|
Stochastic Chains With Memory Of Variable Length
Stochastic chains with memory of variable length are a family of stochastic chains of finite order in a finite alphabet, such as, for every time pass, only one finite suffix of the past, called context, is necessary to predict the next symbol. These models were introduced in the information theory literature by Jorma Rissanen in 1983, as a universal tool to data compression, but recently have been used to model data in different areas such as biology, linguistics and music. Definition A stochastic chain with memory of variable length is a stochastic chain (X_n)_, taking values in a finite alphabet A, and characterized by a probabilistic context tree (\tau,p), so that *\tau is the group of all contexts. A context X_,\ldots,X_, being l the size of the context, is a finite portion of the past X_,\ldots,X_, which is relevant to predict the next symbol X_; *p is a family of transition probabilities associated with each context. History The class of stochastic chains with memory of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables. Stochastic processes are widely used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appear to vary in a random manner. Examples include the growth of a bacterial population, an electrical current fluctuating due to thermal noise, or the movement of a gas molecule. Stochastic processes have applications in many disciplines such as biology, chemistry, ecology, neuroscience, physics, image processing, signal processing, control theory, information theory, computer science, cryptography and telecommunications. Furthermore, seemingly random changes in financial markets have motivated the extensive use of stochastic processes in finance. Applications and the study of phenomena have in turn inspired the proposal of new stochastic processes. Examples of such stochastic processes include the Wiener process or Brownian motion process, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
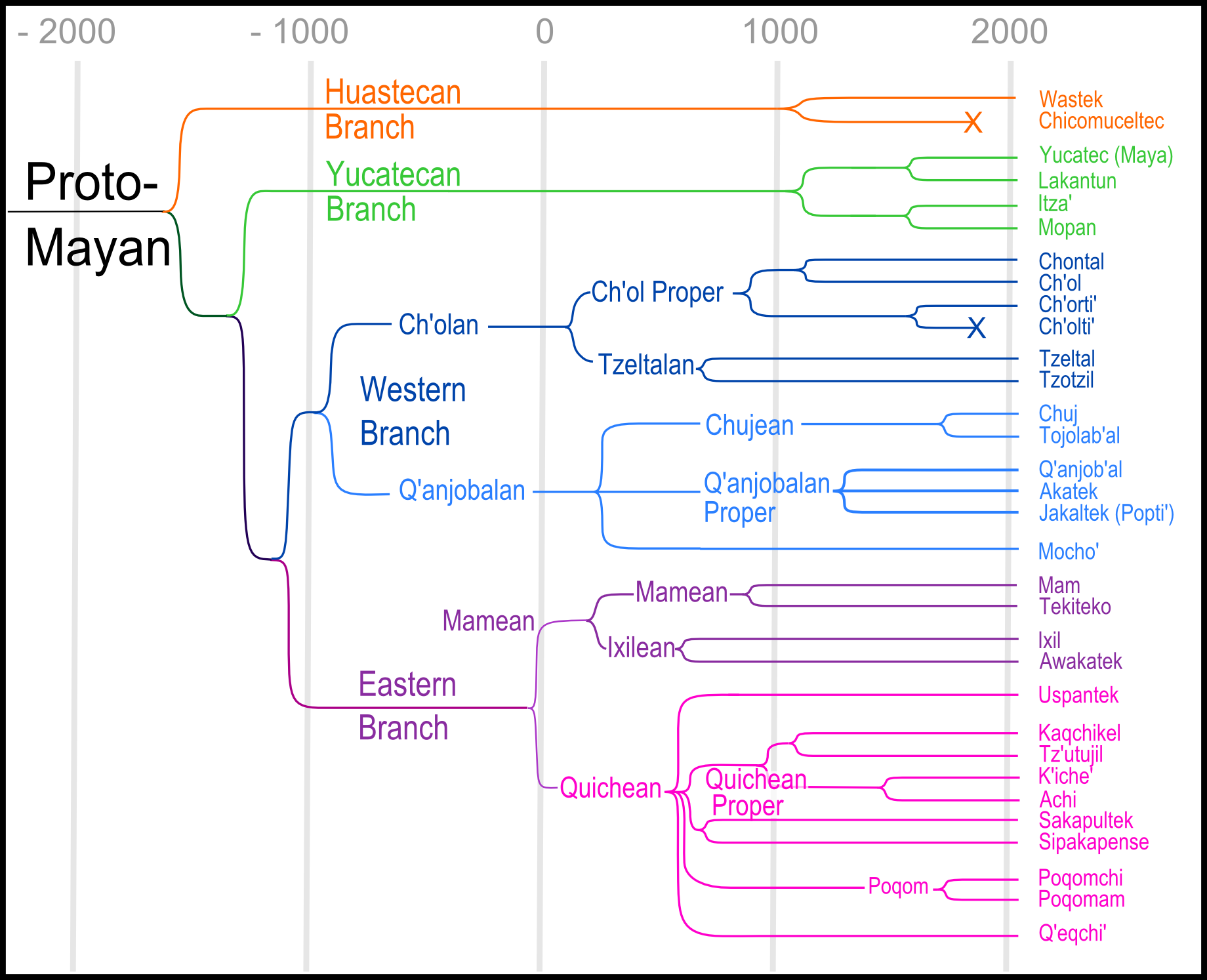
Tree Model
In historical linguistics, the tree model (also Stammbaum, genetic, or cladistic model) is a model of the evolution of languages analogous to the concept of a family tree, particularly a phylogenetic tree in the biological evolution of species. As with species, each language is assumed to have evolved from a single parent or "mother" language, with languages that share a common ancestor belonging to the same language family. Popularized by the German linguist August Schleicher in 1853, François (2014). the tree model has always been a common method of describing genetic relationships between languages since the first attempts to do so. It is central to the field of comparative linguistics, which involves using evidence from known languages and observed rules of language feature evolution to identify and describe the hypothetical proto-languages ancestral to each language family, such as Proto-Indo-European and the Indo-European languages. However, this is largely a theoretic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable-order Markov Model
In the mathematical theory of stochastic processes, variable-order Markov (VOM) models are an important class of models that extend the well known Markov chain models. In contrast to the Markov chain models, where each random variable in a sequence with a Markov property depends on a fixed number of random variables, in VOM models this number of conditioning random variables may vary based on the specific observed realization. This realization sequence is often called the ''context''; therefore the VOM models are also called ''context trees''. VOM models are nicely rendered by colorized probabilistic suffix trees (PST). The flexibility in the number of conditioning random variables turns out to be of real advantage for many applications, such as statistical analysis, classification and prediction. Example Consider for example a sequence of random variables, each of which takes a value from the ternary alphabet . Specifically, consider the string ' constructed from infinite concate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Random Variables
Independent or Independents may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups * Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s * Independents (Oporto artist group), a Portuguese artist group historically linked to abstract art and to Fernando Lanhas, the central figure of Portuguese abstractionism Music Groups, labels, and genres * Independent music, a number of genres associated with independent labels * Independent record label, a record label not associated with a major label * Independent Albums, American albums chart Albums * ''Independent'' (Ai album), 2012 * ''Independent'' (Faze album), 2006 * ''Independent'' (Sacred Reich album), 1993 Songs * "Independent" (song), a 2007 song by Webbie * "Independent", a 2002 song by Ayumi Hamasaki from '' H'' News and media organizations * ''The Independent'', a British online newspaper. * ''The Malta Independent'', a Mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Matrix
In mathematics, a stochastic matrix is a square matrix used to describe the transitions of a Markov chain. Each of its entries is a nonnegative real number representing a probability. It is also called a probability matrix, transition matrix, substitution matrix, or Markov matrix. The stochastic matrix was first developed by Andrey Markov at the beginning of the 20th century, and has found use throughout a wide variety of scientific fields, including probability theory, statistics, mathematical finance and linear algebra, as well as computer science and population genetics. There are several different definitions and types of stochastic matrices: :A right stochastic matrix is a real square matrix, with each row summing to 1. :A left stochastic matrix is a real square matrix, with each column summing to 1. :A doubly stochastic matrix is a square matrix of nonnegative real numbers with each row and column summing to 1. In the same vein, one may define a stochastic vector (also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Space
A state space is the set of all possible configurations of a system. It is a useful abstraction for reasoning about the behavior of a given system and is widely used in the fields of artificial intelligence and game theory. For instance, the toy problem Vacuum World has a discrete finite state space in which there are a limited set of configurations that the vacuum and dirt can be in. A "counter" system, where states are the natural numbers starting at 1 and are incremented over time has an infinite discrete state space. The angular position of an undamped pendulum is a continuous (and therefore infinite) state space. Definition In the theory of dynamical systems, the state space of a discrete system defined by a function ''ƒ'' can be modeled as a directed graph where each possible state of the dynamical system is represented by a vertex with a directed edge from ''a'' to ''b'' if and only if ''ƒ''(''a'') = ''b''. This is known as a state diagram. For a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical System
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, fluid dynamics, the flow of water in a pipe, the Brownian motion, random motion of particles in the air, and population dynamics, the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real number, real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a Set (mathematics), set, without the need of a Differentiability, smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Galves
Jefferson Antonio Galves, known simply as Antonio Galves, is a Brazilian mathematician, professor of the Institute of Mathematics and Statistics of the University of São Paulo and member of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences. His field of studies is related to statistician issues models, in particular models that have stochasticity and variable range of memory. In 2007 he won the National Order of Scientific Merit. Professor Galves is also the leader of NeuroMat, a research center established in 2013 at the University of São Paulo that is dedicated to integrating mathematical modeling and theoretical neuroscience Computational neuroscience (also known as theoretical neuroscience or mathematical neuroscience) is a branch of neuroscience which employs mathematical models, computer simulations, theoretical analysis and abstractions of the brain to u .... Galves–Löcherbach model The Galves–Löcherbach model is a model with intrinsic stochasticity for biological n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffix Tree
In computer science, a suffix tree (also called PAT tree or, in an earlier form, position tree) is a compressed trie containing all the suffixes of the given text as their keys and positions in the text as their values. Suffix trees allow particularly fast implementations of many important string operations. The construction of such a tree for the string S takes time and space linear in the length of S. Once constructed, several operations can be performed quickly, for instance locating a substring in S, locating a substring if a certain number of mistakes are allowed, locating matches for a regular expression pattern etc. Suffix trees also provide one of the first linear-time solutions for the longest common substring problem. These speedups come at a cost: storing a string's suffix tree typically requires significantly more space than storing the string itself. History The concept was first introduced by . Rather than the suffix S ..n/math>, Weiner stored in his trie the ''pref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jorma Rissanen
Jorma Johannes Rissanen (October 20, 1932 – May 9, 2020) was an information theorist, known for originating the minimum description length (MDL) principle and practical approaches to arithmetic coding for lossless data compression. His work inspired the development of the theory of stochastic chains with memory of variable length. Education and career Rissanen was born in Pielisjärvi (now Lieksa in Finland and grew up in Kemi, a border town between Finland and Sweden. He moved to Helsinki and studied at the Helsinki University of Technology, where he obtained his Master’s degree in electrical engineering in 1956 and licentiate in control theory in 1960. He studied there under Olli Lokki and Hans Blomberg. Rissanen became an IBM researcher since 1960, first in Stockholm, Sweden, while still a Ph.D. student under Hans Blomberg. Most of his PhD work was done remotely as a result and he received his Ph.D. from the Helsinki University of Technology in 1965 with a topic on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable-order Markov Model
In the mathematical theory of stochastic processes, variable-order Markov (VOM) models are an important class of models that extend the well known Markov chain models. In contrast to the Markov chain models, where each random variable in a sequence with a Markov property depends on a fixed number of random variables, in VOM models this number of conditioning random variables may vary based on the specific observed realization. This realization sequence is often called the ''context''; therefore the VOM models are also called ''context trees''. VOM models are nicely rendered by colorized probabilistic suffix trees (PST). The flexibility in the number of conditioning random variables turns out to be of real advantage for many applications, such as statistical analysis, classification and prediction. Example Consider for example a sequence of random variables, each of which takes a value from the ternary alphabet . Specifically, consider the string ' constructed from infinite concate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markov Chain
A Markov chain or Markov process is a stochastic model describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event. Informally, this may be thought of as, "What happens next depends only on the state of affairs ''now''." A countably infinite sequence, in which the chain moves state at discrete time steps, gives a discrete-time Markov chain (DTMC). A continuous-time process is called a continuous-time Markov chain (CTMC). It is named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov. Markov chains have many applications as statistical models of real-world processes, such as studying cruise control systems in motor vehicles, queues or lines of customers arriving at an airport, currency exchange rates and animal population dynamics. Markov processes are the basis for general stochastic simulation methods known as Markov chain Monte Carlo, which are used for simulating sampling from complex probability dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |