|
Stretchable Electronics
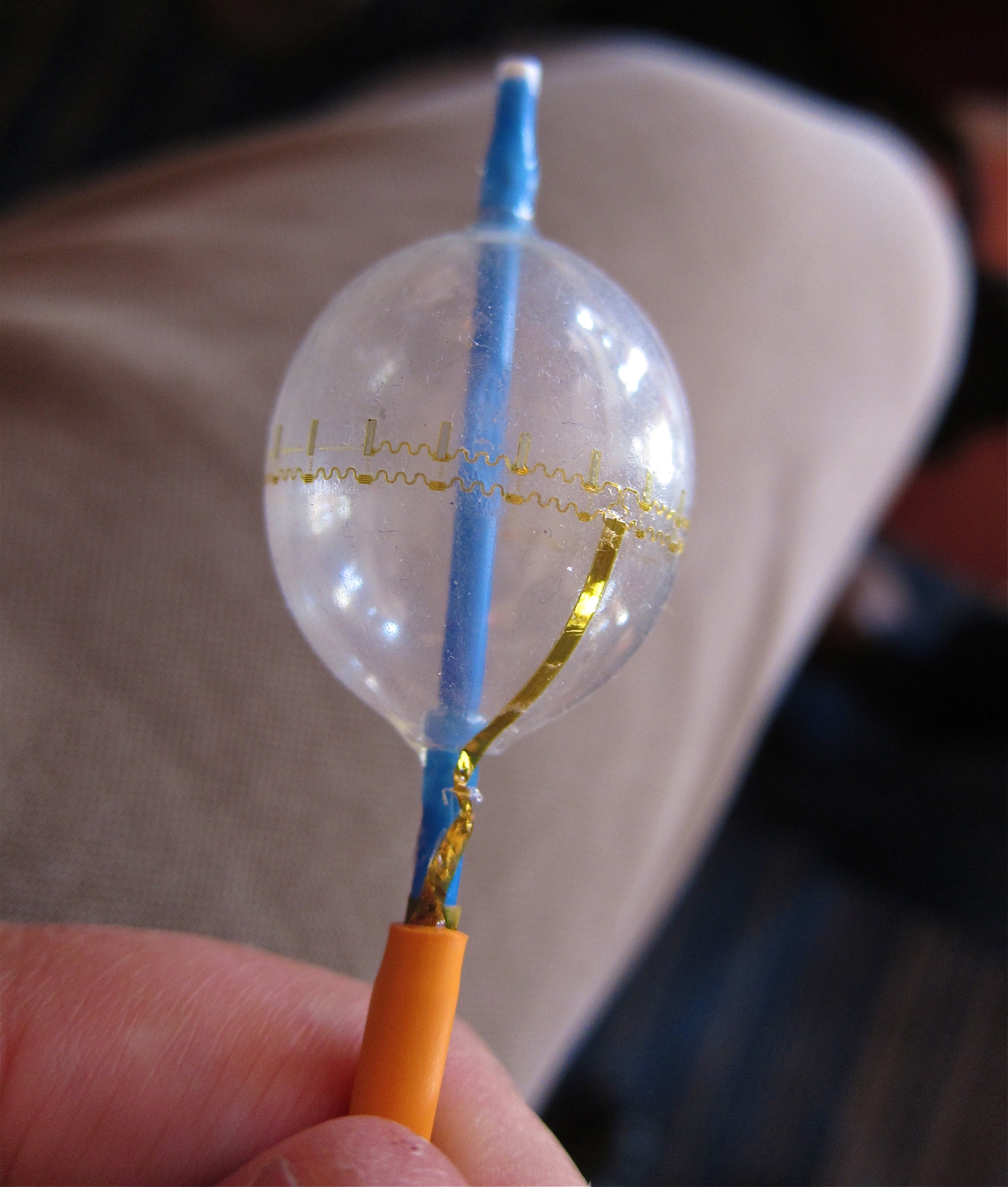
Stretchable electronics, also known as elastic electronics or elastic circuits, is a group of technologies for building electronic circuits by depositing or embedding electronic devices and circuits onto stretchable substrates such as silicones or polyurethanes, to make a completed circuit that can experience large strains without failure. In the simplest case, stretchable electronics can be made by using the same components used for rigid printed circuit boards, with the rigid substrate cut (typically in a serpentine pattern) to enable in-plane stretchability. However, many researchers have also sought intrinsically stretchable conductors, such as liquid metals. One of the major challenges in this domain is designing the substrate and the interconnections to be stretchable, rather than flexible (see Flexible electronics) or rigid (Printed Circuit Boards). Typically, polymers are chosen as substrates or material to embed. When bending the substrate, the outermost radius of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain (materials Science)
In physics, deformation is the continuum mechanics transformation of a body from a ''reference'' configuration to a ''current'' configuration. A configuration is a set containing the positions of all particles of the body. A deformation can occur because of external loads, intrinsic activity (e.g. muscle contraction), body forces (such as gravity or electromagnetic forces), or changes in temperature, moisture content, or chemical reactions, etc. Strain is related to deformation in terms of ''relative'' displacement of particles in the body that excludes rigid-body motions. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered. In a continuous body, a deformation field results from a stress field due to applied forces or because of some changes in the temperature field of the body. The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stretch Sensor
A stretch sensor is a sensor which can be used to measure deformation and stretching forces such as tension or bending. They are usually made from a material that is itself soft and stretchable. Most stretch sensors fall into one of three categories. The first type consists of an electrical conductor for which the electrical resistance changes (usually increases) substantially when the sensor is deformed. The second type consists of a capacitor for which the capacitance changes under deformation. Known properties of the sensor can then be used to deduce the deformation from the resistance/capacitance. Both the rheostatic and capacitive types often take the form of a cord, tape, or mesh. The third type of sensor uses high performance piezoelectric systems in soft, flexible/stretchable formats for measuring signals using the capability of piezoelectric materials to interconvert mechanical and electrical forms of energy. Applications Wearable stretch sensors can be used for ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
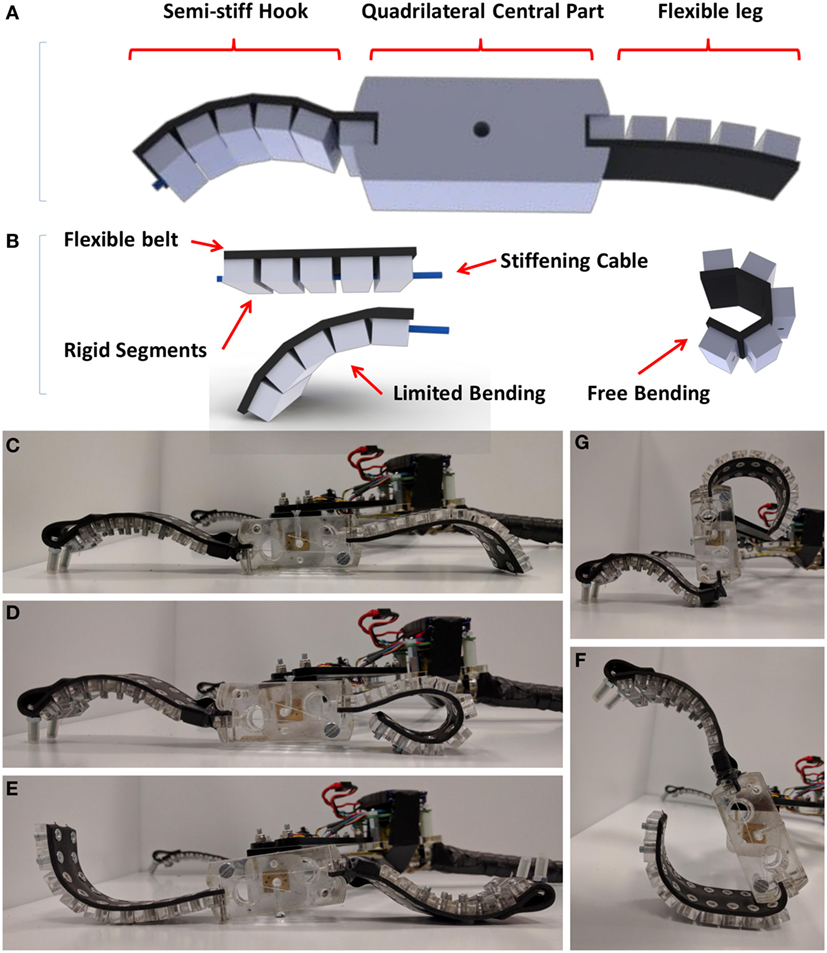
Soft Robotics
Soft robotics is a subfield of robotics that concerns the design, control, and fabrication of robots composed of compliant materials, instead of rigid links. In contrast to rigid-bodied robots built from metals, ceramics and hard plastics, the compliance of soft robots can improve their safety when working in close contact with humans. Types and designs The goal of soft robotics is the design and construction of robots with physically flexible-bodies and electronics. Sometimes softness is limited to part of the machine. For example, rigid-bodied robotic arms can employ soft end effectors to gently grab and manipulate delicate or irregularly shaped objects. Most rigid-bodied mobile robots also strategically employ soft components, such as foot pads to absorb shock or springy joints to store/release elastic energy. However, the field of soft robotics generally leans toward machines that are predominately or entirely soft. Robots with entirely soft bodies have tremendous potenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanotubes
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers. ''Single-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') are one of the allotropes of carbon, intermediate between fullerene cages and flat graphene, with diameters in the range of a nanometre. Although not made this way, single-wall carbon nanotubes can be idealized as cutouts from a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms rolled up along one of the Bravais lattice vectors of the hexagonal lattice to form a hollow cylinder. In this construction, periodic boundary conditions are imposed over the length of this roll-up vector to yield a helical lattice of seamlessly bonded carbon atoms on the cylinder surface. ''Multi-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consisting of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes weakly bound together by van der Waals interactions in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. This is not to be confused with experiments done ''in vitro'' ("within the glass"), i.e., in a laboratory environment using test tubes, Petri dishes, etc. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Skin
Electronic skin refers to flexible, stretchable and self-healing electronics that are able to mimic functionalities of human or animal skin. The broad class of materials often contain sensing abilities that are intended to reproduce the capabilities of human skin to respond to environmental factors such as changes in heat and pressure. Advances in electronic skin research focuses on designing materials that are stretchy, robust, and flexible. Research in the individual fields of flexible electronics and tactile sensing has progressed greatly; however, electronic skin design attempts to bring together advances in many areas of materials research without sacrificing individual benefits from each field. The successful combination of flexible and stretchable mechanical properties with sensors and the ability to self-heal would open the door to many possible applications including soft robotics, prosthetics, artificial intelligence and health monitoring. Recent advances in the field of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flesh
Flesh is any aggregation of soft tissues of an organism. Various multicellular organisms have soft tissues that may be called "flesh". In mammals, including humans, ''flesh'' encompasses muscles, fats and other loose connective tissues, but sometimes excluding non-muscular organs (liver, lung, spleen, kidney) and typically discarded parts (hard tendon, brain tissue, intestines, etc.). In a culinary context, consumable animal flesh is called meat, while processed visceral tissues are known as offal. In particular animal groups such as vertebrates, molluscs and arthropods, the flesh is distinguished from tougher body structures such as bone, shell and scute, respectively. In plants, the "flesh" is the juicy, edible structures such as the mesocarp of fruits and melons as well as soft tubers, rhizomes and taproots, as opposed to tougher structures like nuts and stems. In fungi, ''flesh'' refers to trama, the soft, inner portion of a mushroom, or fruit body. A more restrictive u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
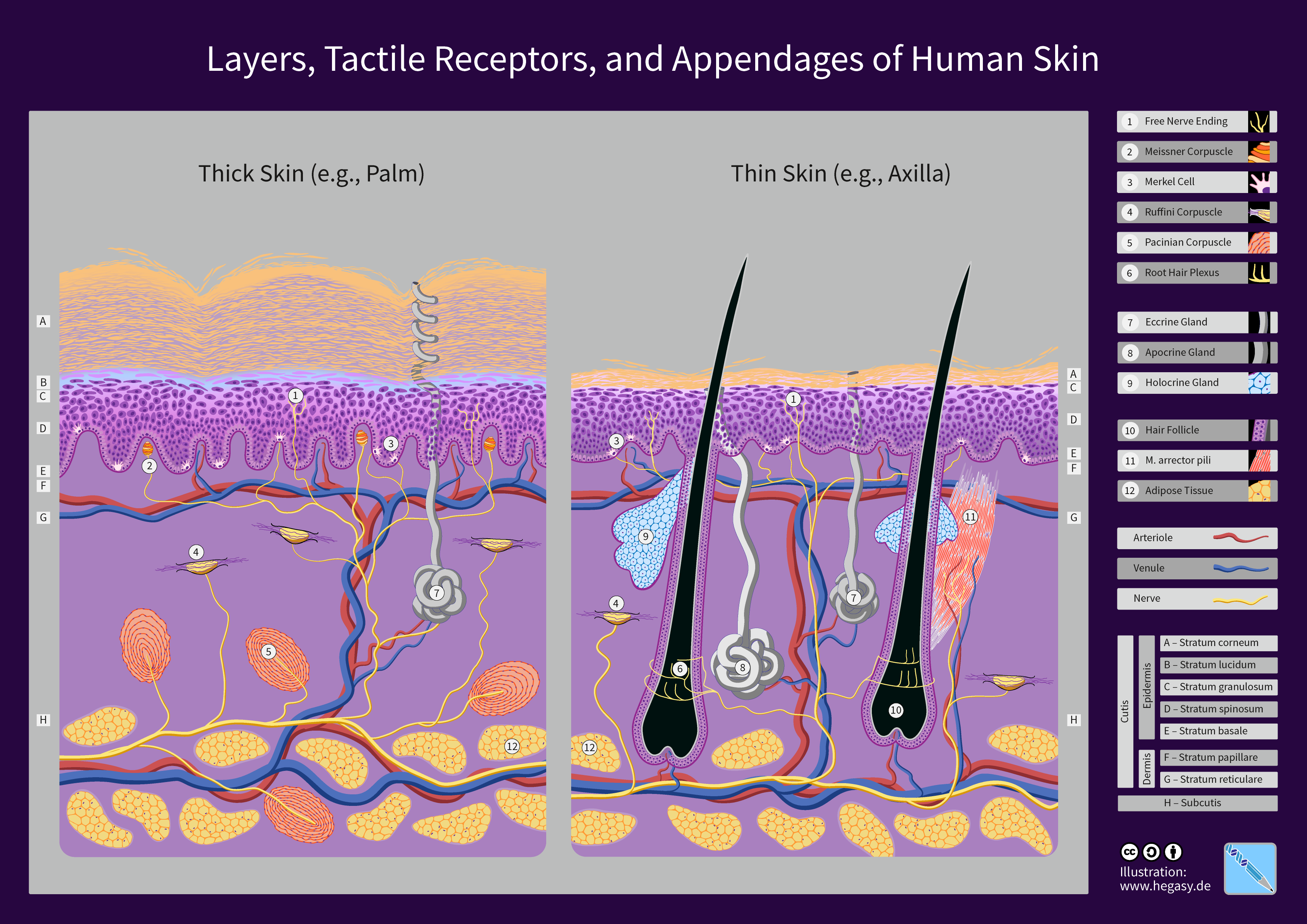
Human Skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective ''cutaneous'' literally means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'', skin). Because it interfaces with the environment, skin plays an important immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive water loss. Its other functions are insulation, temperature regulation, sensation, synthesis of vitamin D, and the protection of vitamin B folates. Severely damaged skin will try to heal by forming scar tissue. This is often discoloured and depigmented. In humans, skin pigmentation (af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler–Bernoulli Beam Theory
Euler–Bernoulli beam theory (also known as engineer's beam theory or classical beam theory) is a simplification of the linear theory of elasticity which provides a means of calculating the load-carrying and deflection characteristics of beams. It covers the case corresponding to small deflections of a beam that is subjected to lateral loads only. By ignoring the effects of shear deformation and rotatory inertia, it is thus a special case of Timoshenko–Ehrenfest beam theory. It was first enunciated circa 1750, but was not applied on a large scale until the development of the Eiffel Tower and the Ferris wheel in the late 19th century. Following these successful demonstrations, it quickly became a cornerstone of engineering and an enabler of the Second Industrial Revolution. Additional mathematical models have been developed, such as plate theory, but the simplicity of beam theory makes it an important tool in the sciences, especially structural and mechanical engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicone
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, silicone rubber, silicone resin, and silicone caulk. Chemistry More precisely called polymerized siloxanes or polysiloxanes, silicones consist of an inorganic silicon–oxygen backbone chain (⋯−Si−O−Si−O−Si−O−⋯) with two organic groups attached to each silicon center. Commonly, the organic groups are methyl. The materials can be cyclic or polymeric. By varying the −Si−O− chain lengths, side groups, and crosslinking, silicones can be synthesized with a wide variety of properties and compositions. They can vary in consistency from liquid to gel to rubber to hard plastic. The most common si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'', mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |