 |
Stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air high in the sky and the cool layers of air in the low sky, close to the planetary surface of the Earth. The increase of temperature with altitude is a result of the absorption of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation by the ozone layer. The temperature inversion is in contrast to the troposphere, near the Earth's surface, where temperature decreases with altitude. Between the troposphere and stratosphere is the tropopause border that demarcates the beginning of the temperature inversion. Near the equator, the lower edge of the stratosphere is as high as , at midlatitudes around , and at the poles about . Temperatures range from an average of near the tropopause to an average of near the mesosphere. Stratospheric temperatures also var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Earth's Atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention ( greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation). By mole fraction (i.e., by number of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of Water vapor#Water vapor in Earth's atmosphere, water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air composition, temperature, and atmospheric pressure vary with altitude. Within the atmosphere, air suitable for use in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Atmospheric Stratification
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention ( greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation). By mole fraction (i.e., by number of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air composition, temperature, and atmospheric pressure vary with altitude. Within the atmosphere, air suitable for use in photosynthesis by terrestrial plants and breathing of terrestrial animals is found only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Ozone Layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in relation to other gases in the stratosphere. The ozone layer contains less than 10 parts per million of ozone, while the average ozone concentration in Earth's atmosphere as a whole is about 0.3 parts per million. The ozone layer is mainly found in the lower portion of the stratosphere, from approximately above Earth, although its thickness varies seasonally and geographically. The ozone layer was discovered in 1913 by the French physicists Charles Fabry and Henri Buisson. Measurements of the sun showed that the radiation sent out from its surface and reaching the ground on Earth is usually consistent with the spectrum of a black body with a temperature in the range of , except that there was no radiation below a wavelength of about 310&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary that demarcates the troposphere from the stratosphere; which are two of the five layers of the atmosphere of Earth. The tropopause is a thermodynamic gradient-stratification layer, that marks the end of the troposphere, and lies approximately above the equatorial regions, and approximately above the polar regions. Definition Rising from the planetary surface of the Earth, the tropopause is the atmospheric level where the air ceases to become cool with increased altitude, and becomes dry, devoid of water vapor. The tropopause is the boundary that demarcates the troposphere from the stratosphere, and is the part of the atmosphere where there occurs an abrupt change in the environmental lapse rate (ELR), from a positive rate in the troposphere to a negative rate in the stratosphere. The ELR indicates the lowest level at which the lapse rate decreases to 2°C/km or less, provided that the average lapse-rate, between that level and all ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and '' sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Polar Vortex
A circumpolar vortex, or simply polar vortex, is a large region of cold, rotating air that encircles both of Earth's polar regions. Polar vortices also exist on other rotating, low- obliquity planetary bodies. The term polar vortex can be used to describe two distinct phenomena; the stratospheric polar vortex, and the tropospheric polar vortex. The stratospheric and tropospheric polar vortices both rotate in the direction of the Earth's spin, but they are distinct phenomena that have different sizes, structures, seasonal cycles, and impacts on weather. The stratospheric polar vortex is an area of high-speed, cyclonically rotating winds around 15 km to 50 km high, poleward of 50°, and is strongest in winter. It forms in Autumn when Arctic or Antarctic temperatures cool rapidly as the polar night begins. The increased temperature difference between the pole and the tropics causes strong winds and the Coriolis effect causes the vortex to spin up. The stratospheric pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Mesosphere
The mesosphere (; ) is the third layer of the atmosphere, directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere, temperature decreases as altitude increases. This characteristic is used to define its limits: it begins at the top of the stratosphere (sometimes called the stratopause), and ends at the mesopause, which is the coldest part of Earth's atmosphere, with temperatures below . The exact upper and lower boundaries of the mesosphere vary with latitude and with season (higher in winter and at the tropics, lower in summer and at the poles), but the lower boundary is usually located at altitudes from above sea level, and the upper boundary (the mesopause) is usually from . The stratosphere and mesosphere are sometimes collectively referred to as the "middle atmosphere", which spans altitudes approximately between above Earth's surface. The mesopause, at an altitude of , separates the mesosphere from the thermosphere—the second-outermost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F), produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane. They are also commonly known by the DuPont brand name Freon. The most common representative is dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12 or Freon-12). Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants, propellants (in aerosol applications), and solvents. Because CFCs contribute to ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, the manufacture of such compounds has been phased out under the Montreal Protocol, and they are being replaced with other products such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) including R-410A and R-134a. Structure, properties and production As in simpler alkanes, carbon in the CFCs bond with tetrahedral symmetry. Because the fluorine and chlorine atoms differ greatly in size and effective charge from hydrogen and from each othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Stratopause
The stratopause (formerly mesopeak) is the level of the atmosphere which is the boundary between two layers: the stratosphere and the mesosphere. In the stratosphere, the temperature increases with altitude, and the stratopause is the region where a maximum in the temperature occurs. This atmospheric feature is not exclusive to Earth, but also occurs on any other planet or moon with an atmosphere. On Earth, the stratopause is above sea level. The atmospheric pressure Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ... is around of the pressure at sea level. The temperature in the stratopause is . See also * Jet stream * Maximum parcel level References External links * {{Earth's atmosphere Atmospheric boundaries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
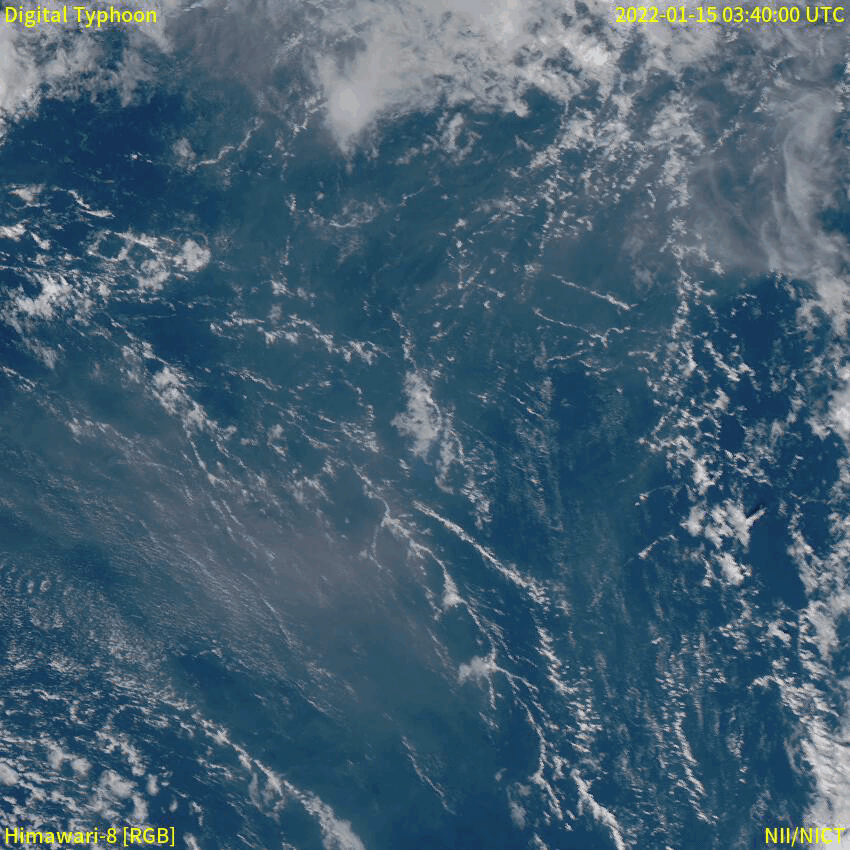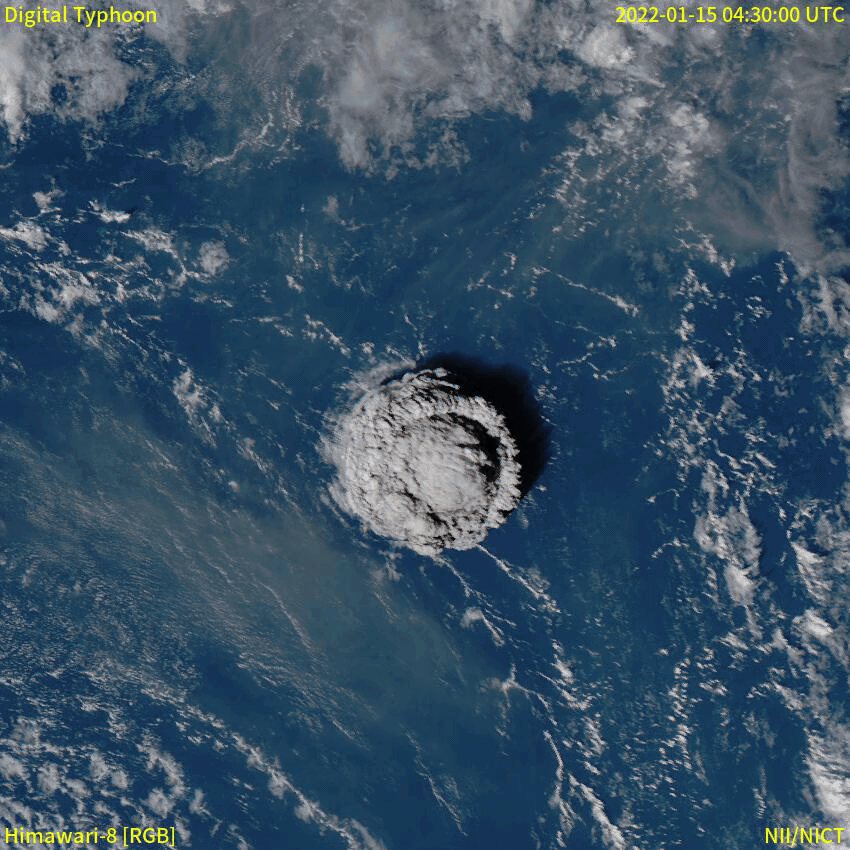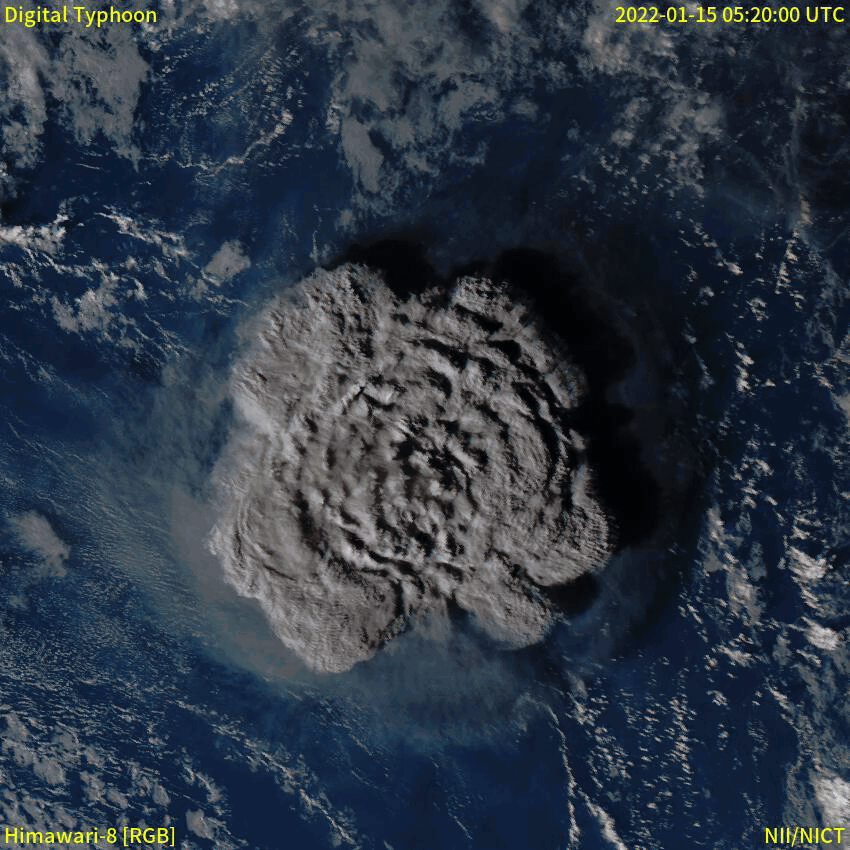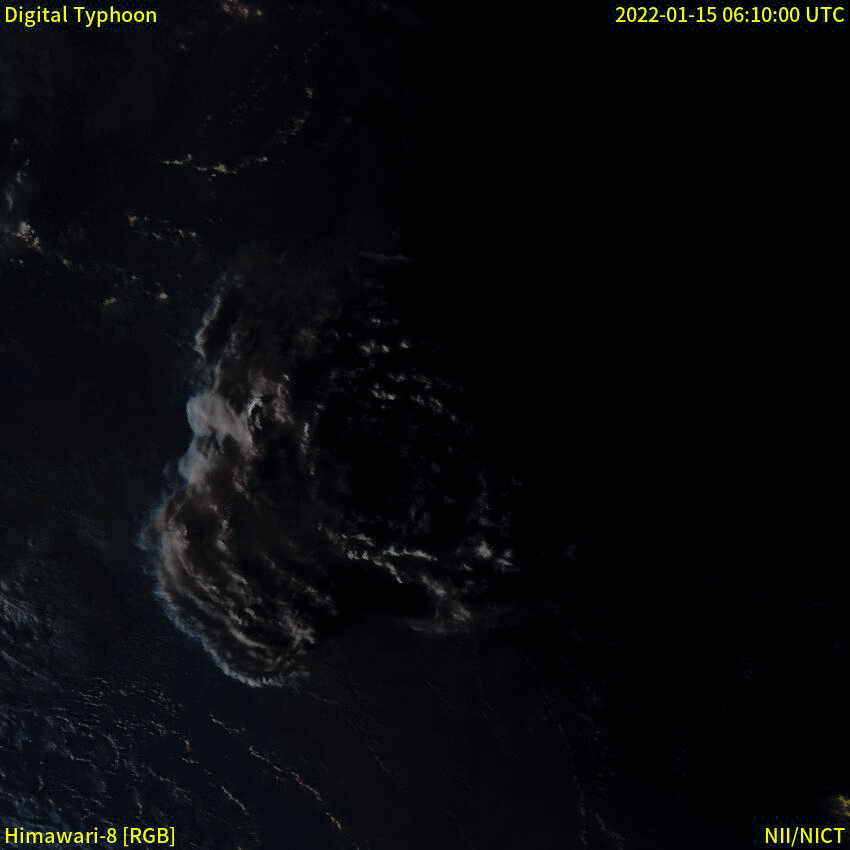 |
Eruption Column
An eruption column or eruption plume is a cloud of super-heated ash and tephra suspended in gases emitted during an explosive volcanic eruption. The volcanic materials form a vertical column or plume that may rise many kilometers into the air above the vent of the volcano. In the most explosive eruptions, the eruption column may rise over , penetrating the stratosphere. Stratospheric injection of aerosols by volcanoes is a major cause of short-term climate change. A common occurrence in explosive eruptions is ''column collapse'' when the eruption column is or becomes too dense to be lifted high into the sky by air convection, and instead falls down the slopes of the volcano to form pyroclastic flows or surges (although the latter is less dense). On some occasions, if the material is not dense enough to fall, it may create pyrocumulonimbus clouds. Formation Eruption columns form in explosive volcanic activity, when the high concentration of volatile materials in the risin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
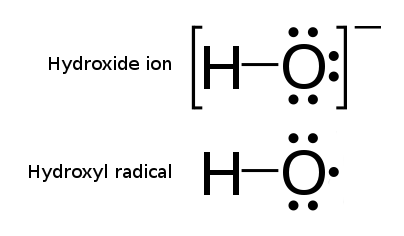 |
Hydroxyl Radical
The hydroxyl radical is the diatomic molecule . The hydroxyl radical is very stable as a dilute gas, but it decays very rapidly in the condensed phase. It is pervasive in some situations. Most notably the hydroxyl radicals are produced from the decomposition of hydroperoxides (ROOH) or, in atmospheric chemistry, by the reaction of excited atomic oxygen with water. It is also important in the field of radiation chemistry, since it leads to the formation of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, which can enhance corrosion and SCC in coolant systems subjected to radioactive environments. In organic synthesis, hydroxyl radicals are most commonly generated by photolysis of 1-hydroxy-2(1''H'')-pyridinethione. Notation The unpaired electron of the hydroxyl radical is officially represented by a middle dot, •, beside the O. Biology Hydroxyl radicals can occasionally be produced as a byproduct of immune action. Macrophages and microglia most frequently generate this compound wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |