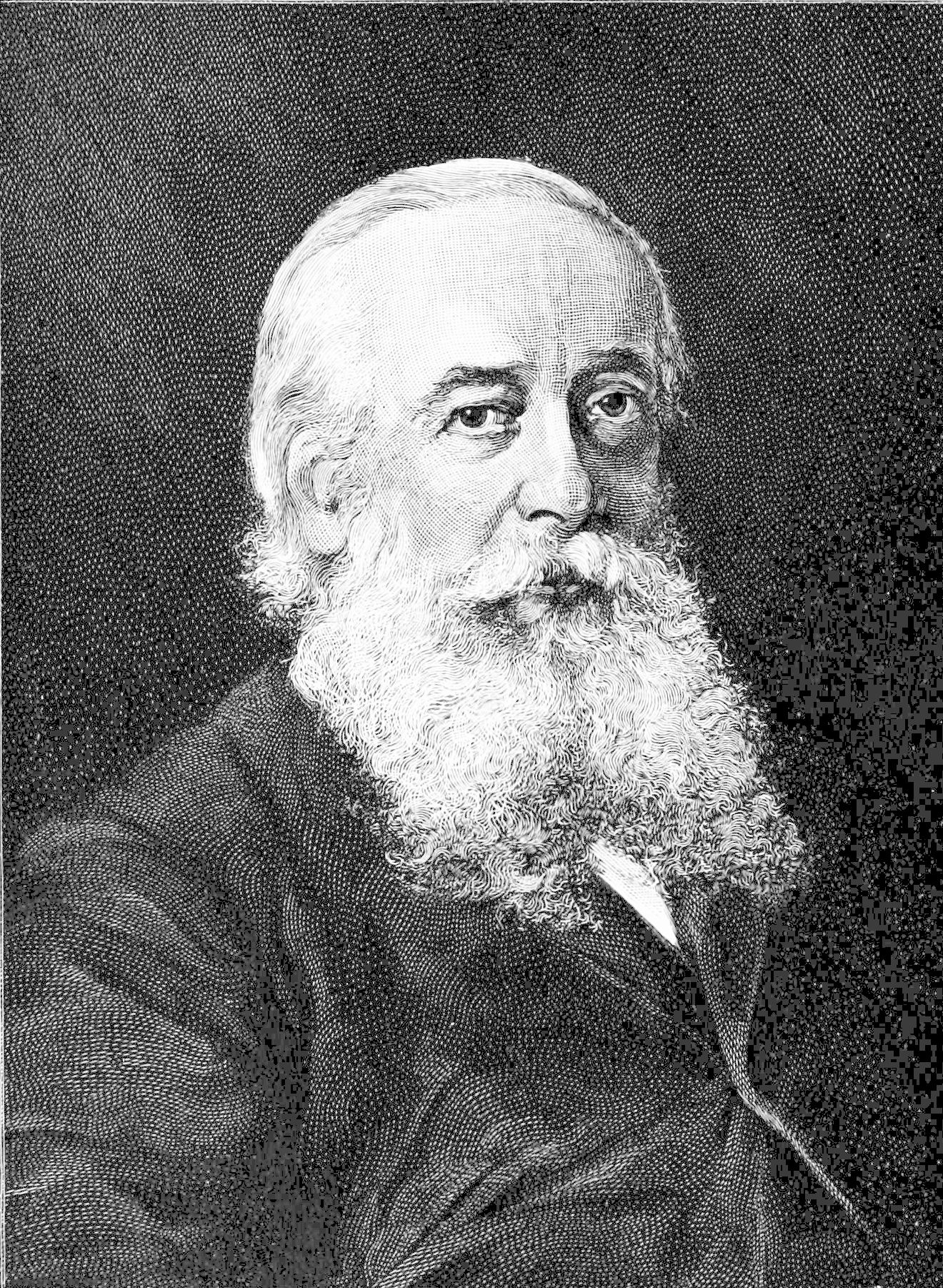|
Stichopus Herrmanni
''Stichopus herrmanni'', or Herrmann's sea cucumber, is a species of holothuroidean echinoderm in the family Stichopodidae. It is found in the tropical, western Indo-Pacific Ocean, at depths down to . This and several other species are known as curryfish and are harvested commercially; it is called ''gama'' in Indonesia. Description ''Stichopus herrmanni'' is a large species of sea cucumber, growing up to long. The body is cylindrical with a flat sole. The body wall is rough and wrinkled, without large swellings but with orange-brown papillae (conical fleshy protuberances). The mouth is surrounded by eight to sixteen feeding tentacles and the sole bears short tube feet. The colour is variable, in some locations being greyish-brown, greenish-brown, or sandy-brown, while in others being mustard-yellow, orange-brown or green and brown. Distribution and habitat ''Stichopus herrmanni'' is found in the tropical west Indo-Pacific region. Its range extends from the east coast of Afric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Semper
Carl Gottfried Semper (July 6, 1832, Altona, Hamburg – May 29, 1893, Würzburg) was a German ethnologist and animal ecologist. Career Semper attended the Hanover Polytechnic from 1851 to 1854 and achieved a Ph.D. in zoology from the University of Würzburg in 1856. He traveled to the Philippines and Palau two years later, staying in the region until 1865 in association with Museum Godeffroy. Semper published several works detailing his observations and experiences among Pacific peoples. In addition to his written work, he delivered lectures at the Lowell Technological Institute (now merged into the University of Massachusetts Lowell) near Boston and maintained a large collection of animal specimens. His work in Palau is especially noted as comprising one of the very few reliable accounts of cultural practices that are today severely diminished by Westernization. Semper is also praised for his humane and even-handed attitude toward indigenous cultures. Semper was an early suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holothuroidea
Sea cucumbers are echinoderms from the class Holothuroidea (). They are marine animals with a leathery skin and an elongated body containing a single, branched gonad. Sea cucumbers are found on the sea floor worldwide. The number of holothurian () species worldwide is about 1,717, with the greatest number being in the Asia-Pacific region. Many of these are gathered for human consumption and some species are cultivated in aquaculture systems. The harvested product is variously referred to as '' trepang'', ''namako'', ''bêche-de-mer'', or ''balate''. Sea cucumbers serve a useful role in the marine ecosystem as they help recycle nutrients, breaking down detritus and other organic matter, after which bacteria can continue the decomposition process. Like all echinoderms, sea cucumbers have an endoskeleton just below the skin, calcified structures that are usually reduced to isolated microscopic ossicles (or sclerietes) joined by connective tissue. In some species these can sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea lilies or "stone lilies". Adult echinoderms are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth, from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,000 living species, making it the second-largest grouping of deuterostomes, after the chordates. Echinoderms are the largest entirely marine phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian. The echinoderms are important both ecologically and geologically. Ecologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the biotic desert of the deep sea, as well as shallower oceans. Most echinoderms are able to reproduce asexually and regenerate tissue, organs, and limbs; in some cases, they can undergo complete regeneration from a single limb. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stichopodidae
The Stichopodidae are a family of sea cucumbers, part of the order Synallactida. Description Members of this family are mostly large or medium-sized holothuroids with a squarish cross-section, a flat ventral surface, and large, fleshy, cone-shaped projections. Their mouths are surrounded by 20 peltate tentacles. They are usually found on soft substrates, such as sand or rubble. Genera List of genera according to the World Register of Marine Species: * genus '' Apostichopus'' Liao, 1980 (8 species, North Pacific) * genus '' Astichopus'' Clark, 1922 (1 species, Caribbean) * genus '' Australostichopus'' Levin in Moraes et al., 2004 (1 species, New Zealand and southern Australia) * genus '' Eostichopus'' Cutress & Miller, 1982 (1 species, Caribbean) * genus '' Isostichopus'' Deichmann, 1958 (3 species, warm East Pacific and Atlantic) * genus '' Neostichopus'' Deichmann, 1948 (1 species, South Africa) * genus '' Parastichopus'' Clark, 1922 (2 species, Atlantic and North Pacific) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Cucumber
Sea cucumbers are echinoderms from the class Holothuroidea (). They are marine animals with a leathery skin and an elongated body containing a single, branched gonad. Sea cucumbers are found on the sea floor worldwide. The number of holothurian () species worldwide is about 1,717, with the greatest number being in the Asia-Pacific region. Many of these are gathered for human consumption and some species are cultivated in aquaculture systems. The harvested product is variously referred to as '' trepang'', ''namako'', ''bêche-de-mer'', or ''balate''. Sea cucumbers serve a useful role in the marine ecosystem as they help recycle nutrients, breaking down detritus and other organic matter, after which bacteria can continue the decomposition process. Like all echinoderms, sea cucumbers have an endoskeleton just below the skin, calcified structures that are usually reduced to isolated microscopic ossicles (or sclerietes) joined by connective tissue. In some species these can sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Cucumber
Sea cucumbers are echinoderms from the class Holothuroidea (). They are marine animals with a leathery skin and an elongated body containing a single, branched gonad. Sea cucumbers are found on the sea floor worldwide. The number of holothurian () species worldwide is about 1,717, with the greatest number being in the Asia-Pacific region. Many of these are gathered for human consumption and some species are cultivated in aquaculture systems. The harvested product is variously referred to as '' trepang'', ''namako'', ''bêche-de-mer'', or ''balate''. Sea cucumbers serve a useful role in the marine ecosystem as they help recycle nutrients, breaking down detritus and other organic matter, after which bacteria can continue the decomposition process. Like all echinoderms, sea cucumbers have an endoskeleton just below the skin, calcified structures that are usually reduced to isolated microscopic ossicles (or sclerietes) joined by connective tissue. In some species these can sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tube Feet
Tube feet (technically podia) are small active tubular projections on the oral face of an echinoderm, whether the arms of a starfish, or the undersides of sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers; they are more discreet though present on brittle stars, and have only a feeding function in feather stars. They are part of the water vascular system. Structure and function Tube feet function in locomotion, feeding, and respiration. The tube feet in a starfish are arranged in grooves along the arms. They operate through hydraulic pressure. They are used to pass food to the oral mouth at the center, and can attach to surfaces. A starfish that is inverted turns one arm over and attaches it to a solid surface, and levers itself the right way up. Tube feet allow these different types of animals to stick to the ocean floor and move slowly. Each tube foot consists of two parts: the ampulla and the podium. The ampulla is a water-filled sac contained in the body of the animal that contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biology)
In biology, a substrate is the surface on which an organism (such as a plant, fungus, or animal) lives. A substrate can include biotic or abiotic materials and animals. For example, encrusting algae that lives on a rock (its substrate) can be itself a substrate for an animal that lives on top of the algae. Inert substrates are used as growing support materials in the hydroponic cultivation of plants. In biology substrates are often activated by the nanoscopic process of substrate presentation. In agriculture and horticulture * Cellulose substrate * Expanded clay aggregate (LECA) * Rock wool * Potting soil * Soil In animal biotechnology Requirements for animal cell and tissue culture Requirements for animal cell and tissue culture are the same as described for plant cell, tissue and organ culture (In Vitro Culture Techniques: The Biotechnological Principles). Desirable requirements are (i) air conditioning of a room, (ii) hot room with temperature recorder, (iii) microscope r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the order Alismatales (in the clade of monocotyledons). Seagrasses evolved from terrestrial plants which recolonised the ocean 70 to 100 million years ago. The name ''seagrass'' stems from the many species with long and narrow leaves, which grow by rhizome extension and often spread across large "meadows" resembling grassland; many species superficially resemble terrestrial grasses of the family Poaceae. Like all autotrophic plants, seagrasses photosynthesize, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Most species undergo submarine pollination and complete their life cycle underwater. While it was previously believed this pollination was carried out without pollinators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stichopus Vastus
''Stichopus vastus'' is a species of sea cucumber in the family Stichopodidae The Stichopodidae are a family of sea cucumbers, part of the order Synallactida. Description Members of this family are mostly large or medium-sized holothuroids with a squarish cross-section, a flat ventral surface, and large, fleshy, cone-s .... It is found on the seabed in the tropical, western Indo-Pacific Ocean. References External links * Stichopodidae Animals described in 1887 {{Holothuroidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stichopus Ocellatus
''Stichopus ocellatus'' is a species of sea cucumber in the family Stichopodidae The Stichopodidae are a family of sea cucumbers, part of the order Synallactida. Description Members of this family are mostly large or medium-sized holothuroids with a squarish cross-section, a flat ventral surface, and large, fleshy, cone-s .... It is found on the seabed in the tropical, western Indo-Pacific region. References Stichopodidae Animals described in 2002 IUCN Red List data deficient species {{Holothuroidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union For Conservation Of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable". Over the past decades, IUCN has widened its focus beyond conservation ecology and now incorporates issues related to sustainable development in its projects. IUCN does not itself aim to mobilize the public in support of nature conservation. It tries to influence the actions of governments, business and other stakeholders by providing information and advice and through building partnerships. The organization is best known to the wider pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |