|
Strain Tensor
In mechanics, strain is defined as relative deformation, compared to a position configuration. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered. Strain has dimension of a length ratio, with SI base units of meter per meter (m/m). Hence strains are dimensionless and are usually expressed as a decimal fraction or a percentage. Parts-per notation is also used, e.g., parts per million or parts per billion (sometimes called "microstrains" and "nanostrains", respectively), corresponding to μm/m and nm/m. Strain can be formulated as the spatial derivative of displacement: \boldsymbol \doteq \cfrac\left(\mathbf - \mathbf\right) = \boldsymbol'- \boldsymbol, where is the identity tensor. The displacement of a body may be expressed in the form , where is the reference position of material po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanics
Mechanics () is the area of physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among Physical object, physical objects. Forces applied to objects may result in Displacement (vector), displacements, which are changes of an object's position relative to its environment. Theoretical expositions of this branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece, for instance, in the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes (see History of classical mechanics and Timeline of classical mechanics). During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, Christiaan Huygens, and Isaac Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. As a branch of classical physics, mechanics deals with bodies that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of light. It can also be defined as the physical science that deals with the motion of and forces on bodies not in the quantum realm. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (physics)
In geometry and mechanics, a displacement is a vector whose length is the shortest distance from the initial to the final position of a point P undergoing motion. It quantifies both the distance and direction of the net or total motion along a straight line from the initial position to the final position of the point trajectory. A displacement may be identified with the translation that maps the initial position to the final position. Displacement is the shift in location when an object in motion changes from one position to another. For motion over a given interval of time, the displacement divided by the length of the time interval defines the average velocity (a vector), whose magnitude is the average speed (a scalar quantity). Formulation A displacement may be formulated as a '' relative position'' (resulting from the motion), that is, as the final position of a point relative to its initial position . The corresponding displacement vector can be defined as the differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
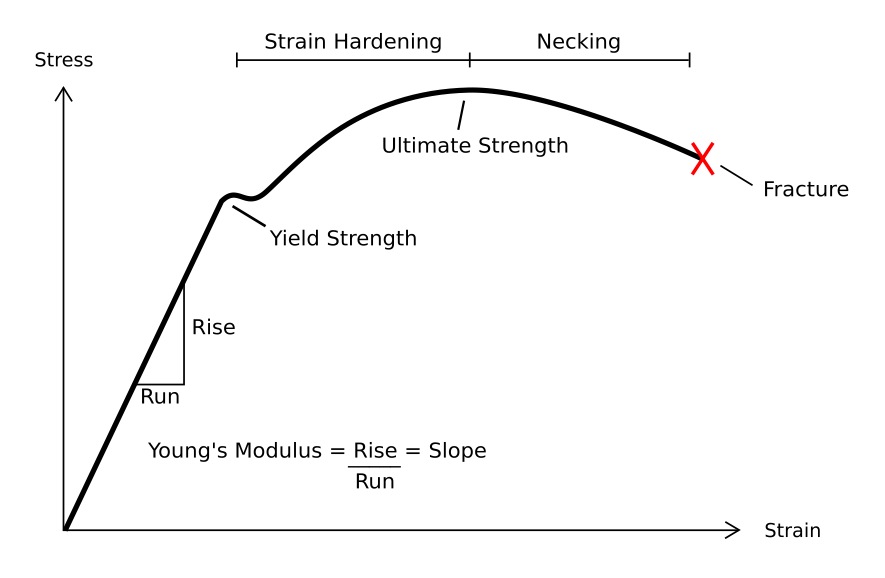
Elongation (mechanics)
In physics and continuum mechanics, deformation is the change in the shape or size of an object. It has dimension of length with SI unit of metre (m). It is quantified as the residual displacement of particles in a non- rigid body, from an configuration to a configuration, excluding the body's average translation and rotation (its rigid transformation). A ''configuration'' is a set containing the positions of all particles of the body. A deformation can occur because of external loads, intrinsic activity (e.g. muscle contraction), body forces (such as gravity or electromagnetic forces), or changes in temperature, moisture content, or chemical reactions, etc. In a continuous body, a ''deformation field'' results from a stress field due to applied forces or because of some changes in the conditions of the body. The relation between stress and strain (relative deformation) is expressed by constitutive equations, e.g., Hooke's law for linear elastic materials. Defor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastomers
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and Elasticity (physics), elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus (E) and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic polymer'', is often used interchangeably with ''Synthetic rubber, rubber'', although the latter is preferred when referring to Vulcanization, vulcanisates. Each of the monomers which link to form the polymer is usually a compound of several Chemical elements, elements among carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and silicon. Elastomers are amorphous polymers maintained above their glass transition temperature, so that considerable Segmental motion, molecular reconformation is feasible without breaking of covalent bonds. Rubber-like solids with elastic properties are called elastomers. Polymer chains are held together in these materials by relatively weak molecule, intermolecular bonds, which permit the polymers to stretch in r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deformation (engineering)
In engineering, deformation (the change in size or shape of an object) may be ''elastic'' or ''plastic''. If the deformation is negligible, the object is said to be ''rigid''. Main concepts Occurrence of deformation in engineering applications is based on the following background concepts: * ''Displacements'' are any change in position of a point on the object, including whole-body translations and rotations ( rigid transformations). * ''Deformation'' are changes in the relative position between internals points on the object, excluding rigid transformations, causing the body to change shape or size. * ''Strain'' is the ''relative'' ''internal'' deformation, the dimensionless change in shape of an infinitesimal cube of material relative to a reference configuration. Mechanical strains are caused by mechanical stress, ''see stress-strain curve''. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinitesimal Strain Theory
In continuum mechanics, the infinitesimal strain theory is a mathematical approach to the description of the deformation of a solid body in which the displacements of the material particles are assumed to be much smaller (indeed, infinitesimally smaller) than any relevant dimension of the body; so that its geometry and the constitutive properties of the material (such as density and stiffness) at each point of space can be assumed to be unchanged by the deformation. With this assumption, the equations of continuum mechanics are considerably simplified. This approach may also be called small deformation theory, small displacement theory, or small displacement-gradient theory. It is contrasted with the finite strain theory where the opposite assumption is made. The infinitesimal strain theory is commonly adopted in civil and mechanical engineering for the stress analysis of structures built from relatively stiff elastic materials like concrete and steel, since a common goal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Tissue
Soft tissue connective tissue, connects and surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligaments, Adipose tissue, fat, fibrous tissue, Lymphatic vessel, lymph and blood vessels, fasciae, and synovial membranes. Soft tissue is Tissue (biology), tissue in the body that is not hard tissue, hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. It is sometimes defined by what it is not – such as "nonepithelial, extraskeletal mesenchyme exclusive of the reticuloendothelial system and glia". Composition The characteristic substances inside the extracellular matrix of soft tissue are the collagen, elastin and ground substance. Normally the soft tissue is very hydrated because of the ground substance. The fibroblasts are the most common cell responsible for the production of soft tissues' fibers and ground substance. Variations of fibroblasts, like chondroblasts, may also produce these substances. Mechanical character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously motion, move and Deformation (physics), deform (''flow'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are Matter, substances which cannot resist any shear force applied to them. Although the term ''fluid'' generally includes both the liquid and gas phases, its definition varies among branches of science. Definitions of ''solid'' vary as well, and depending on field, some substances can have both fluid and solid properties. Non-Newtonian fluids like Silly Putty appear to behave similar to a solid when a sudden force is applied. Substances with a very high viscosity such as Pitch (resin), pitch appear to behave like a solid (see pitch drop experiment) as well. In particle physics, the concept is extended to include fluidic matters other than liquids or gases. A fluid in medicine or biology refers to any liquid constituent of the body (body fluid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasticity (physics)
In physics and materials science, plasticity (also known as plastic deformation) is the ability of a solid material to undergo permanent Deformation (engineering), deformation, a non-reversible change of shape in response to applied forces. For example, a solid piece of metal being bent or pounded into a new shape displays plasticity as permanent changes occur within the material itself. In engineering, the transition from Elasticity (physics), elastic behavior to plastic behavior is known as Yield (engineering), yielding. Plastic deformation is observed in most materials, particularly metals, soils, Rock (geology), rocks, concrete, and foams. However, the physical mechanisms that cause plastic deformation can vary widely. At a crystalline scale, plasticity in metals is usually a consequence of dislocations. Such defects are relatively rare in most crystalline materials, but are numerous in some and part of their crystal structure; in such cases, plastic crystallinity can resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus (E) and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic polymer'', is often used interchangeably with ''rubber'', although the latter is preferred when referring to vulcanisates. Each of the monomers which link to form the polymer is usually a compound of several elements among carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and silicon. Elastomers are amorphous polymers maintained above their glass transition temperature, so that considerable molecular reconformation is feasible without breaking of covalent bonds. Rubber-like solids with elastic properties are called elastomers. Polymer chains are held together in these materials by relatively weak intermolecular bonds, which permit the polymers to stretch in response to macroscopic stresses. Elastomers are usually thermosets (requiring vulcanization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Strain Theory
In continuum mechanics, the finite strain theory—also called large strain theory, or large deformation theory—deals with deformations in which strains and/or rotations are large enough to invalidate assumptions inherent in infinitesimal strain theory. In this case, the undeformed and deformed configurations of the continuum are significantly different, requiring a clear distinction between them. This is commonly the case with elastomers, plastically deforming materials and other fluids and biological soft tissue. Displacement field Deformation gradient tensor The deformation gradient tensor \mathbf F(\mathbf X,t) = F_ \mathbf e_j \otimes \mathbf I_K is related to both the reference and current configuration, as seen by the unit vectors \mathbf e_j and \mathbf I_K\,\!, therefore it is a '' two-point tensor''. Two types of deformation gradient tensor may be defined. Due to the assumption of continuity of \chi(\mathbf X,t)\,\!, \mathbf F has the inverse \mathbf H = \ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuum Mechanics
Continuum mechanics is a branch of mechanics that deals with the deformation of and transmission of forces through materials modeled as a ''continuous medium'' (also called a ''continuum'') rather than as discrete particles. Continuum mechanics deals with ''deformable bodies'', as opposed to rigid bodies. A continuum model assumes that the substance of the object completely fills the space it occupies. While ignoring the fact that matter is made of atoms, this provides a sufficiently accurate description of matter on length scales much greater than that of inter-atomic distances. The concept of a continuous medium allows for intuitive analysis of bulk matter by using differential equations that describe the behavior of such matter according to physical laws, such as mass conservation, momentum conservation, and energy conservation. Information about the specific material is expressed in constitutive relationships. Continuum mechanics treats the physical properties of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |