|
Stereoscopic Depth Rendition
Stereoscopic depth rendition specifies how the depth of a three-dimensional object is encoded in a stereoscopic reconstruction. It needs attention to ensure a realistic depiction of the three-dimensionality of viewed scenes and is a specific instance of the more general task of 3D rendering of objects in two-dimensional displays. Depth in stereograms A stereogram consists of a pair of two-dimensional frames, one for each eye. Common to both are the widths and heights of objects; their depth is encoded in the differences between right and left eye views. The geometric relationship between an object's third dimension and these position differences is presented below and depends on the location of the stereo-camera lenses and the observer's eyes. Other factors, however, contribute to the depth seen in a stereoscopic view and whether it corresponds to that in the actual object; the act of viewing a stereoscopic display often alters observers' three-dimensional perception. Stereoscopi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoscopic
Stereoscopy (also called stereoscopics, or stereo imaging) is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope. Most stereoscopic methods present a pair of two-dimensional images to the viewer. The left image is presented to the left eye and the right image is presented to the right eye. When viewed, the human brain perceives the images as a single 3D view, giving the viewer the perception of 3D depth. However, the 3D effect lacks proper focal depth, which gives rise to the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict. Stereoscopy is distinguished from other types of 3D displays that display an image in three full dimensions, allowing the observer to increase information about the 3-dimensional objects being displayed by head and eye mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Rendering
3D rendering is the 3D computer graphics process of converting 3D models into 2D images on a computer. 3D renders may include photorealistic effects or non-photorealistic styles. Rendering methods Rendering is the final process of creating the actual 2D image or animation from the prepared scene. This can be compared to taking a photo or filming the scene after the setup is finished in real life. Several different, and often specialized, rendering methods have been developed. These range from the distinctly non-realistic wireframe rendering through polygon-based rendering, to more advanced techniques such as: scanline rendering, ray tracing, or radiosity. Rendering may take from fractions of a second to days for a single image/frame. In general, different methods are better suited for either photorealistic rendering, or real-time rendering. Real-time Rendering for interactive media, such as games and simulations, is calculated and displayed in real time, at rates o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoscopy
Stereoscopy (also called stereoscopics, or stereo imaging) is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope. Most stereoscopic methods present a pair of two-dimensional images to the viewer. The left image is presented to the left eye and the right image is presented to the right eye. When viewed, the human brain perceives the images as a single 3D view, giving the viewer the perception of 3D depth. However, the 3D effect lacks proper focal depth, which gives rise to the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict. Stereoscopy is distinguished from other types of 3D displays that display an image in three full dimensions, allowing the observer to increase information about the 3-dimensional objects being displayed by head and eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
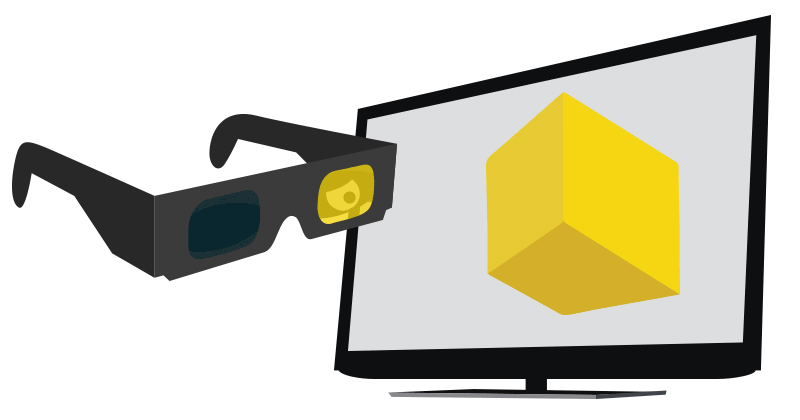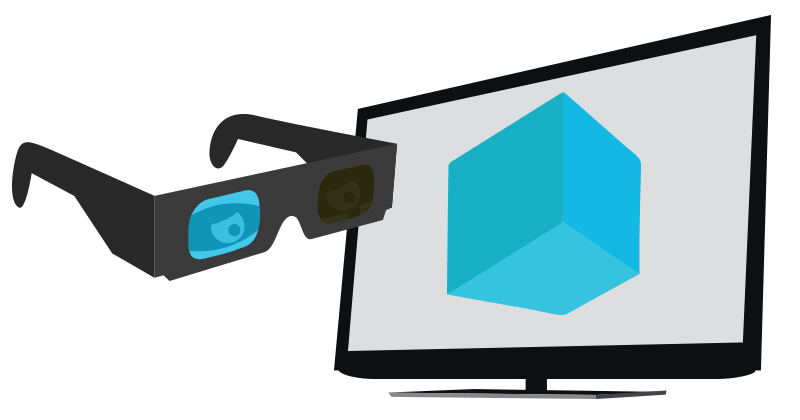
Active Shutter 3D System
An active shutter 3D system (a.k.a. alternate frame sequencing, alternate image, AI, alternating field, field sequential or eclipse method) is a technique of displaying stereoscopic 3D images. It works by only presenting the image intended for the left eye while blocking the right eye's view, then presenting the right-eye image while blocking the left eye, and repeating this so rapidly that the interruptions do not interfere with the perceived fusion of the two images into a single 3D image. Modern active shutter 3D systems generally use liquid crystal shutter glasses (also called "LC shutter glasses" or "active shutter glasses"). Each eye's glass contains a liquid crystal layer which has the property of becoming opaque when voltage is applied, being otherwise transparent. The glasses are controlled by a timing signal that allows the glasses to alternately block one eye, and then the other, in synchronization with the refresh rate of the screen. The timing synchronization to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritz Von Rohr
Moritz von Rohr (4 April 1868 – 20 June 1940) was an optical scientist at Carl Zeiss in Jena, Germany. A street in Jena is named after him: Moritz-von-Rohr-Straße, near Carl-Zeiss-Promenade and Otto-Schott-Straße. Life Moritz von Rohr was born in Lonzyn near Hohensalza, then part of the Prussian Grand Duchy of Posen, but now in Poland and known as Łążyn, near Inowrocław. He obtained a doctorate of philosophy at the University of Berlin in 1892. Inventions Von Rohr is usually credited with the design of the first aspheric lenses for eyeglasses. He invented the eyeglass lens designs that became the Zeiss Punktal lenses. He also developed a method of computing depth of field from a camera's entrance pupil location and diameter, without reference to focal length and f-number In optics, the f-number of an optical system such as a camera lens is the ratio of the system's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil ("clear aperture").Smith, Warren ''Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Film
3D films are motion pictures made to give an illusion of three-dimensional solidity, usually with the help of special glasses worn by viewers. They have existed in some form since 1915, but had been largely relegated to a niche in the motion picture industry because of the costly hardware and processes required to produce and display a 3D film, and the lack of a standardized format for all segments of the entertainment business. Nonetheless, 3D films were prominently featured in the 1950s in American cinema, and later experienced a worldwide resurgence in the 1980s and 1990s driven by IMAX high-end theaters and Disney-themed venues. 3D films became increasingly successful throughout the 2000s, peaking with the success of 3D presentations of ''Avatar'' in December 2009, after which 3D films again decreased in popularity. Certain directors have also taken more experimental approaches to 3D filmmaking, most notably celebrated auteur Jean-Luc Godard in his film ''Goodbye to Language' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
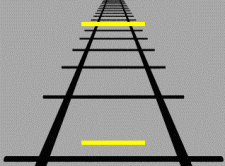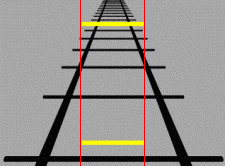
Subjective Constancy
Subjective constancy or perceptual constancy is the perception of an object or quality as constant even though our sensation of the object changes. While the physical characteristics of an object may not change, in an attempt to deal with the external world, the human perceptual system has mechanisms that adjust to the stimulus. Visual There are several types of perceptual constancies in visual perception: * ''Size constancy'' is one type of visual subjective constancy. Within a certain range, people's perception of one particular object's size will not change, regardless of changes in distance or the video size change on the retina. The perception of image is still based upon the actual size of the perceptual characteristics. According to optical principles, for the same object, the size of the image on the retina changes as the distance from the object to the observer changes. The greater the distance, the smaller the image is sensed by the retina. When someone is observing an ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |