|
String-net
In condensed matter physics, a string-net is an extended object whose collective behavior has been proposed as a physical mechanism for topological order by Michael A. Levin and Xiao-Gang Wen. A particular string-net model may involve only closed loops; or networks of oriented, labeled strings obeying branching rules given by some gauge group; or still more general networks. Overview The string-net model is claimed to show the derivation of photons, electrons, and U(1) gauge charge, small (relative to the Planck mass) but nonzero masses, and suggestions that the leptons, quarks, and gluons can be modeled in the same way. In other words, string-net condensation provides a unified origin for photons and electrons (or gauge bosons and fermions). It can be viewed as an origin of light and electron (or gauge interactions and Fermi statistics). However, their model does not account for the chiral coupling between the fermions and the SU(2) gauge bosons in the standard m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Order
In physics, topological order is a kind of order in the zero-temperature phase of matter (also known as quantum matter). Macroscopically, topological order is defined and described by robust ground state degeneracy and quantized non-Abelian geometric phases of degenerate ground states. Microscopically, topological orders correspond to patterns of long-range quantum entanglement. States with different topological orders (or different patterns of long range entanglements) cannot change into each other without a phase transition. Various topologically ordered states have interesting properties, such as (1) topological degeneracy and fractional statistics or non-abelian statistics that can be used to realize a topological quantum computer; (2) perfect conducting edge states that may have important device applications; (3) emergent gauge field and Fermi statistics that suggest a quantum information origin of elementary particles; See also (4) topological entanglement entropy tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiao-Gang Wen
Xiao-Gang Wen (; born November 26, 1961) is a Chinese-American physicist. He is a Cecil and Ida Green Professor of Physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Distinguished Visiting Research Chair at the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics. His expertise is in condensed matter theory in strongly correlated electronic systems. In Oct. 2016, he was awarded the Oliver E. Buckley Condensed Matter Prize. He is the author of a book in advanced quantum many-body theory entitled ''Quantum Field Theory of Many-body Systems: From the Origin of Sound to an Origin of Light and Electrons'' (Oxford University Press, 2004). Early life and education Wen attended the University of Science and Technology of China and earned a B.S. in Physics in 1982. In 1982, Wen came to the US for graduate school via the CUSPEA program, which was organized by Prof. T. D. Lee. He attended Princeton University, from which be attained an M.A. in Physics in 1983 and a Ph.D in Physics in 1987. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Network
In physics, a spin network is a type of diagram which can be used to represent states and interactions between particles and fields in quantum mechanics. From a mathematical perspective, the diagrams are a concise way to represent multilinear functions and functions between representations of matrix groups. The diagrammatic notation can thus greatly simplify calculations. Roger Penrose described spin networks in 1971. Spin networks have since been applied to the theory of quantum gravity by Carlo Rovelli, Lee Smolin, Jorge Pullin, Rodolfo Gambini and others. Spin networks can also be used to construct a particular functional on the space of connections which is invariant under local gauge transformations. Definition Penrose's definition A spin network, as described in Penrose (1971),R. Penrose (1971a), "Angular momentum: an approach to combinatorial spacetime," in T. Bastin (ed.), ''Quantum Theory and Beyond'', Cambridge University Press (this paper can be found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Gravity
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics; it deals with environments in which neither gravitational nor quantum effects can be ignored, such as in the vicinity of black holes or similar compact astrophysical objects, such as neutron stars. Three of the four fundamental forces of physics are described within the framework of quantum mechanics and quantum field theory. The current understanding of the fourth force, gravity, is based on Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which is formulated within the entirely different framework of classical physics. However, that description is incomplete: describing the gravitational field of a black hole in the general theory of relativity leads physical quantities, such as the spacetime curvature, to diverge at the center of the black hole. This signals the breakdown of the general theory of relativity and the need for a theory that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
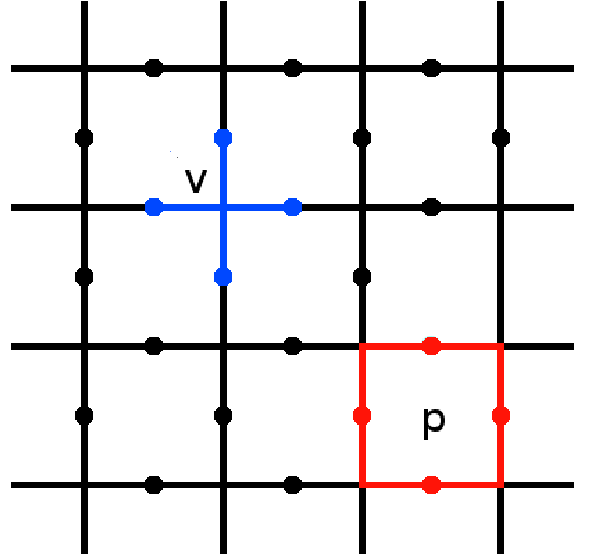
Toric Code
The toric code is a topological quantum error correcting code, and an example of a stabilizer code, defined on a two-dimensional spin lattice. It is the simplest and most well studied of the quantum double models. It is also the simplest example of topological order—''Z''2 topological order (first studied in the context of ''Z''2 spin liquid in 1991). The toric code can also be considered to be a ''Z''2 lattice gauge theory in a particular limit. It was introduced by Alexei Kitaev. The toric code gets its name from its periodic boundary conditions, giving it the shape of a torus. These conditions give the model translational invariance, which is useful for analytic study. However, some experimental realizations require open boundary conditions, allowing the system to be embedded on a 2D surface. The resulting code is typically known as the planar code. This has identical behaviour to the toric code in most, but not all, cases. Error correction and computation The toric code i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop Quantum Gravity
Loop quantum gravity (LQG) is a theory of quantum gravity, which aims to merge quantum mechanics and general relativity, incorporating matter of the Standard Model into the framework established for the pure quantum gravity case. It is an attempt to develop a quantum theory of gravity based directly on Einstein's geometric formulation rather than the treatment of gravity as a force. As a theory LQG postulates that the structure of space and time is composed of finite loops woven into an extremely fine fabric or network. These networks of loops are called spin networks. The evolution of a spin network, or spin foam, has a scale above the order of a Planck length, approximately 10−35 meters, and smaller scales are meaningless. Consequently, not just matter, but space itself, prefers an atomic structure. The areas of research, which involves about 30 research groups worldwide, share the basic physical assumptions and the mathematical description of quantum space. Research has ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces ( electromagnetic, weak and strong interactions - excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying all known elementary particles. It was developed in stages throughout the latter half of the 20th century, through the work of many scientists worldwide, with the current formulation being finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, proof of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and the Higgs boson (2012) have added further credence to the Standard Model. In addition, the Standard Model has predicted various properties of weak neutral currents and the W and Z bosons with great accuracy. Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge successes in providing experimental predictions, it leaves some phenomena unexplained. It falls short of being a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torus
In geometry, a torus (plural tori, colloquially donut or doughnut) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space about an axis that is coplanar with the circle. If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a ring shape and is called a torus of revolution. If the axis of revolution is tangent to the circle, the surface is a horn torus. If the axis of revolution passes twice through the circle, the surface is a spindle torus. If the axis of revolution passes through the center of the circle, the surface is a degenerate torus, a double-covered sphere. If the revolved curve is not a circle, the surface is called a '' toroid'', as in a square toroid. Real-world objects that approximate a torus of revolution include swim rings, inner tubes and ringette rings. Eyeglass lenses that combine spherical and cylindrical correction are toric lenses. A torus should not be confused with a ''solid torus'', which is form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z2 Spin Liquid
Z (or z) is the 26th and last letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual names in English are ''zed'' () and ''zee'' (), with an occasional archaic variant ''izzard'' ()."Z", ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "zee", ''op. cit''. Name and pronunciation In most English-speaking countries, including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand and the United Kingdom, the letter's name is ''zed'' , reflecting its derivation from the Greek ''zeta'' (this dates to Latin, which borrowed Y and Z from Greek), but in American English its name is ''zee'' , analogous to the names for B, C, D, etc., and deriving from a late 17th-century English dialectal form. Another English dialectal form is ''izzard'' . This dates from the mid-18th century and probably derives f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbertsmithite
Herbertsmithite is a mineral with chemical structure Zn Cu3( OH)6 Cl2. It is named after the mineralogist Herbert Smith (1872–1953) and was first found in 1972 in Chile. It is polymorphous with kapellasite and closely related to paratacamite. Herbertsmithite is generally found in and around Anarak, Iran, hence its other name, anarakite. Herbertsmithite is associated with copper mineralizations in syenitic porphyries and granites in Chile and in Triassic dolomite formations in Iran. It has also been reported from the Osborn District in the Big Horn Mountains of Maricopa County, Arizona and the Lavrion District Mines of Attica, Greece. Herbertsmithite has a vitreous luster and is fairly transparent with a light-green to blue green color. Herbertsmithite has a Mohs hardness of between 3 and 3.5 and is known to have a brittle tenacity. The crystal's density has been calculated at 3.76 g/cm3. Herbertsmithite, in a pure synthetic form, was discovered in 2012 to be able to exhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simone Severini
Simone Severini is an Italian-born British computer scientist. He is currently Professor of Physics of Information at University College London, and Director of Quantum Computing at Amazon Web Services. Work Severini worked in quantum information science and complex systems. Together with Adan Cabello and Andreas Winter, he defined a graph-theoretic framework for studying quantum contextuality, and together with Tomasz Konopka, Fotini Markopoulou, and Lee Smolin, he introduced a random graph model of spacetime called quantum graphity. He served as an editor of Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. In 2015 he was one of the first scientific advisors of Cambridge Quantum Computing, with Béla Bollobás, Imre Leader, and Fernando Brandão. In network theory, he co-introduced the Braunstein–Ghosh–Severini entropy In network theory, the Braunstein–Ghosh–Severini entropy (BGS entropy) of a network is the von Neumann entropy of a density matrix given by a normali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |