|
Stirling Tolbooth
Stirling Tolbooth is a municipal building in Broad Street, Stirling, Scotland. The structure, which was the original meeting place of Stirling Burgh Council, is a Category A listed building. History The first building on the site was a medieval tollbooth which was completed in 1473. After the old tolbooth became dilapidated in the late 17th century, burgh officials decided to procure a new structure: the new building was designed by Sir William Bruce in the Scottish baronial style, built by a master mason, Harry Livingstone, in ashlar stone and was completed in 1705. The design involved an asymmetrical main frontage with a hall block of three bays and a six-stage tower facing onto Broad Street; the hall block featured a door in the right hand bay and sash windows with architraves in the other bays on three floors. The six-stage tower, which slightly projected forward, essentially survived intact from the 15th century structure although it had to be refaced. It featured a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stirling
Stirling (; sco, Stirlin; gd, Sruighlea ) is a city in central Scotland, northeast of Glasgow and north-west of Edinburgh. The market town, surrounded by rich farmland, grew up connecting the royal citadel, the medieval old town with its merchants and tradesmen, the Old Bridge and the port. Located on the River Forth, Stirling is the administrative centre for the Stirling council area, and is traditionally the county town of Stirlingshire. Proverbially it is the strategically important "Gateway to the Highlands". It has been said that "Stirling, like a huge brooch clasps Highlands and Lowlands together". Similarly "he who holds Stirling, holds Scotland" is often quoted. Stirling's key position as the lowest bridging point of the River Forth before it broadens towards the Firth of Forth made it a focal point for travel north or south. When Stirling was temporarily under Anglo-Saxon sway, according to a 9th-century legend, it was attacked by Danish invaders. The sound of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radicalism (historical)
Radicalism (from French , "radical") or classical radicalism was a historical political movement representing the leftward flank of liberalism during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and a precursor to social liberalism, social democracy and modern progressivism. Its earliest beginnings were found in Great Britain with the Levellers during the English Civil War, and the later Radical Whigs. During the 19th century in the United Kingdom, continental Europe, and Latin America, the term ''radical'' came to denote a progressive liberal ideology inspired by the French Revolution. Historically, radicalism emerged in an early form with the French Revolution and the similar movements it inspired in other countries. It grew prominent during the 1830s in the United Kingdom with the Chartists and Belgium with the Revolution of 1830, then across Europe in the 1840s–1850s during the Revolutions of 1848. In contrast to the social conservatism of existing liberal politics, radica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Stirling (city)
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Chambers And Town Halls In Scotland
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Buildings Completed In 1705
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Listed Buildings In Stirling, Stirling
This is a list of listed buildings in the burgh of Stirling, Scotland. List Key Notes References * All entries, addresses and coordinates are based on data froHistoric Scotland This data falls under thOpen Government Licence {{Lists of listed buildings in Stirling (council area) Stirling Stirling (; sco, Stirlin; gd, Sruighlea ) is a city in central Scotland, northeast of Glasgow and north-west of Edinburgh. The market town, surrounded by rich farmland, grew up connecting the royal citadel, the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Category A Listed Buildings In Stirling
This is a list of Category A listed buildings in the Stirling council area in central Scotland. In Scotland, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of "special architectural or historic interest". Category A structures are those considered to be "buildings of national or international importance, either architectural or historic, or fine little-altered examples of some particular period, style or building type." Listing was begun by a provision in the Town and Country Planning (Scotland) Act 1947, and the current legislative basis for listing is the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) (Scotland) Act 1997. The authority for listing rests with Historic Scotland, an executive agency of the Scottish Government, which inherited this role from the Scottish Development Department in 1991. Once listed, severe restrictions are imposed on the modifications allowed to a building's structure or its fittings. Listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Murphy (architect)
Richard Murphy OBE (born 24 April 1955) is a British architect and businessman. He is the founder and principal architect of Richard Murphy Architects, an architectural firm operating in Edinburgh. He is a winner of the 2016 RIBA House of the year. Life Richard Murphy completed his studies at Newcastle University and Edinburgh University.Art Daily 31 July 201Press Release: Royal Scottish Academy of Art & Architecture celebrates 21 years of Richard Murphy Architects/ref> In 1991 he formed an Edinburgh architectural firm, Richard Murphy Architects, and it has since grown to over twenty architects. In the early years, his firm focused on designing extensions to houses and mews conversions however have subsequently diversified onto education, healthcare, the arts and commercial work. They have worked on several UK National Lottery-funded buildings. In 1995 Murphy designed the first of the UK's Maggie's Centres, in Edinburgh, which now acts as the administrative headquarters for Magg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipal Buildings, Stirling
The Municipal Buildings are based in Corn Exchange Road, Stirling, Scotland. The structure, which was the meeting place of Stirling Burgh Council, is a Category B listed building. History The first municipal building in the city was the Stirling Tolbooth in Broad Street which was completed in 1705. Burgh leaders then relocated to The Athenaeum in King Street in 1875. In the late 19th century, civic leaders decided to erect a more substantial municipal complex to address the growing needs of the city: the site they selected was occupied by a long narrow building, the old corn exchange. The old corn exchange had been the venue for the weekly grain markets in the 19th century but had also been used for public meetings and theatre performances. A statue of the former Prime Minister and local member of parliament, Sir Henry Campbell-Bannerman, designed by Paul Raphael Montford was unveiled to the southwest of the proposed complex by the then Prime Minister, H. H. Asquith, in Novemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
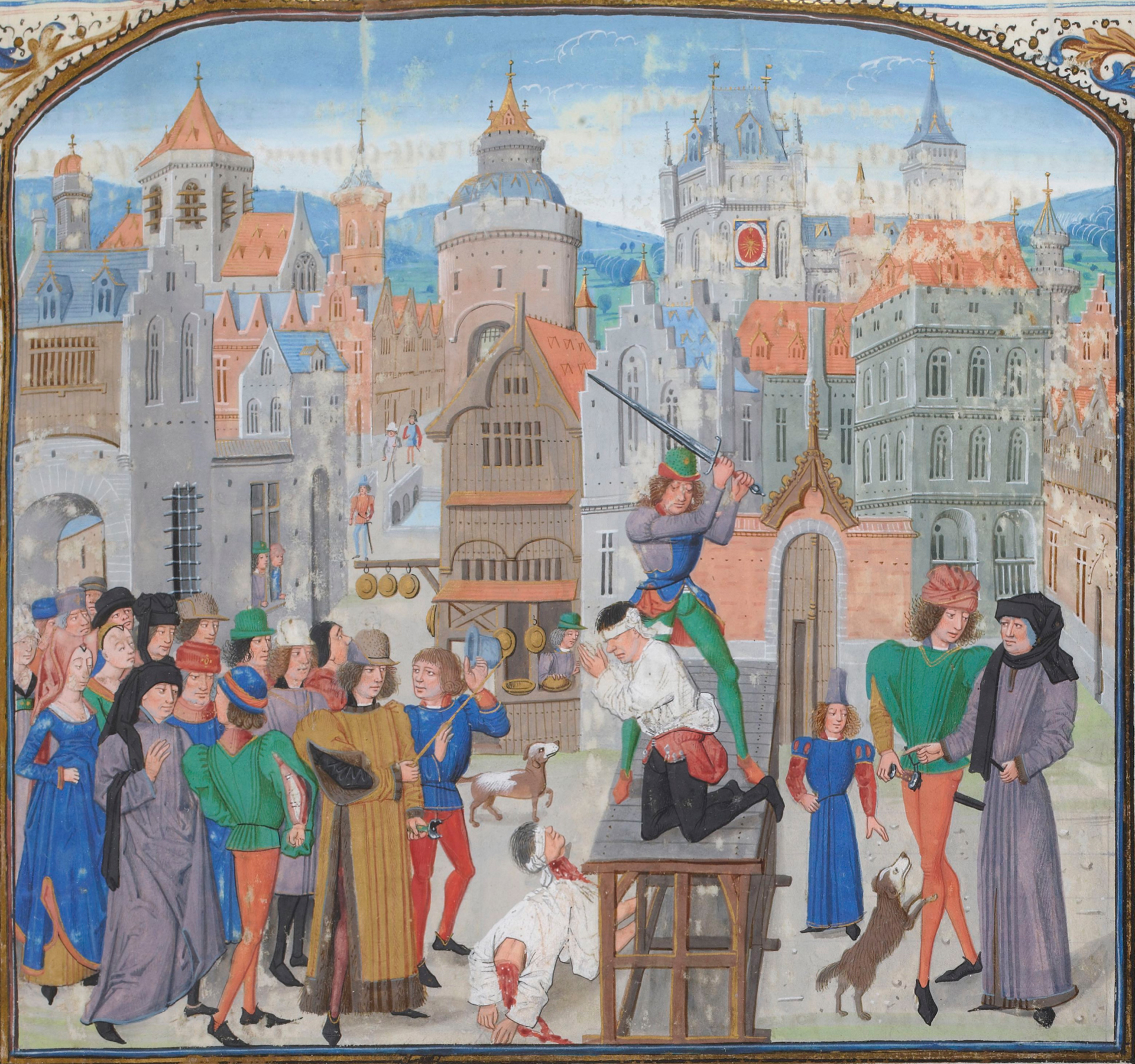
Decapitation
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the involuntary functions that are needed for the body to function. The term ''beheading'' refers to the act of deliberately decapitating a person, either as a means of murder or as an execution; it may be performed with an axe, sword, knife, machete or by mechanical means such as a guillotine or chainsaw. An executioner who carries out executions by beheading is sometimes called a headsman. Accidental decapitation can be the result of an explosion, a car or industrial accident, improperly administered execution by hanging or other violent injury. Suicide by decapitation is rare but not unknown. The national laws of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Qatar permit beheading; however, in practice, Saudi Arabia is the only country that continues to behead i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanging
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging in this sense is "specifically to put to death by suspension by the neck", though it formerly also referred to crucifixion and death by impalement in which the body would remain "hanging". Hanging has been a common method of capital punishment since medieval times, and is the primary execution method in numerous countries and regions. The first known account of execution by hanging was in Homer's ''Odyssey'' (Book XXII). In this specialised meaning of the common word ''hang'', the past and past participle is ''hanged'' instead of ''hung''. Hanging is a common method of suicide in which a person applies a ligature to the neck and brings about unconsciousness and then death by suspension or partial suspension. Methods of judicial hanging T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplomats, or its secret services for a hostile and foreign power, or attempting to kill its head of state. A person who commits treason is known in law as a traitor. Historically, in common law countries, treason also covered the murder of specific social superiors, such as the murder of a husband by his wife or that of a master by his servant. Treason (i.e. disloyalty) against one's monarch was known as ''high treason'' and treason against a lesser superior was ''petty treason''. As jurisdictions around the world abolished petty treason, "treason" came to refer to what was historically known as high treason. At times, the term ''traitor'' has been used as a political epithet, regardless of any verifiable treasonable action. In a civil war or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |