|
Structured-light 3D Scanner
A structured-light 3D scanner is a 3D scanning device for measuring the three-dimensional shape of an object using projected light patterns and a camera system. Principle Projecting a narrow band of light onto a three-dimensionally shaped surface produces a line of illumination that appears distorted from other perspectives than that of the projector, and can be used for geometric reconstruction of the surface shape (light section). A faster and more versatile method is the projection of patterns consisting of many stripes at once, or of arbitrary fringes, as this allows for the acquisition of a multitude of samples simultaneously. Seen from different viewpoints, the pattern appears geometrically distorted due to the surface shape of the object. Although many other variants of structured light projection are possible, patterns of parallel stripes are widely used. The picture shows the geometrical deformation of a single stripe projected onto a simple 3D surface. The displace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Scanning
3D scanning is the process of analyzing a real-world object or environment to collect data on its shape and possibly its appearance (e.g. color). The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D models. A 3D scanner can be based on many different technologies, each with its own limitations, advantages and costs. Many limitations in the kind of objects that can be digitised are still present. For example, optical technology may encounter many difficulties with dark, shiny, reflective or transparent objects. For example, industrial computed tomography scanning, structured-light 3D scanners, LiDAR and Time Of Flight 3D Scanners can be used to construct digital 3D models, without destructive testing. Collected 3D data is useful for a wide variety of applications. These devices are used extensively by the entertainment industry in the production of movies and video games, including virtual reality. Other common applications of this technology include augmented realit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting photographic images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant imagery and other phenomena. The term photogrammetry was coined by the Prussian architect Albrecht Meydenbauer, which appeared in his 1867 article "Die Photometrographie." There are many variants of photogrammetry. One example is the extraction of three-dimensional measurements from two-dimensional data (i.e. images); for example, the distance between two points that lie on a plane parallel to the photographic image plane can be determined by measuring their distance on the image, if the scale of the image is known. Another is the extraction of accurate color ranges and values representing such quantities as albedo, specular reflection, metallicity, or ambient occlusion from photographs of materials for the purposes of physically base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PrimeSense
PrimeSense was an Israeli 3D sensing company based in Tel Aviv. PrimeSense had offices in Israel, North America, Japan, Singapore, Korea, China and Taiwan. PrimeSense was bought by Apple Inc. for $360 million on November 24, 2013. History PrimeSense was a fabless semiconductor company and provided products in the area of sensory inputs for consumer and commercial markets. PrimeSense's technology had been originally applied to gaming but was later applied in other fields. PrimeSense was best known for licensing the hardware design and chip used in Microsoft's Kinect motion-sensing system for the Xbox 360 in 2010. The company had been founded in 2005 to explore depth-sensing cameras which they had demonstrated to developers at the 2006 Game Developers Conference. Microsoft had been looking on its own at 3D camera technology applications to its Xbox line of consoles, and engaged with PrimeSense after the conference to help establish the direction the technology needed to go t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simultaneous Localization And Mapping
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is the computational problem of constructing or updating a map of an unknown environment while simultaneously keeping track of an agent's location within it. While this initially appears to be a chicken-and-egg problem, there are several algorithms known for solving it in, at least approximately, tractable time for certain environments. Popular approximate solution methods include the particle filter, extended Kalman filter, covariance intersection, and GraphSLAM. SLAM algorithms are based on concepts in computational geometry and computer vision, and are used in robot navigation, robotic mapping and odometry for virtual reality or augmented reality. SLAM algorithms are tailored to the available resources and are not aimed at perfection but at operational compliance. Published approaches are employed in self-driving cars, unmanned aerial vehicles, autonomous underwater vehicles, planetary rovers, newer domestic robots and eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Project Tango
Tango (formerly named Project Tango, while in testing) was an augmented reality computing platform, developed and authored by the Advanced Technology and Projects (ATAP), a skunkworks division of Google. It used computer vision to enable mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to detect their position relative to the world around them without using GPS or other external signals. This allowed application developers to create user experiences that include indoor navigation, 3D mapping, physical space measurement, environmental recognition, augmented reality, and windows into a virtual world. The first product to emerge from ATAP, Tango was developed by a team led by computer scientist Johnny Lee, a core contributor to Microsoft's Kinect. In an interview in June 2015, Lee said, "We're developing the hardware and software technologies to help everything and everyone understand precisely where they are, anywhere." Google produced two devices to demonstrate the Tango tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accomplishes a task with very little (if any) insight into exactly how it does so. It is essentially the process of opening up or dissecting a system to see how it works, in order to duplicate or enhance it. Depending on the system under consideration and the technologies employed, the knowledge gained during reverse engineering can help with repurposing obsolete objects, doing security analysis, or learning how something works. Although the process is specific to the object on which it is being performed, all reverse engineering processes consist of three basic steps: Information extraction, Modeling, and Review. Information extraction refers to the practice of gathering all relevant information for performing the operation. Modeling refers to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-aided Design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software are helpful in protecting products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used. Its use in designing electronic systems is known as ''electronic design automation'' (''EDA''). In mechanical design it is known as ''mechanical design automation'' (''MDA''), which includes the process of creating a technical drawing with the use of computer software. CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector-based graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
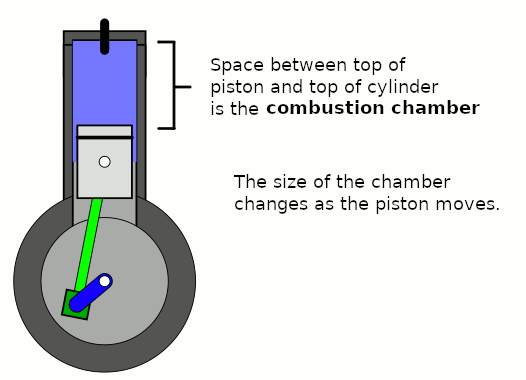
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such that the bottom of combustion chamber is roughly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting photographic images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant imagery and other phenomena. The term photogrammetry was coined by the Prussian architect Albrecht Meydenbauer, which appeared in his 1867 article "Die Photometrographie." There are many variants of photogrammetry. One example is the extraction of three-dimensional measurements from two-dimensional data (i.e. images); for example, the distance between two points that lie on a plane parallel to the photographic image plane can be determined by measuring their distance on the image, if the scale of the image is known. Another is the extraction of accurate color ranges and values representing such quantities as albedo, specular reflection, metallicity, or ambient occlusion from photographs of materials for the purposes of physically base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelet
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that begins at zero, increases or decreases, and then returns to zero one or more times. Wavelets are termed a "brief oscillation". A taxonomy of wavelets has been established, based on the number and direction of its pulses. Wavelets are imbued with specific properties that make them useful for signal processing. For example, a wavelet could be created to have a frequency of Middle C and a short duration of roughly one tenth of a second. If this wavelet were to be convolved with a signal created from the recording of a melody, then the resulting signal would be useful for determining when the Middle C note appeared in the song. Mathematically, a wavelet correlates with a signal if a portion of the signal is similar. Correlation is at the core of many practical wavelet applications. As a mathematical tool, wavelets can be used to extract information from many different kinds of data, including but not limited to au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, which will output a function depending on temporal frequency or spatial frequency respectively. That process is also called ''analysis''. An example application would be decomposing the waveform of a musical chord into terms of the intensity of its constituent pitches. The term ''Fourier transform'' refers to both the frequency domain representation and the mathematical operation that associates the frequency domain representation to a function of space or time. The Fourier transform of a function is a complex-valued function representing the complex sinusoids that comprise the original function. For each frequency, the magnitude ( absolute value) of the complex value represents the amplitude of a constituent complex sinusoid wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)