|
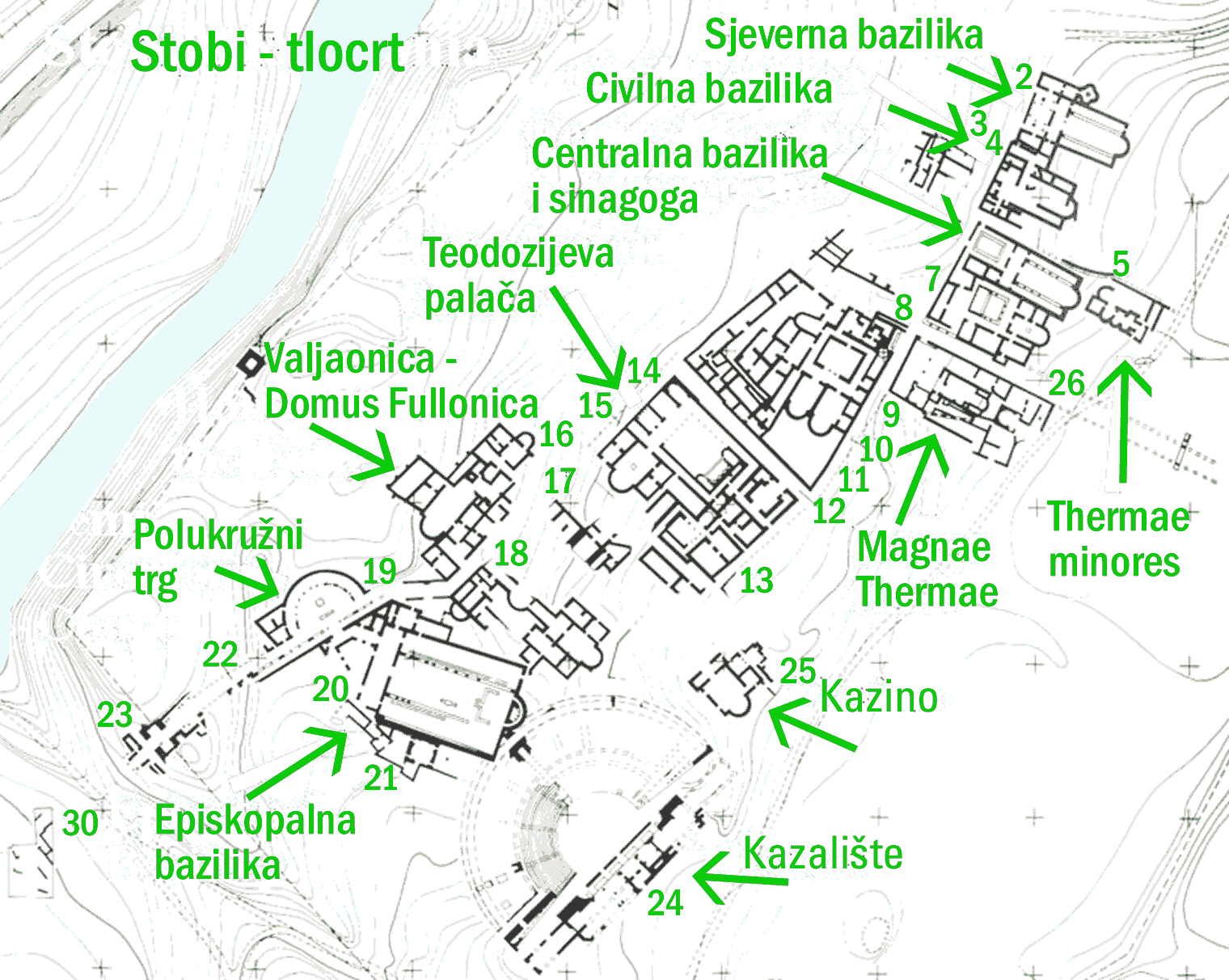
Stobi Theater
Stobi or Stoboi ( grc, Στόβοι, Stóboi; la, Stobi; mk, Стоби, Stobi), was an ancient town of Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Ancient Rome, Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia, Gradsko, North Macedonia, on the main road that leads from the Danube to the Aegean Sea and is considered by many to be the most famous archaeological site in North Macedonia. Stobi was built where the Crna River (Vardar), Erigon (Crna River) joins the Vardar, Axios (Vardar), making it strategically important as a center for both trade and warfare. The pre-Roman period Stobi developed from a Paeonian settlement established in the Archaic Greece, Archaic period. Located on the northern side of a terrace, the early town covered an area of about . Its proximity to the junction of the Erigón and Axiós Rivers as well as its position in the fertile central Vardar valley allowed it qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gradsko, North Macedonia
Gradsko ( mk, Градско, ) is a village (despite the word ''grad'' meaning "town") located in the central part of North Macedonia. It is the seat of the Gradsko municipality. It is located very close to the main motorway which links Gevgelija on North Macedonia's border with Greece. History It was the ancient Paeonian capital of Stobi.Wilkes, J. J. The Illyrians, 1992, , Page 18, "... northeastward course through an area of mountains to join the Vardar below Titov Veles near the ancient Paeonian capital of Stobi (Gradsko). Though marshy in some areas this plain - the ancient Pelagonia - has supported a large population from prehistoric ..." Demographics According to the 2002 census, the village had a total of 2,219 inhabitants. Ethnic groups in the village include:Macedonian Census (2002) ''Book 5 - Total population according to the Ethnic Affiliation, Mother Tongue and Religion'' The State Statistical Office, Skopje, 2002, p. 87. * Macedonians 1,920 *Turks 7 *Serbs 14 *Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bylazora
Bylazora or Vilazora ( grc, Βυλάζωρα) was a Paeonian city from the period of early classic antiquity. It is located near the village of Knezhje, which is part of the municipality of Sveti Nikole in North Macedonia. History Polybius tells us: In 219 BC, the Dardanians collected their forces for a raid into Macedonia and at that time Bylazora must already have been in their hands. With its location at Sveti Nikole, Bylazora commanded the entrance to a long defile and, no less important, a route southwestwards into Pelagonia via the Babuna Valley, or Raec Valley into Styberra and interior of the Macedonian Kingdom. It can be assumed that Bylazora, as the largest Paeonian town, must have been in Dardanian possession when Philip V captured it in 217 BC, with the aim of garrisoning it and ending Dardanian raids. Bylazora is also mentioned by Livy in his "The History of Rome" when Perseus in 168 BC arranged military support from the Gauls who were campaigning in Desudaba, Mae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
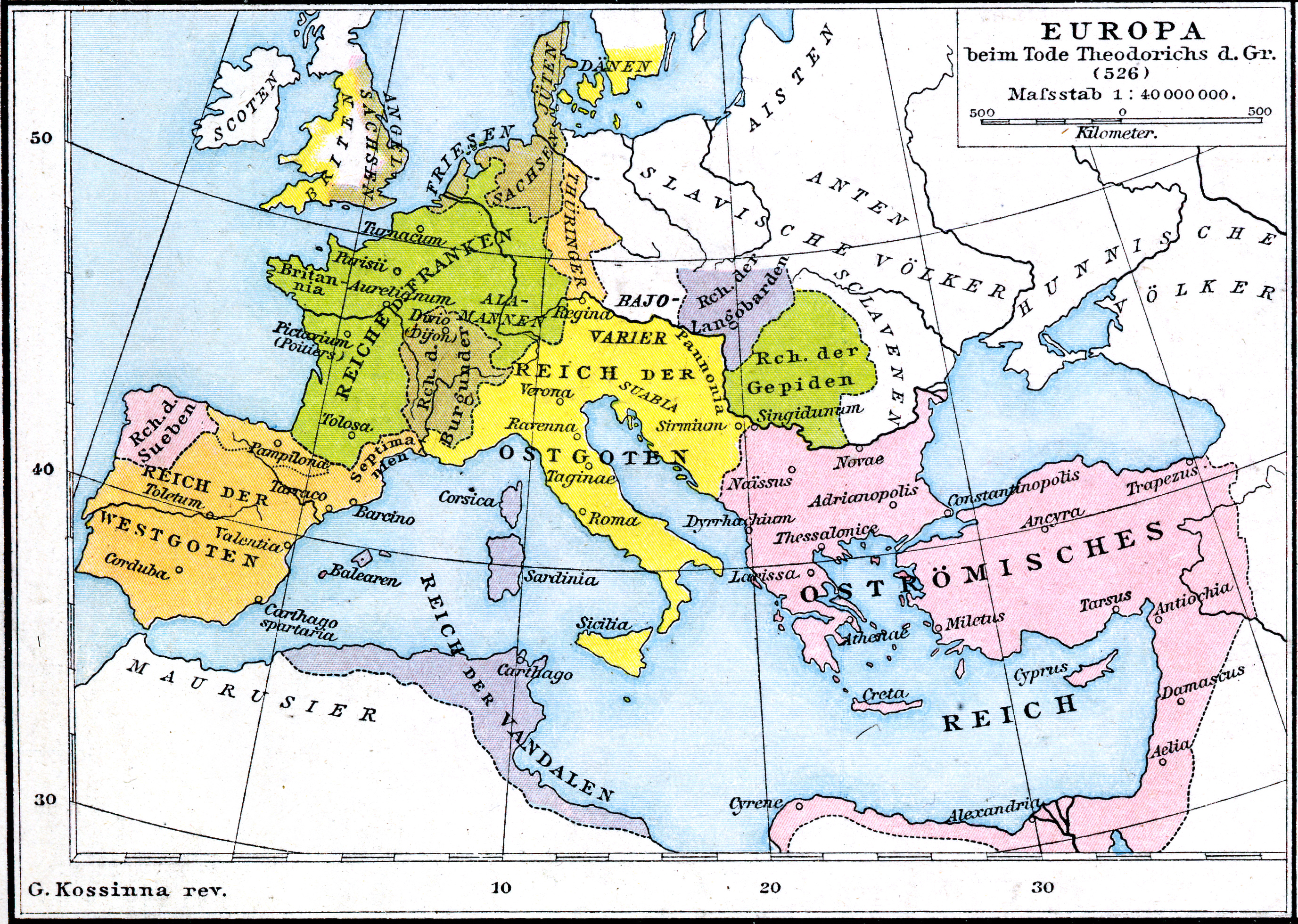
Ostrogothic
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century, having crossed the Lower Danube. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under the influence of the Amal dynasty, the family of Theodoric the Great. After the death of Attila and collapse of the Hunnic empire represented by the Battle of Nedao in 453, the Amal family began to form their kingdom in Pannonia. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths, but instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodoric to invade Italy and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two civil wars, and recognized the Catholic orthodoxy of Nicene Christians as the Roman Empire's state religion. Theodosius was the last emperor to rule the entire Roman Empire before its administration was permanently split between two separate courts (one western, the other eastern). Born in Hispania, Theodosius was the son of a high-ranking general, Theodosius the Elder, under whose guidance he rose through the ranks of the Roman Army. Theodosius held independent command in Moesia in 374, where he had some success against the invading Sarmatians. Not long afterwards, he was forced into retirement, and his father was executed under obscure circumstances. Theodosius soon regained his position following a series of intrigues and executions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ius Italicum
''Ius Italicum'' (Latin, Italian or Italic law) was a law in the early Roman Empire that allowed the emperors to grant cities outside Italy the legal fiction that they were on Italian soil. This meant that the city would be governed under Roman law rather than local law, would have a greater degree of autonomy in their relations with provincial governors, and that people born in the city automatically gained Roman citizenship. As Rome citizens, people were able to buy and sell property, were exempt from land tax, and the poll tax and were entitled to protection under Roman law. ''Ius Italicum'' was the highest liberty a municipality or province could obtain and was considered very favorable. Emperors, such as Augustus and Septimius Severus, made use of the law during their reign. Augustus' enactment of the law Emperor Augustus was one of the first Emperors to implement the law of ''Ius Italicum'' during his reign. During Emperor Augustus' reign he gave land-grants to veterans wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (pl. ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ("duty holders"), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the privileges and protections of citizenship. Every citizen was a . The distinction of was not made in the Roman Kingdom; instead, the immediate neighbours of the city were invited or compelled to transfer their populations to the urban structure of Rome, where they took up residence in neighbourhoods and became Romans ''per se''. Under the Roman Republic the practical considerations of incorporating communities into the city-state of Rome forced the Romans to devise the concept of , a distinct state under the jurisdiction of Rome. It was necessary to distinguish various types of and other settlements, such as the colony. In the early Roman Empire these distinctions began to disappear; for example, when Pliny the Elder served in the Roman army, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Principate, which is the first phase of the Roman Empire, and Augustus is considered one of the greatest leaders in human history. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult as well as an era associated with imperial peace, the ''Pax Romana'' or ''Pax Augusta''. The Roman world was largely free from large-scale conflict for more than two centuries despite continuous wars of imperial expansion on the empire's frontiers and the year-long civil war known as the "Year of the Four Emperors" over the imperial succession. Originally named Gaius Octavius, he was born into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian ''gens'' Octavia. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was named in Caesar' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonia (Roman Province)
Macedonia ( grc-gre, Μακεδονία) was a province of the Roman Empire, encompassing the territory of the former Antigonid Kingdom of Macedonia, which had been conquered by Rome in 168 BC at the conclusion of the Third Macedonian War. The province was created in 146 BC, after the Roman general Quintus Caecilius Metellus defeated Andriscus of Macedon, the last self-styled king of Macedonia in the Fourth Macedonian War. The province incorporated the former kingdom of Macedonia with the addition of Epirus, Thessaly, and parts of Illyria, Paeonia and Thrace. During the Republican period, the province was of great military significance, as the main bulwark protecting the Aegean region from attacks from the north. The Via Egnatia, which crossed the province from west to east was of great strategic importance, providing the main overland link between Rome and its domains in the Eastern Mediterranean. In this period, campaigns against the Dardani and Scordisci to the north and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus Of Macedon
Perseus ( grc-gre, Περσεύς; 212 – 166 BC) was the last king ('' Basileus'') of the Antigonid dynasty, who ruled the successor state in Macedon created upon the death of Alexander the Great. He was the last Antigonid to rule Macedon, after losing the Battle of Pydna on 22 June 168 BC; subsequently, Macedon came under Roman rule. Early life Perseus was the son of king Philip V of Macedon and a concubine, probably Polycratia of Argos. His father spent most of his reign attempting to maintain Macedonian hegemony over Greece against heavy Greek resistance and, in his later reign, against a expansionist Roman Republic. In this regard Philip V would fail as following defeat in the Second Macedonian War, he would have to accept Roman power in Greece and would later help Rome in the War against Nabis (195 BC) and Aetolian War (191-189 BC). Perseus is recorded as having commanded Macedonian troops in both the Second Macedonian War and Aetolian War. Being a son of a concubine, Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |