|
Stow, Massachusetts
Stow is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The town is located west of Boston, in the MetroWest region of Massachusetts. The population was 7,174 at the 2020 United States Census. Stow was officially incorporated in 1683 with an area of approximately . Over centuries it gave up land as newer, smaller towns were created, ceding land to Harvard (1732), Shirley (1765), Boxborough (1783), Hudson (1866) and Maynard (1871). Stow now has an area of . With the exception of factories at Assabet Village and Rock Bottom (later Maynard and Gleasondale), Stow was primarily sparsely settled farm and orchard land until the 1950s. History Previous to its incorporation in 1683, Stow was called Pompositticut Plantation. Stow was officially incorporated in 1683. The earliest Colonial settlers, , were Matthew Boon and John Kettell, who settled the land of Tantamous (Jethro), a Native American, whose land was called "Pompocitticut." Boon settled by a pond (later bearing his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Kettell
John Kettell (c.1639-c.1676 or 1685 or c.1690) (also known as John Kettle) was an early settler, cooper, and explorer in what is Maynard, Massachusetts and Stow, Massachusetts. Kettell's family was taken captive by Native Americans in King Philips War in 1676. Biography John Kettell was born in Charlestown, Massachusetts to Richard Kettle, a cooper, and Esther (Ward) and was baptized there in December 1639. Kettell had several siblings including Nathaniel, Joseph, Jonathan, Samuel, and Hannah. Kettell was likely a cooper. Kettell first married Sarah Goodnow, the daughter of Edmund Goodnow of Sudbury, Massachusetts, and they had three children, John, Sarah, and Joseph. After Sarah's death, John married Elizabeth Ward of Ipswich and had more children, including Jonathan, possibly James, and another daughter. Around 1660 Kettell and Matthew Boon settled in what later became Stow and Maynard as the first settlers in that area. Kettle likely lived "in the vicinity of Pompassiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxborough, Massachusetts
Boxborough is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 5,506 at the 2020 census. The town name is often simplified to "Boxboro" on highway signs and official documents. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , of which is land and , or 0.48%, is water. Boxborough is bordered by Littleton to the north, Acton to the east, Stow to the south, and Harvard to the west. Prior to incorporation in 1783, the area that is now Boxborough was part of Stow, Harvard, and Littleton. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 4,868 people, 1,853 households, and 1,271 families residing in the town. The population density was . There were 1,906 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the town was 88.82% White, 0.33% African American, 0.02% Native American, 8.48% Asian, 0.37% from other races, and 1.97% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.13% of the pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Year's Day
New Year's Day is a festival observed in most of the world on 1 January, the first day of the year in the modern Gregorian calendar. 1 January is also New Year's Day on the Julian calendar, but this is not the same day as the Gregorian one. Whilst most solar calendars (like the Gregorian and Julian) begin the year regularly at or near the northern winter solstice, cultures that observe a lunisolar or lunar calendar celebrate their New Year (such as the Chinese New Year and the Islamic New Year) at less fixed points relative to the solar year. In pre-Christian Rome under the Julian calendar, the day was dedicated to Janus, god of gateways and beginnings, for whom January is also named. From Roman times until the middle of the 18th century, the new year was celebrated at various stages and in various parts of Christian Europe on 25 December, on 1 March, on 25 March and on the movable feast of Easter. In the present day, with most countries now using the Gregorian calendar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butternut Squash
Butternut squash (''Cucurbita moschata''), known in Australia and New Zealand as butternut pumpkin or gramma, is a type of winter squash that grows on a vine. It has a sweet, nutty taste similar to that of a pumpkin. It has tan-yellow skin and orange fleshy pulp with a compartment of seeds in the blossom end. When ripe, it turns increasingly deep orange, and becomes sweeter and richer. It is a good source of fiber, vitamin C, magnesium, and potassium; and it is a source of vitamin A. Although botanically a fruit (specifically, a berry), butternut squash is used culinarily as a vegetable that can be roasted, sautéed, toasted, puréed for soups such as squash soup, or mashed to be used in casseroles, breads, muffins, and pies. It is part of the same squash family as ponca, waltham, pumpkin, and calabaza. History The word ''squash'' comes from the Narragansett word ''askutasquash'', meaning "eaten raw or uncooked",Victor E. Boswell and Else Bostelmann. "Our Vegetable Travele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assabet River National Wildlife Refuge
The Assabet River National Wildlife Refuge (ARNWR; formerly referred to as the U.S. Army's Fort Devens-Sudbury Training Annex) is a protected National Wildlife Refuge located approximately west of Boston and west of the Eastern Massachusetts National Wildlife Refuge Complex Headquarters, along the Assabet River. It is located in portions of the towns of Hudson, Maynard, Stow and Sudbury. The Assabet River National Wildlife Refuge consists of two separate pieces of land. The larger northern section is just north of Hudson Road, extending north to the Assabet River. The southern section is located to the south of Hudson Road. There is a visitor center located in the northern section on Winterberry Way. Wildlife and habitat The refuge contains a diverse mixture of pine and hardwood forest, old fields, and wetland habitats, including vernal pools. The refuge is an "important feeding and breeding areas for migratory birds and other wildlife." The rare Blanding's turtle species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
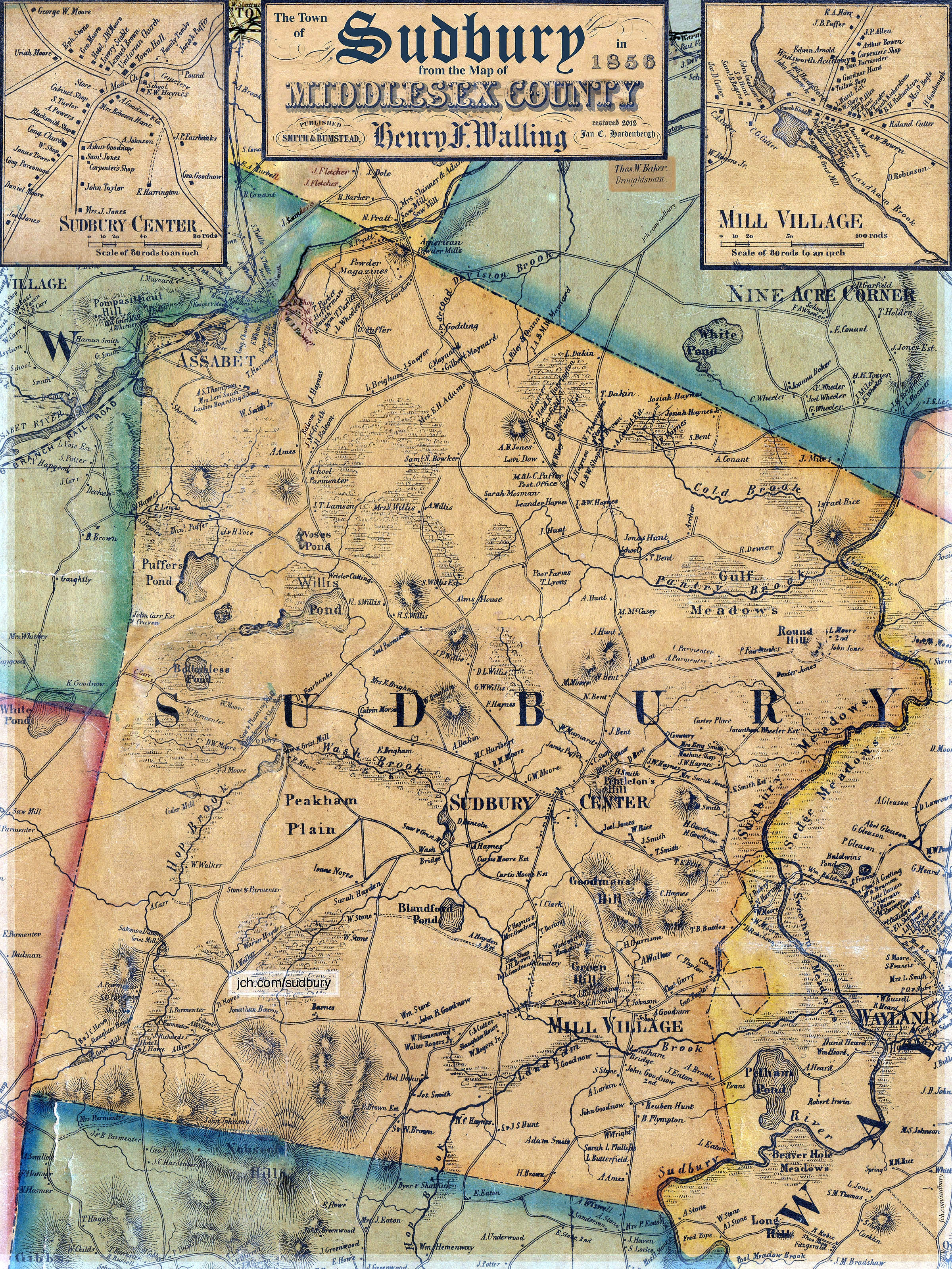
Sudbury, Massachusetts
Sudbury is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. At the 2020 census, it had a population of 18,934. The town, located in Greater Boston's MetroWest region, has a rich colonial history. History Incorporated in 1639, the boundaries of Sudbury included (by 1653) what is now Wayland (which split off in 1780, initially as East Sudbury), and parts of present day Framingham, Marlborough, Stow and Maynard (the latter town splitting off in 1871). Nipmuc Indians lived in what is now Sudbury, including Tantamous, a medicine man, and his son Peter Jethro, who deeded a large parcel of land to Sudbury for settlement in 1684.Gutteridge, William H. (1921)''A Brief History of the Town of Maynard, Massachusetts'' Maynard, MA: Town of Maynard, p. 13-16 The original town center and meetinghouse were located near the Sudbury River at what is now known as Wayland's North Cemetery. For the residents on the west side of the river, it was a treacherous passage in the winter and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maynard, Massachusetts
Maynard is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The town is located 22 miles west of Boston, in the MetroWest and Greater Boston region of Massachusetts and borders Acton, Concord, Stow and Sudbury. The town's population was 10,746 as of the 2020 United States Census. Maynard is located on the Assabet River, a tributary of the Concord River. A large part of the Assabet River National Wildlife Refuge is located within the town, and the Assabet River Rail Trail connects the Refuge and downtown Maynard to the South Acton commuter rail station. Historic downtown Maynard is home to many shops, restaurants, galleries, a movie theater, and the former Assabet Woolen Mill, which produced wool fabrics from 1846 to 1950, including cloth for Union Army uniforms during the Civil War. Maynard was the headquarters for Digital Equipment Corporation from 1957 to 1998. Owners of the former mill complex currently lease space to office and light-industry businesses. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
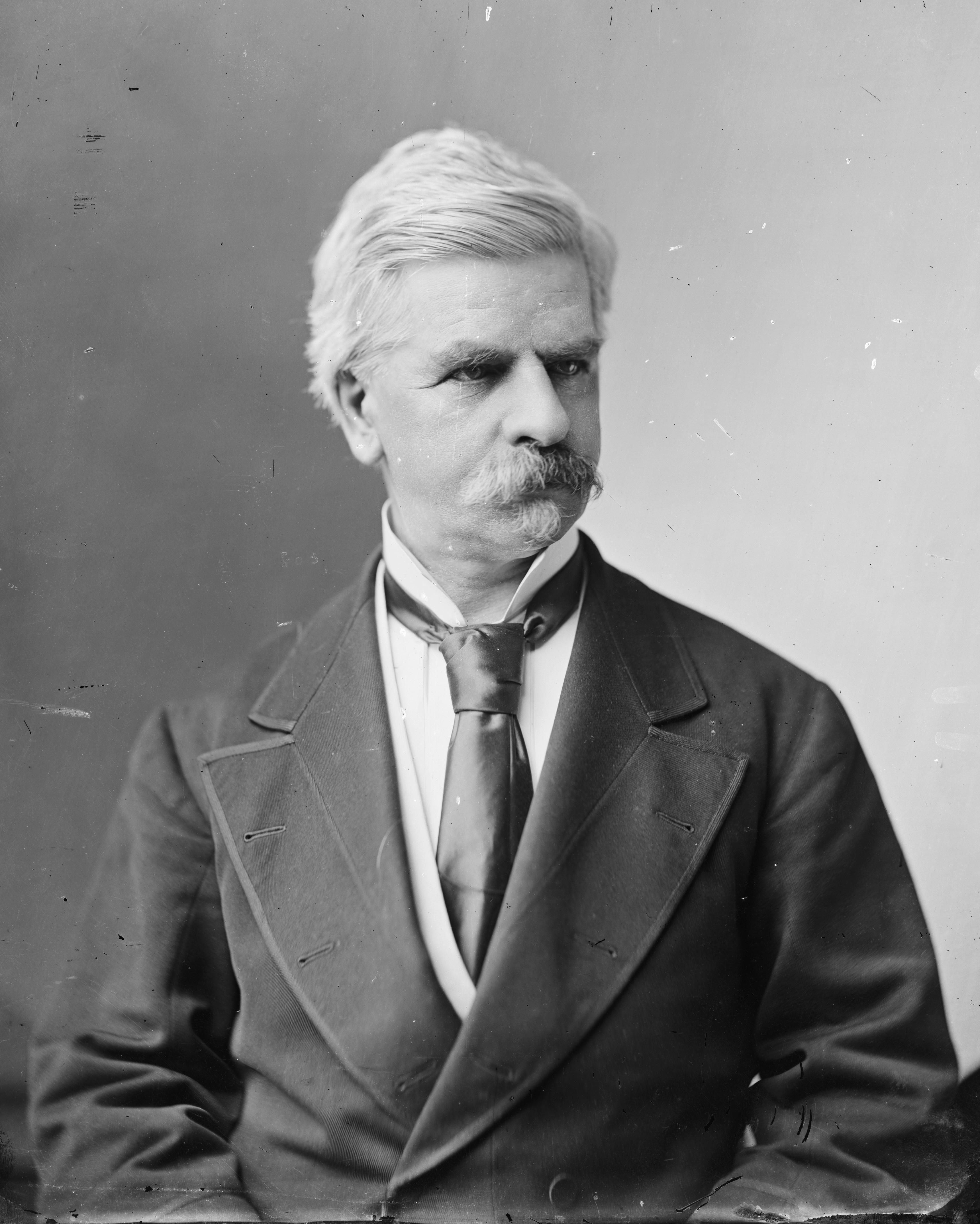
Henry Gardner
Henry Joseph Gardner (June 14, 1819 – July 21, 1892) was the List of Governors of Massachusetts, 23rd Governor of Massachusetts, serving from 1855 to 1858. Gardner, a Know Nothing, was elected governor as part of the sweeping victory of Know Nothing candidates in the Massachusetts elections of 1854. Born in Dorchester, Massachusetts, Dorchester, Gardner was a dry goods merchant from Boston active in the local United States Whig Party, Whig Party in the early 1850s. With the sudden and secretive rise of the Nativism (politics)#Nativism in the United States, nativist Know Nothings in 1854, Gardner opportunistically repudiated previously-held positions, and joined the movement, winning a landslide victory over Whig Emory Washburn. During his three terms in office the Know Nothing legislatures enacted legislation on a wide-ranging reform agenda, and made several significant changes to the Constitution of Massachusetts, state constitution, including important electoral refo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), gaining independence from the British Crown and establishing the United States of America as the first nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of liberal democracy. American colonists objected to being taxed by the Parliament of Great Britain, a body in which they had no direct representation. Before the 1760s, Britain's American colonies had enjoyed a high level of autonomy in their internal affairs, which were locally governed by colonial legislatures. During the 1760s, however, the British Parliament passed a number of acts that were intended to bring the American colonies under more direct rule from the British metropole and increasingly intertwine the economies of the colonies with those of Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Provincial Congress
The Massachusetts Provincial Congress (1774–1780) was a provisional government created in the Province of Massachusetts Bay early in the American Revolution. Based on the terms of the colonial charter, it exercised ''de facto'' control over the rebellious portions of the province, and after the British withdrawal from Boston in March 1776, the entire province. When Massachusetts Bay declared its independence in 1776, the Congress continued to govern under this arrangement for several years. Increasing calls for constitutional change led to a failed proposal for a constitution produced by the Congress in 1778, and then a successful constitutional convention that produced a constitution for the state in 1780. The Provincial Congress came to an end with elections in October 1780. Termination of the provincial assembly On May 20, 1774, the Parliament of Great Britain passed the Massachusetts Government Act in an attempt to better assert its authority in the often troublesome col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receiver General
A receiver general (or receiver-general) is an officer responsible for accepting payments on behalf of a government, and for making payments to a government on behalf of other parties. See also * Treasurer * Receiver General for Canada * Receiver General of Cornwall * Receiver-General of the Duchy of Lancaster * Receiver General of the Isle of Man * Receiver General of Jamaica The Receiver General of Jamaica was the public official in Jamaica responsible for receiving and disbursing money of the Government of Jamaica. The receiver was able to appoint a number of deputies to work on his behalf. List of Receivers General ... {{Job-stub Government occupations Political office-holders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |