|
Structure Editor
A structure editor, also structured editor or projectional editor, is any document editor that is cognizant of the document's underlying structure. Structure editors can be used to edit hierarchical or marked up text, computer programs, diagrams, chemical formulas, and any other type of content with clear and well-defined structure. In contrast, a text editor is any document editor used for editing plain text files. Typically, the benefits of text and structure editing are combined in the user interface of a single hybrid tool. For example, Emacs is fundamentally a text editor, but supports the manipulation of words, sentences, and paragraphs as structures that are inferred from the text. Conversely, Dreamweaver is fundamentally a structure editor for marked up web documents, but supports the display and manipulation of raw HTML text as well. Similarly, molecule editors typically support both graphical and textual input. Structure editing predominates when content is graphical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a Complex network, network featuring many-to-many Link (geometry), links, or a lattice (order), lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, Ant colony, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of Structural load, load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and nonbuilding structure, non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Processors
A word processor is an electronic device (later a computer software application) for text, composing, editing, formatting, and printing. The word processor was a stand-alone office machine in the 1960s, combining the keyboard text-entry and printing functions of an electric typewriter with a recording unit, either tape or floppy disk (as used by the Wang machine) with a simple dedicated computer processor for the editing of text. Although features and designs varied among manufacturers and models, and new features were added as technology advanced, the first word processors typically featured a monochrome display and the ability to save documents on memory cards or diskettes. Later models introduced innovations such as spell-checking programs, and improved formatting options. As the more versatile combination of personal computers and printers became commonplace, and computer software applications for word processing became popular, most business machine companies stopped manuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Context-free Grammar
In formal language theory, a context-free grammar (CFG) is a formal grammar whose production rules are of the form :A\ \to\ \alpha with A a ''single'' nonterminal symbol, and \alpha a string of terminals and/or nonterminals (\alpha can be empty). A formal grammar is "context-free" if its production rules can be applied regardless of the context of a nonterminal. No matter which symbols surround it, the single nonterminal on the left hand side can always be replaced by the right hand side. This is what distinguishes it from a context-sensitive grammar. A formal grammar is essentially a set of production rules that describe all possible strings in a given formal language. Production rules are simple replacements. For example, the first rule in the picture, :\langle\text\rangle \to \langle\text\rangle = \langle\text\rangle ; replaces \langle\text\rangle with \langle\text\rangle = \langle\text\rangle ;. There can be multiple replacement rules for a given nonterminal symbol. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be graphical. They are a kind of computer language. The description of a programming language is usually split into the two components of syntax (form) and semantics (meaning), which are usually defined by a formal language. Some languages are defined by a specification document (for example, the C programming language is specified by an ISO Standard) while other languages (such as Perl) have a dominant implementation that is treated as a reference. Some languages have both, with the basic language defined by a standard and extensions taken from the dominant implementation being common. Programming language theory is the subfield of computer science that studies the design, implementation, analysis, characterization, and classification of programming languages. Definitions There are many considerations when defining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Development Environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to computer programmers for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source code editor, build automation tools and a debugger. Some IDEs, such as NetBeans and Eclipse, contain the necessary compiler, interpreter, or both; others, such as SharpDevelop and Lazarus, do not. The boundary between an IDE and other parts of the broader software development environment is not well-defined; sometimes a version control system or various tools to simplify the construction of a graphical user interface (GUI) are integrated. Many modern IDEs also have a class browser, an object browser, and a class hierarchy diagram for use in object-oriented software development. Overview Integrated development environments are designed to maximize programmer productivity by providing tight-knit components with similar user interfaces. IDEs present a single pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
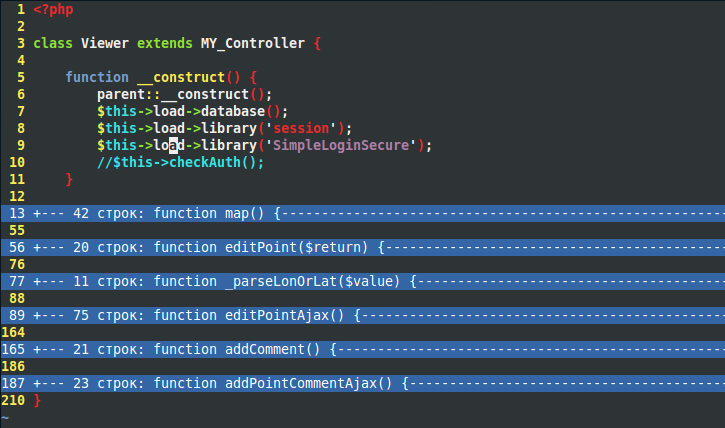
Code Folding
Code or text folding, or less commonly holophrasting, is a feature of some graphical user interfaces that allows the user to selectively hide ("fold") or display ("unfold") parts of a document. This allows the user to manage large amounts of text while viewing only those subsections that are currently of interest. It is typically used with documents which have a natural tree structure consisting of nested elements. Other names for these features include expand and collapse, code hiding, and outlining. In Microsoft Word, the feature is called "collapsible outlining". Many user interfaces provide disclosure widgets for code folding in a sidebar, indicated for example by a triangle that points sideways (if collapsed) or down (if expanded), or by a /code> box for collapsible (expanded) text, and a /code> box for expandable (collapsed) text. Code folding is found in text editors, source code editors, and IDEs. The folding structure typically follows the syntax tree of the progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax Highlighting
Syntax highlighting is a feature of text editors that are used for programming, scripting, or markup languages, such as HTML. The feature displays text, especially source code, in different colours and fonts according to the category of terms. This feature facilitates writing in a structured language such as a programming language or a markup language as both structures and syntax errors are visually distinct. This feature is also employed in many programming related contexts (such as programming manuals), either in the form of colorful books or online websites to make understanding code snippets easier for readers. Highlighting does not affect the meaning of the text itself; it is intended only for human readers. Syntax highlighting is a form of secondary notation, since the highlights are not part of the text meaning, but serve to reinforce it. Some editors also integrate syntax highlighting with other features, such as spell checking or code folding, as aids to editing wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source Code Editor
A source-code editor is a text editor program designed specifically for editing source code of computer programs. It may be a standalone application or it may be built into an integrated development environment (IDE) or web browser. Source-code editors are a fundamental programming tool, as the fundamental job of programmers is to write and edit source code. Characteristics Source-code editors have characteristics specifically designed to simplify and speed up typing of source code, such as syntax highlighting, indentation, autocomplete and brace matching functionality. These editors also provide a convenient way to run a compiler, interpreter, debugger, or other program relevant for the software-development process. So, while many text editors like Notepad can be used to edit source code, if they don't enhance, automate or ease the editing of code, they are not ''source-code editors''. Structure editors are a different form of source-code editor, where instead of editing r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Document Type Definition
A document type definition (DTD) is a set of ''markup declarations'' that define a ''document type'' for an SGML-family markup language ( GML, SGML, XML, HTML). A DTD defines the valid building blocks of an XML document. It defines the document structure with a list of validated elements and attributes. A DTD can be declared inline inside an XML document, or as an external reference. XML uses a subset of SGML DTD. , newer XML namespace-aware schema languages (such as W3C XML Schema and ISO RELAX NG) have largely superseded DTDs. A namespace-aware version of DTDs is being developed as Part 9 of ISO DSDL. DTDs persist in applications that need special publishing characters, such as the XML and HTML Character Entity References, which derive from larger sets defined as part of the ISO SGML standard effort. Associating DTDs with documents A DTD is associated with an XML or SGML document by means of a document type declaration (DOCTYPE). The DOCTYPE appears in the syntactic fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XML Editor
An XML editor is a markup language editor with added functionality to facilitate the editing of XML. This can be done using a plain text editor, with all the code visible, but XML editors have added facilities like tag completion and menus and buttons for tasks that are common in XML editing, based on data supplied with document type definition (DTD) or the XML tree. There are also graphical XML editors that hide the code in the background and present the content to the user in a more user-friendly format, approximating the rendered version or editing forms. This is helpful for situations where people who are not fluent in XML code need to enter information in XML based documents such as time sheets and expenditure reports. And even if the user is familiar with XML, use of such editors, which take care of syntax details, is often faster and more convenient. Functionality beyond syntax highlighting An XML editor goes beyond the syntax highlighting offered by many plaintext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisp (programming Language)
Lisp (historically LISP) is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in 1960, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket and Clojure. Lisp was originally created as a practical mathematical notation for computer programs, influenced by (though not originally derived from) the notation of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus. It quickly became a favored programming language for artificial intelligence (AI) research. As one of the earliest programming languages, Lisp pioneered many ideas in computer science, including tree data structures, automatic storage management, dynamic typing, conditionals, higher-order functions, recursion, the self-hosting compiler, and the rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Grammar
In formal language theory, a grammar (when the context is not given, often called a formal grammar for clarity) describes how to form strings from a language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax. A grammar does not describe the meaning of the strings or what can be done with them in whatever context—only their form. A formal grammar is defined as a set of production rules for such strings in a formal language. Formal language theory, the discipline that studies formal grammars and languages, is a branch of applied mathematics. Its applications are found in theoretical computer science, theoretical linguistics, formal semantics, mathematical logic, and other areas. A formal grammar is a set of rules for rewriting strings, along with a "start symbol" from which rewriting starts. Therefore, a grammar is usually thought of as a language generator. However, it can also sometimes be used as the basis for a " recognizer"—a function in computing tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |