|
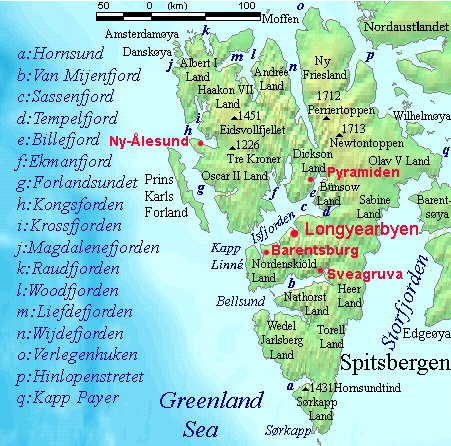
Storfjorden, Svalbard
Storfjorden (English: ''Great Fjord'') is the body of water separating Spitsbergen in the west from Barentsøya and Edgeøya to the east. Its southern limits are Kikutodden in Sørkapp Land east to Håøya, Tiholmane, Brækmoholmane, and Menkeøyane in Thousand Islands and northeast to Negerpynten—the southeastern promontory of Edgeøya. Its limits on its eastern side are Sundneset on the northern side of Freemansundet south to Palibinramten on the northwest coast of Edgeøya. The northern part is called Ginevra Bay, which lies between Olav V Land and Barentsøya. It ends at Heleysundet Heleysundet ( en, Heley Sound) is a narrow sound between Kükenthaløya and Spitsbergen. It is known for its violent tidal races. Heleysundet was discovered (and named) by the 60-ton ship ''John Ellis'' in 1617, which had been sent out by the Mu .... Storfjorden was historically known as ''Wybe Jans Water'', named after the Frisian whaler Wybe Jansz van Stavoren. The fjord was first l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginevrabotnen
Ginevra Bay ( no, Ginevrabotnen) is the inner part of Storfjorden, Svalbard, between Barentsøya and Spitsbergen Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norw .... It is named after James Lamont's vessel ''Ginevra''. References Fjords of Svalbard Barentsøya Landforms of Spitsbergen {{svalbard-fjord-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negerpynten
Negerpynten (Negro Point) is a headland at Edgeøya, Svalbard. It is the southernmost point of Edgeøya, and has a length of about two kilometers. The rock consists of dark shales, and reaches 326 m.a.s.l. The bay Tjuvfjorden is located between Negerpynten and Kvalpynten Kvalpynten (Whale Point) is a headland at Edgeøya, Svalbard Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coa ... further northwest. To the east is the strait Halvmånesundet. References Headlands of Svalbard Edgeøya {{svalbard-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fjords Of Svalbard
In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Germany, Greenland, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Ireland, Kamchatka, the Kerguelen Islands, Labrador, Newfoundland, New Zealand, Norway, Novaya Zemlya, Nunavut, Quebec, the Patagonia region of Argentina and Chile, Russia, South Georgia Island, Tasmania, United Kingdom, and Washington state. Norway's coastline is estimated to be long with its nearly 1,200 fjords, but only long excluding the fjords. Formation A true fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by ice segregation and abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. According to the standard model, glaciers formed in pre-glacial valleys with a gently sloping valley floor. The work of the glacier then left an overdeepened U-shaped valley that ends abruptly at a valley or trough end. Such valleys are fjords when floo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heleysundet
Heleysundet ( en, Heley Sound) is a narrow sound between Kükenthaløya and Spitsbergen. It is known for its violent tidal races. Heleysundet was discovered (and named) by the 60-ton ship ''John Ellis'' in 1617, which had been sent out by the Muscovy Company to explore to the south-eastwards of Spitsbergen. The sound was named after the Englishman William Heley (born 1594/95), a supercargo and vice-admiral of the English whaling Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution. It was practiced as an organized industr ... fleet from 1617 to 1623. References *Conway, W. M. 1906. No Man's Land: A History of Spitsbergen from Its Discovery in 1596 to the Beginning of the Scientific Exploration of the Country. Cambridge: At the University Press. * Johansen, B. J. (ed.) 2009.Søraust-Svalbard's geology and landscape In: ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olav V Land
Olav V Land is a peninsula in eastern Spitsbergen Island, Svalbard named after Olav V of Norway. It is covered by the Olav V Icefield, measuring about .''Glacier Atlas of Svalbard and Jan Mayen''. 1993. Oslo: Norsk polarinstitutt, p. 32. The only larger ice cap in the Svalbard Archipelago is Austfonna in Nordaustlandet Nordaustlandet (sometimes translated as North East Land) is the second-largest island in the archipelago of Svalbard, Norway, with an area of . It lies north east of Spitsbergen, separated by Hinlopen Strait. Much of Nordaustlandet lies under la ..., with an area of . References * http://www.ssb.no/aarbok/kart/i.html Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginevra Bay
Ginevra Bay ( no, Ginevrabotnen) is the inner part of Storfjorden, Svalbard, between Barentsøya and Spitsbergen Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norw .... It is named after James Lamont's vessel ''Ginevra''. References Fjords of Svalbard Barentsøya Landforms of Spitsbergen {{svalbard-fjord-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemansundet
Freemansundet is the sound separating Barentsøya, to the north, from Edgeøya, in the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. Background The straight is named after Alderman Ralph Freeman, who was involved in the English whaling trade in the early 17th century. The polar bear, ''Ursus maritimus'', is a seasonal visitor to the Freemansundet; this species has a genetically distinct deme within the Barents Sea The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territo ... region. Gallery Image:Freeman_strait_2.jpg, Freeman strait Image:Freeman_strait_1.jpg, Freeman strait References External links *Norwegian Polar InstitutPlace names in Norwegian polar areas Straits of Svalbard Edgeøya Barentsøya {{svalbard-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
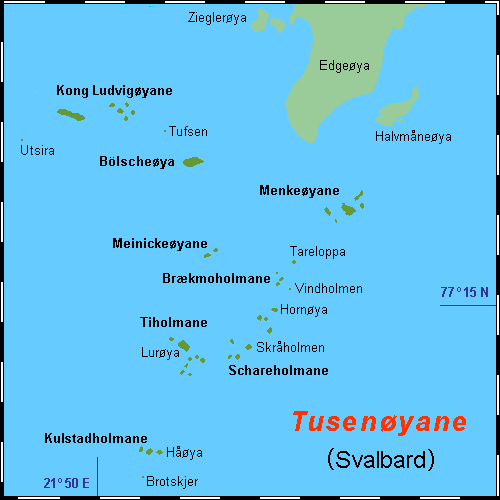
Thousand Islands (Svalbard)
Thousand IslandsDodd, G. J., G. P. Benson, & D. T. Watts. 1996. ''Arctic Pilot'', vol. 2. Taunton, UK: Hydrographer of the Navy, p. 225. ( no, Tusenøyane) is a group of small islands south of Edgeøya. They form part of the Svalbard archipelago. The group consists of over forty islands and islets, including Brotskjer, Kulstadholmane, Utsira, Tufsen, Kong Ludvigøyane, Bölscheøya, Hornøya, Tiholmane, Meinickeøyane, Sletteøya, Schareholmane, Skråholmen, Brækmoholmane, Tareloppa, Vindholmen, and Menkeøyane. History The Dutchman Joris Carolus was the first to distinctly mark a group of small islands south of Edgeøya. The Muscovy Company's map (1625) showed a vague mass of islands as well, some labeled, such as ''Wester I.'', ''Beare Iland'', ''Heling I.'', and the ''Hopeless Iles.'' (perhaps Kong Ludvigøyane). The cartographers Gerard Valck and Peter Schenk the Elder were the first to place a "great vague mass of islands stretching round the coast" south of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)