|
Stonea Camp
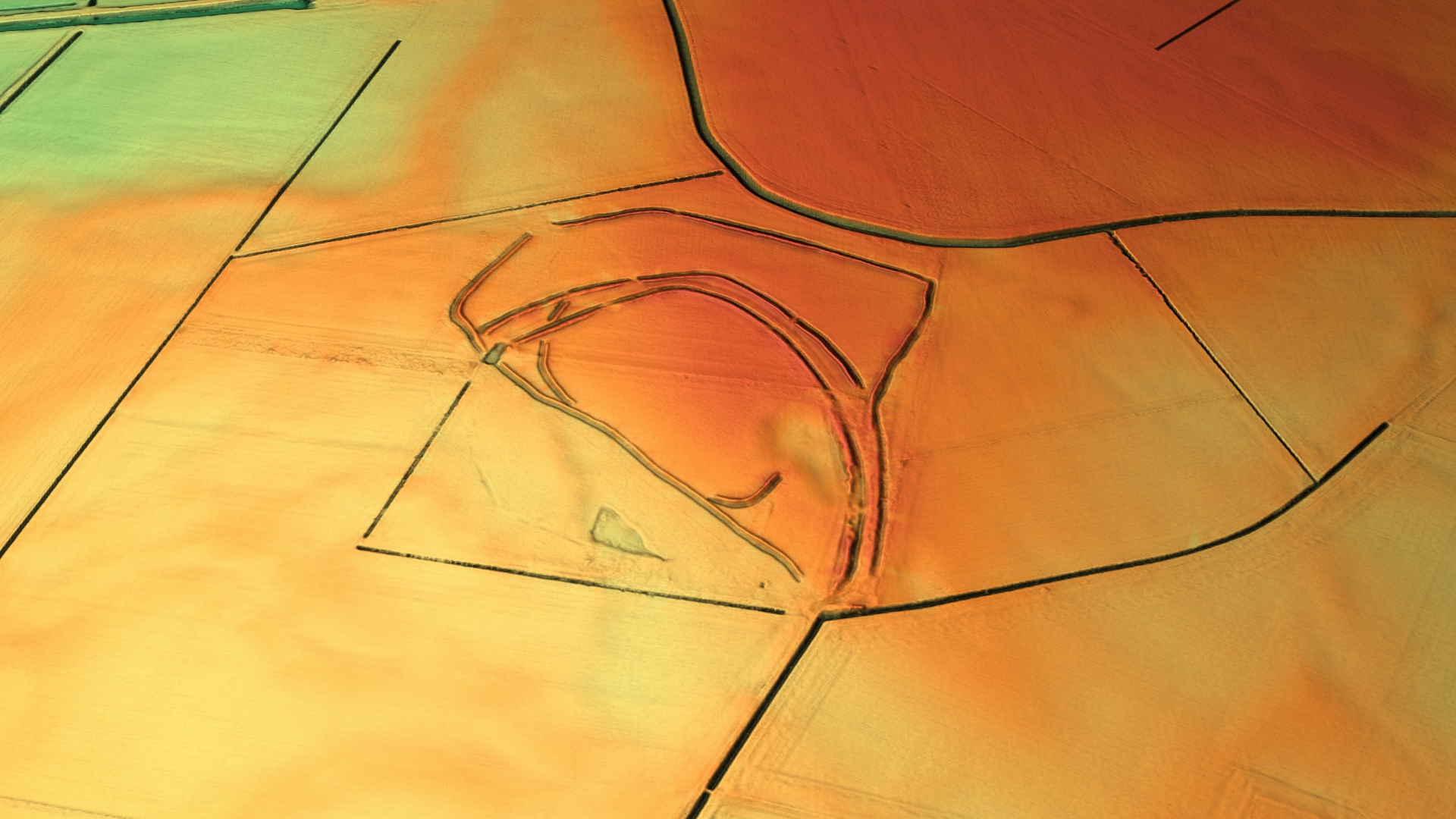
Stonea Camp is an Iron Age multivallate hill fort located at Stonea near March in the Cambridgeshire Fens. Situated on a gravel bank just above sea-level, it is the lowest hill fort in Britain. Around 500 BC, when fortification is thought to have begun at this site, this "hill" would have provided a significant area of habitable land amidst the flooded marshes of the fens. The site exhibits at least two phases of development over several hundred years of settlement, with a D-shaped set of earth banks surrounded by a larger, more formal set of banks and ditches. Roman control The fort is a possible site of the battle of 47 AD mentioned by Tacitus, between the Iceni tribe and a Roman auxiliary force under governor Ostorius Scapula. It has also been speculated that the remains relate to the campaign to subdue the Iceni after the Boudiccan Revolt. Human remains have been found around the site including sword-marked adult bones and the cleaved skull of a child, indicating that the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stonea Camp Digital Terrain Model
Stonea is a Hamlet (place)#United Kingdom, hamlet in Cambridgeshire, England, south east of March, Cambridgeshire, March and part of the parish of Wimblington.Wimblington at Genuki.org.uk, accessed 20 September 2013 Stonea today consists of a scattered collection of farmsteads and houses, the majority sited along Sixteen Foot Bank, a man-made river which forms part of the Middle Level Navigations. The largest settlement is on the bank near the Golden Lion pub. A former Primitive Methodist chapel is now a private residence. This part of Stonea is dissected by a staffed railway crossing on the Ely to Peterborough Line; Stonea railway station closed in 1966. The underpass neighbouring the bridge (which provides a diversion avoiding the level crossing) is said to be the "most bashed rail bridge in Britain", with 33 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia ( Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
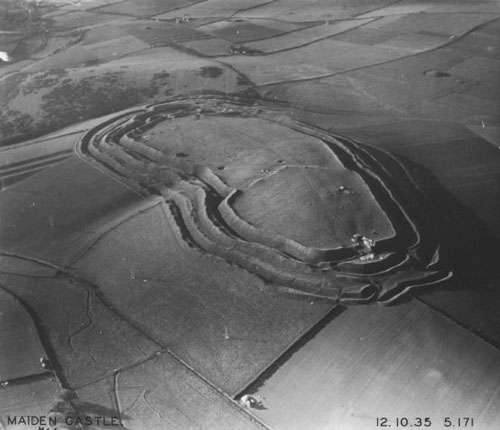
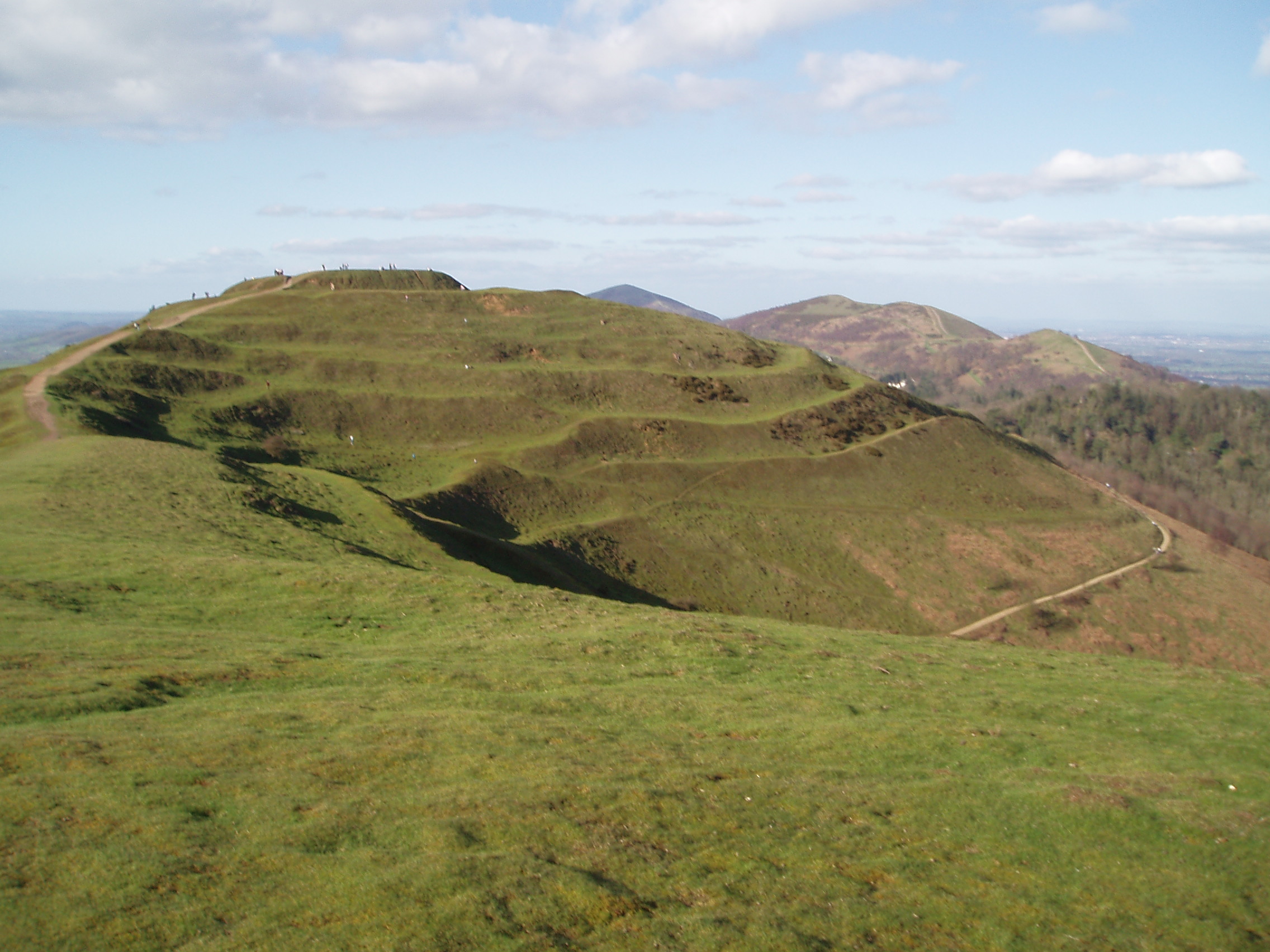
Hill Fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post- Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of earthworks, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. Hillforts developed in the Late Bronze and Early Iron Age, roughly the start of the first millennium BC, and were used in many Celtic areas of central and western Europe until the Roman conquest. Nomenclature The spellings "hill fort", "hill-fort" and "hillfort" are all used in the archaeological literature. The ''Monument Type Thesaurus'' published by the Forum on Information Standards in Heritage lists ''hillfort'' as the preferred term. They all refer to an elevated site with one or more ramparts made of earth, stone and/or wood, with an external dit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post- Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of earthworks, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. Hillforts developed in the Late Bronze and Early Iron Age, roughly the start of the first millennium BC, and were used in many Celtic areas of central and western Europe until the Roman conquest. Nomenclature The spellings "hill fort", "hill-fort" and "hillfort" are all used in the archaeological literature. The ''Monument Type Thesaurus'' published by the Forum on Information Standards in Heritage lists ''hillfort'' as the preferred term. They all refer to an elevated site with one or more ramparts made of earth, stone and/or wood, with an external dit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stonea
Stonea is a hamlet in Cambridgeshire, England, south east of March and part of the parish of Wimblington.Wimblington at Genuki.org.uk, accessed 20 September 2013 Stonea today consists of a scattered collection of farmsteads and houses, the majority sited along Sixteen Foot Bank, a man-made river which forms part of the . The largest settlement is on the bank near the Golden Lion pub. A former chapel is now a private residence. This part of Stonea is dissected by a staffed railway crossing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March, Cambridgeshire
March is a Fenland market town and civil parish in the Isle of Ely area of Cambridgeshire, England. It was the county town of the Isle of Ely which was a separate administrative county from 1889 to 1965. The administrative centre of Fenland District Council is located in the town. The town grew by becoming an important railway centre. Like many Fenland towns, March was once an island surrounded by marshes. It occupied the second largest "island" in the Great Level. As the land was drained, the town grew and prospered as a trading and religious centre. It was also a minor port before, in more recent times, a market town and an administrative and railway centre. March is situated on the banks of the navigable old course of the River Nene, today mainly used by pleasure boats. History March was recorded as ''Merche'' in the Domesday Book of 1086, perhaps from the Old English ''mearc'' meaning 'boundary'. Modern March lies on the course of the Fen Causeway, a Roman road, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a Counties of England, county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the west. The city of Cambridge is the county town. Following the Local Government Act 1972 restructuring, modern Cambridgeshire was formed in 1974 through the amalgamation of two administrative counties: Cambridgeshire and Isle of Ely, comprising the Historic counties of England, historic county of Cambridgeshire (including the Isle of Ely); and Huntingdon and Peterborough, comprising the historic county of Huntingdonshire and the Soke of Peterborough, historically part of Northamptonshire. Cambridgeshire contains most of the region known as Silicon Fen. The county is now divided between Cambridgeshire County Council and Peterborough City Council, which since 1998 has formed a separate Unitary authorities of England, unita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Fens
The Fens, also known as the , in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a system of drainage channels and man-made rivers (Ditch, dykes and drains) and automated pumping stations. There have been unintended consequences to this reclamation, as the land level has continued to sink and the dykes have been built higher to protect it from flooding. Fen is the local term for an individual area of marshland or former marshland. It also designates the type of marsh typical of the area, which has pH, neutral or alkaline water and relatively large quantities of dissolved minerals, but few other plant nutrition, plant nutrients. The Fens are a National Character Area, based on their landscape, biodiversity, geodiversity and economic activity. The Fens lie inland of the Wash, and are an area of nearly in Lincolnshire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars. The surviving portions of his two major works—the ''Annals'' (Latin: ''Annales'') and the ''Histories'' (Latin: ''Historiae'')—examine the reigns of the emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). These two works span the history of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the death of Domitian (96 AD), although there are substantial lacunae in the surviving texts. Tacitus's other writings discuss oratory (in dialogue format, see '' Dialogus de oratoribus''), Germania (in ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Agricola (the general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain), mainly focusing on his campaign in Britannia ('' De vita et moribus Iulii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceni Tribe
The Iceni ( , ) or Eceni were a Brittonic tribe of eastern Britain during the Iron Age and early Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the west, and the Catuvellauni and Trinovantes to the south. In the Roman period, their capital was Venta Icenorum at modern-day Caistor St Edmund. Julius Caesar does not mention the Iceni in his account of his invasions of Britain in 55 and 54 BC, though they may be related to the Cenimagni, whom Caesar notes as living north of the River Thames at that time. The Iceni were a significant power in eastern Britain during Claudius' conquest of Britain in AD 43, in which they allied with Rome. Increasing Roman influence on their affairs led to revolt in AD 47, though they remained nominally independent under king Prasutagus until his death around AD 60. Roman encroachment after Prasutagus' death led his wife Boudica to launch a major revolt f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostorius Scapula
Publius Ostorius Scapula standing at the terrace of the Roman Baths (Bath) Publius Ostorius Scapula (died 52) was a Roman statesman and general who governed Britain from 47 until his death, and was responsible for the defeat and capture of Caratacus. Career Publius Ostorius Scapula was probably the son of Quintus Ostorius Scapula, the first joint commander of the Praetorian Guard appointed by Augustus and later prefect of Egypt. Nothing is known of his early career. He was suffect consul, probably in 46. In the winter of 47 he was appointed the second governor of Roman Britain by the emperor Claudius, succeeding Aulus Plautius. The south and east of the island was securely occupied and alliances had been made with tribes outside the Roman-controlled area, but other tribes continued to resist. Believing a new governor would be reluctant to campaign so late in the year, they staged attacks and uprisings. Ostorius disabused them of this notion and responded vigorously, attacking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. The British Museum was the first public national museum to cover all fields of knowledge. The museum was established in 1753, largely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |