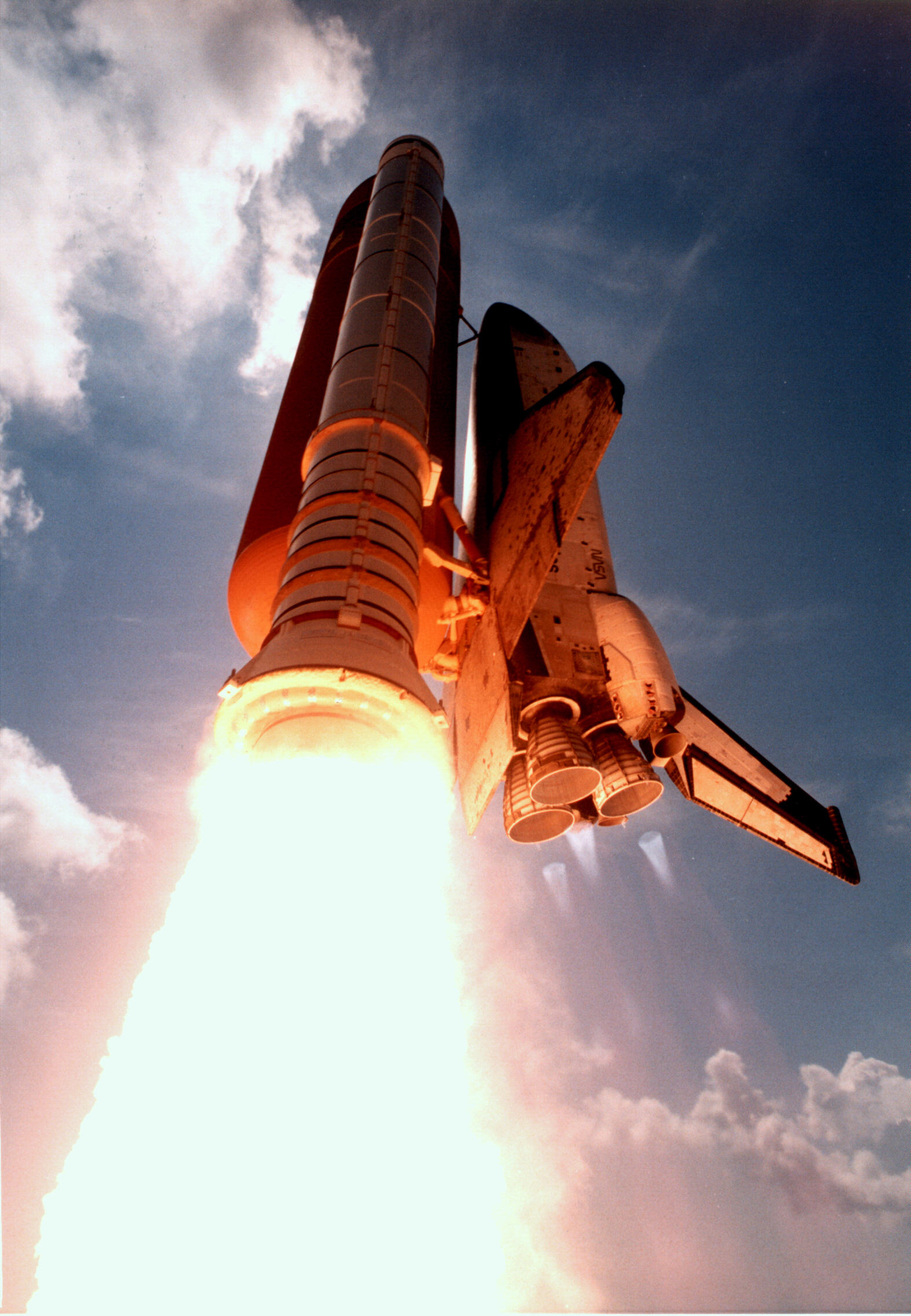
Sts-94 Launch
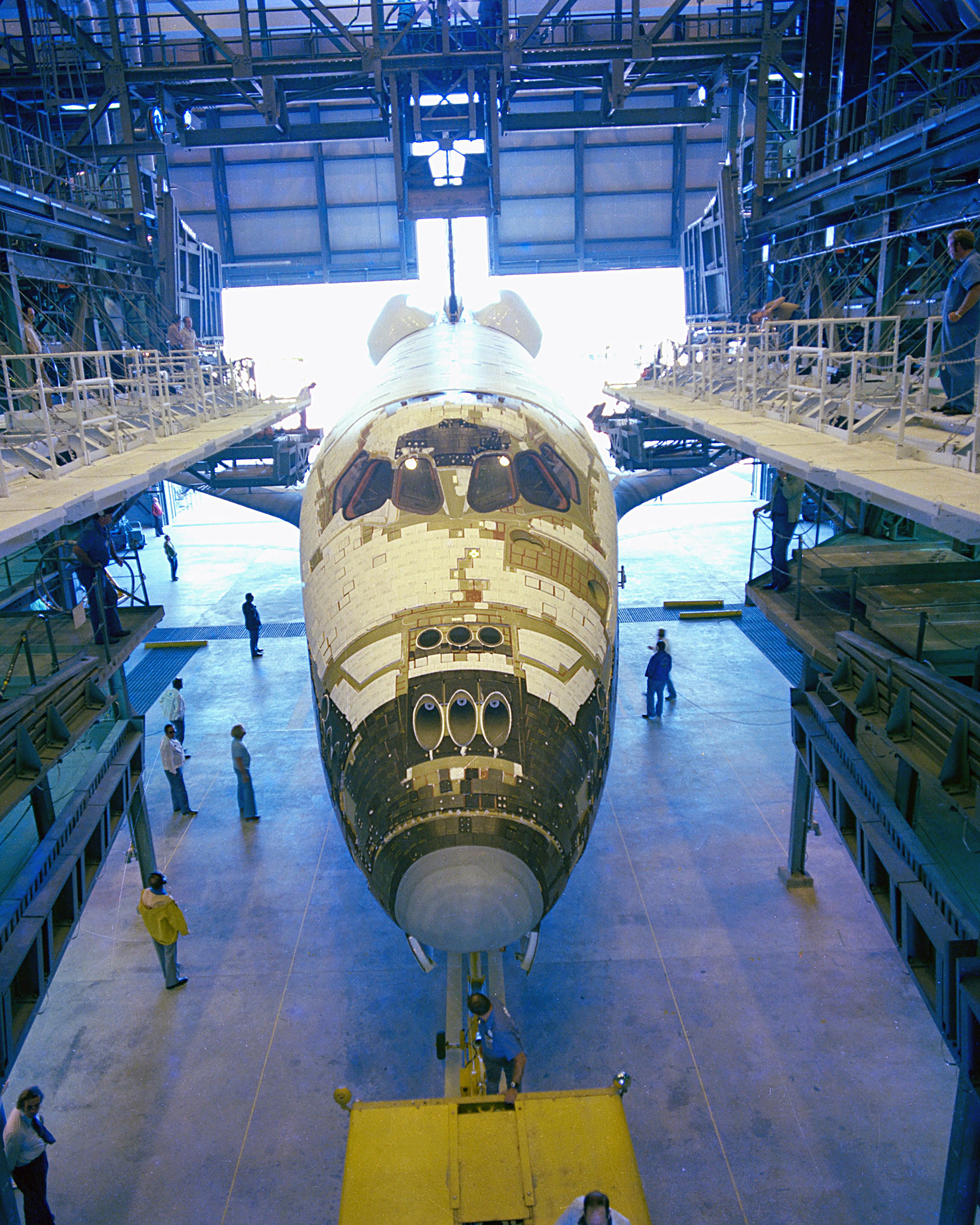
STS-94 was a mission of the United States Space Shuttle '' Columbia'', launched on 1 July 1997. Crew Mission highlights This was a reflight of the STS-83 Microgravity Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL was originally launched on 4 April 1997 at 2:20 pm EST and was intended to be on orbit for 15 days, 16 hours. The mission was cut short due to a problem with Fuel Cell #2 and ''Columbia'' landed on 8 April 1997 after 3 days 23 hours. The primary payload on STS-83 was the Microgravity Science Laboratory (MSL). MSL was a collection of microgravity experiments housed inside a European Spacelab Long Module (LM). It built on the cooperative and scientific foundation of the International Microgravity Laboratory missions (IML-1 on STS-42 and IML-2 on STS-65), the United States Microgravity Laboratory missions (USML-1 on STS-50 and USML-2 on STS-73), the Japanese Spacelab mission (Spacelab-J on STS-47), the Spacelab Life and Microgravity Science Mission (LMS on STS-78) and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Transportation System
The Space Transportation System (STS), also known internally to NASA as the Integrated Program Plan (IPP), was a proposed system of reusable crewed space vehicles envisioned in 1969 to support extended operations beyond the Apollo program. (NASA appropriated the name for its Space Shuttle Program, the only component of the proposal to survive Congressional funding approval). The purpose of the system was two-fold: to reduce the cost of spaceflight by replacing the current method of launching capsules on expendable rockets with reusable spacecraft; and to support ambitious follow-on programs including permanent orbiting space stations around Earth and the Moon, and a human landing mission to Mars. In February 1969, President Richard Nixon appointed a Space Task Group headed by Vice President Spiro Agnew to recommend human space projects beyond Apollo. The group responded in September with the outline of the STS, and three different program levels of effort culminating with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development. The first ( STS-1) of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights (STS-5) beginning in 1982. Five complete Space Shuttle orbiter vehicles were built and flown on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. They launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), conducted science experiments in orbit, participated in the Shuttle-''Mir'' program with Russia, and participated in construction and servicing of the International Space Station (ISS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sts-94 Crew
STS-94 was a mission of the United States Space Shuttle '' Columbia'', launched on 1 July 1997. Crew Mission highlights This was a reflight of the STS-83 Microgravity Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL was originally launched on 4 April 1997 at 2:20 pm EST and was intended to be on orbit for 15 days, 16 hours. The mission was cut short due to a problem with Fuel Cell #2 and ''Columbia'' landed on 8 April 1997 after 3 days 23 hours. The primary payload on STS-83 was the Microgravity Science Laboratory (MSL). MSL was a collection of microgravity experiments housed inside a European Spacelab Long Module (LM). It built on the cooperative and scientific foundation of the International Microgravity Laboratory missions (IML-1 on STS-42 and IML-2 on STS-65), the United States Microgravity Laboratory missions (USML-1 on STS-50 and USML-2 on STS-73), the Japanese Spacelab mission (Spacelab-J on STS-47), the Spacelab Life and Microgravity Science Mission (LMS on STS-78) and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Space Agency
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the merger, ISAS w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-55
STS-55, or Deutschland 2 (D-2), was the 55th overall flight of the NASA Space Shuttle and the 14th flight of Shuttle '' Columbia''. This flight was a multinational Spacelab flight involving 88 experiments from eleven different nations. The experiments ranged from biology sciences to simple Earth observations. Crew Backup crew Mission highlights ''Columbia'' carried to orbit the second reusable German Spacelab D-2 and demonstrated the shuttle's ability for international cooperation, exploration, and scientific research in space. The Spacelab module and an exterior experiment support structure contained in ''Columbia''s payload bay comprised the Spacelab D-2 payload. The first German Spacelab flight, D-1, flew Shuttle mission STS-61-A in October 1985. The United States and Germany gained valuable experience for future space station operations. The D-2 mission, as it was commonly called, augmented the German microgravity research program started by the D-1 mission. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-61-A
STS-61-A (also known as Spacelab D-1) was the 22nd mission of NASA's Space Shuttle program. It was a scientific Spacelab mission, funded and directed by West Germany – hence the non-NASA designation of D-1 (for Deutschland-1). STS-61-A was the ninth and last successful flight of Space Shuttle ''Challenger''. STS-61-A holds the current record for the largest crew - eight people - aboard any single spacecraft for the entire period from launch to landing. The mission carried the NASA/European Space Agency (ESA) Spacelab module into orbit with 76 scientific experiments on board, and was declared a success. Payload operations were controlled from the German Space Operations Center in Oberpfaffenhofen, West Germany, instead of from the regular NASA control center. This was the first spaceflight to include multiple crewmembers from any single country other than the United States or Soviet Union. Crew Backup crew Crew seating arrangements Mission summary Space Shutt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-78
STS-78 was the fifth dedicated Life and Microgravity Spacelab mission for the Space Shuttle program, flown partly in preparation for the International Space Station project. The mission used the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'', which lifted off successfully from Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B on June 20, 1996. This marked the 78th flight of the Space Shuttle and 20th mission for ''Columbia''. Crew Backup crew Mission objectives * Research into the effects of long – duration spaceflight on human physiology in preparation for flights on the International Space Station. * 22 life science and microgravity experiments using the Orbiter's pressurised Life & Microgravity Spacelab module (LM2). * Tests into the use of the Orbiter's Reaction Control System jets to raise the altitude of orbiting satellites. Mission highlights During the 16-day, 21-hour mission, the crew of ''Columbia'' assisted in the preparations for the International Space Station by studying the effects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-47
STS-47 was the 50th NASA Space Shuttle mission of the program, as well as the second mission of the Space Shuttle ''Endeavour''. The mission mainly involved conducting experiments in life and material sciences inside Spacelab-J, a collaborative laboratory inside the shuttle's payload bay sponsored by NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). This mission carried Mamoru Mohri, the first Japanese astronaut aboard the shuttle, Mae Jemison, the first African-American woman to go to space, and the only married couple to fly together on the shuttle, Mark C. Lee and Jan Davis, contrary to NASA policy. Crew Backup crew Crew seating arrangements As female and male astronauts became more prominently integrated with the shuttle program, NASA enacted an unwritten rule that husband/wife couples would not be assigned to the same mission. However, when Lee's and Davis' marriage became known to NASA officials in January 1991, the officials decided to kee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-73
STS-73 was a Space Shuttle program mission, during October–November 1995, on board the Space Shuttle ''Columbia''. The mission was the second mission for the United States Microgravity Laboratory. The crew, who spent 16 days in space, were broken up into 2 teams, the red team and the blue team. The mission also included several Detailed Test Objectives or DTO's. Crew Backup crew Mission highlights The second United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) Spacelab mission was the prime payload on STS-73. The 16-day flight continued a cooperative effort of the U.S. government, universities and industry to push back the frontiers of science and technology in "microgravity", the near-weightless environment of space. On October 26, through pre-recorded video, Mission Commander Ken Bowersox threw out the first pitch for Game 5 of the 1995 World Series between the Cleveland Indians and the Atlanta Braves from orbit. Some of the experiments carried on the USML-2 payload were su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-50
STS-50 (U.S. Microgravity Laboratory-1) was a NASA Space Shuttle mission, the 12th mission of the '' Columbia'' orbiter. ''Columbia'' landed at Kennedy Space Center for the first time ever due to bad weather at Edwards Air Force Base caused by the remnants of Hurricane Darby. Crew Backup crew Crew seating arrangements Mission highlights The U.S. Microgravity Laboratory-1 was a spacelab mission, with experiments in material science, fluid physics and biotechnology. It was the first flight of a Space Shuttle with the Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO) hardware, allowing longer flight durations. Primary payload, U.S. Microgravity Laboratory-1 (USML- 1), made its first flight; featured pressurized Spacelab module. USML-1 first in planned series of flights to advance U.S. microgravity research effort in several disciplines. Experiments conducted were: Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF); Drop Physics Module (DPM); Surface Tension Driven Convection Experiments (STDCE); Zeolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-65
STS-65 was a Space Shuttle program mission of ''Columbia'' launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, 8 July 1994. The commander of this flight was Robert D. Cabana who would go on later to lead the Kennedy Space Center. Crew Backup crew Mission highlights The International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) was the second in a series of Spacelab (SL) flights designed to conduct research in a microgravity environment. The IML concept enabled a scientist to apply results from one mission to the next and to broaden the scope and variety of investigations between missions. Data from the IML missions contributed to the research base for the space station. As the name implies, IML-2 was an international mission. Scientists from the European Space Agency (ESA), Canada, France, Germany and Japan collaborated with NASA on the IML-2 mission to provide the worldwide science community with a variety of complementary facilities and experiments. These facilities and experiments were m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-42
STS-42 was a NASA Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' mission with the Spacelab module. Liftoff was originally scheduled for 8:45 EST (13:45 UTC) on January 22, 1992, but the launch was delayed due to weather constraints. ''Discovery'' successfully lifted off an hour later at 9:52:33 EST (14:52:33 UTC). The main goal of the mission was to study the effects of microgravity on a variety of organisms. The shuttle landed at 8:07:17 PST (16:07:17 UTC) on January 30, 1992, on Runway 22, Edwards Air Force Base, California. STS-42 was the first of two flights in 1992 of ''Discovery'', the second of which occurred during STS-53, which launched on December 2, 1992. The mission was also the last mission of the Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' to have a seven-member crew until STS-82, which was launched on February 11, 1997. Crew Crew seating arrangements Crew notes The crew of STS-42 included West Germany's first astronaut, Ulf D. Merbold, who was making his second spaceflight, and Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)