|
Steppe Mammoth
The steppe mammoth (''Mammuthus trogontherii'', sometimes ''Mammuthus armeniacus'') is an extinct species of Elephantidae that ranged over most of northern Eurasia during the late Early and Middle Pleistocene, approximately 1.8 million-200,000 years ago. It evolved in Siberia during the Early Pleistocene from ''Mammuthus meridionalis''. It was the first stage in the evolution of the steppe and tundra elephants and the ancestor of the woolly mammoth and Columbian mammoth of the later Pleistocene. Populations of steppe mammoth may have persisted in northern China and Mongolia as late as 33,000 years ago. Taxonomy There is confusion about the correct scientific name for the steppe mammoth, either ''Mammuthus armeniacus'' (Falconer 1857) or ''Mammuthus trogontherii'' (Pohlig 1885). Falconer used material from Asian sources while Pohlig worked with fossil remains from Europe and both names appear in scientific publications, adding to the confusion. A first taxonomical overhaul was do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Pohlig
Hans may refer to: __NOTOC__ People * Hans (name), a masculine given name * Hans Raj Hans, Indian singer and politician ** Navraj Hans, Indian singer, actor, entrepreneur, cricket player and performer, son of Hans Raj Hans ** Yuvraj Hans, Punjabi actor and singer, son of Hans Raj Hans * Hans clan, a tribal clan in Punjab, Pakistan Places * Hans, Marne, a commune in France * Hans Island, administrated by Greenland and Canada Arts and entertainment * ''Hans'' (film) a 2006 Italian film directed by Louis Nero * Hans (Frozen), the main antagonist of the 2013 Disney animated film ''Frozen'' * ''Hans'' (magazine), an Indian Hindi literary monthly * ''Hans'', a comic book drawn by Grzegorz Rosiński and later by Zbigniew Kasprzak Other uses * Clever Hans, the "wonder horse" * ''The Hans India'', an English language newspaper in India * HANS device, a racing car safety device *Hans, the ISO 15924 code for Simplified Chinese script See also *Han (other) *Hans im Glück, a Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
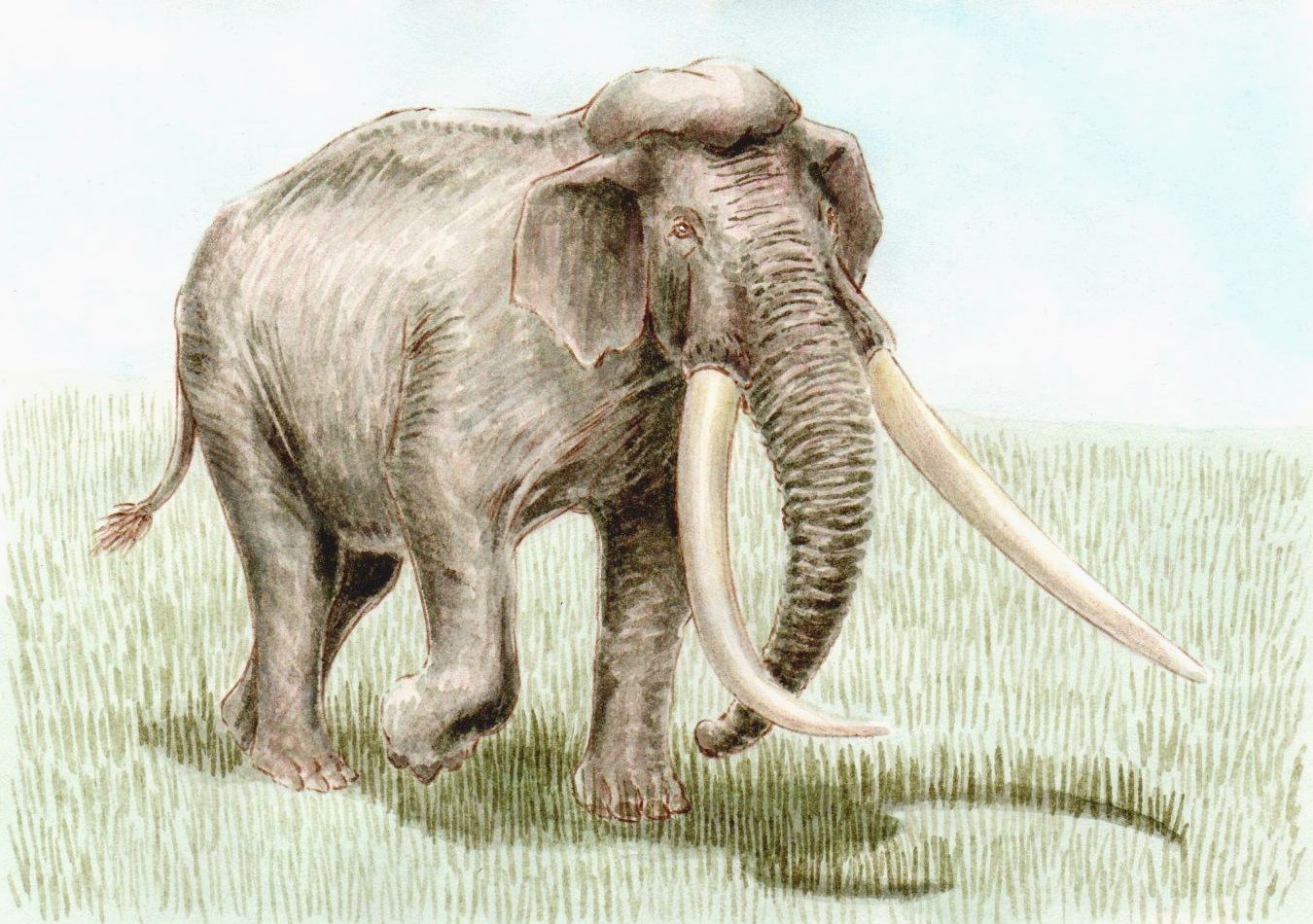
Palaeoloxodon Namadicus
''Palaeoloxodon namadicus'' or the Asian straight-tusked elephant, is an extinct species of prehistoric elephant known from the early Middle to Late Pleistocene of the Indian subcontinent, and possibly also elsewhere in Asia. Some authorities regard it to be a subspecies of ''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'', the European straight-tusked elephant, due to extreme similarities of the tusks. Their skull structure was also different from that of a modern elephant. The grouping of this genus is supported by cranial synapomorphies with other species of ''Palaeoloxodon,'' which includes a large crest at the top of the skull that anchored the splenius muscles used to support the head. Later research suggested that ''P. namadicus'' can be distinguished from ''P. antiquus'' by its less robust limb bones and more stout cranium. Based on the stable isotope ratioes of carbon and oxygen and the morphology of their teeth, it is suggested that ''P. namadicus'' tended towards a grazing diet, as opposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okhansk Rayon
Okhansky District (russian: Оханский райо́н) is an administrative district (raion) of Perm Krai, Russia; one of the administrative divisions of Perm Krai, thirty-three in the krai.Law #416-67 Subdivisions of Russia#Municipal divisions, Municipally, it is incorporated as Okhansky Municipal District.Law #1878-407 It is located in the southwest of the krai. The area of the district is .Encyclopedia of Perm KraiEntry on Okhansky District Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, town of Okhansk. Population: The population of Okhansk accounts for 44.6% of the district's total population. Geography The Kama River is the largest in the district and forms the district's border with Permsky District. History The district was established in December 1923. It was merged into Ochyorsky District on February 1, 1963 but was restored on January 12, 1965. Demographics Ethnic composition: *Russians: 94.3% *Komi-Permyak people: 1.5% *Tatars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammuthus Primigenius
The woolly mammoth (''Mammuthus primigenius'') is an extinct species of mammoth that lived during the Pleistocene until its extinction in the Holocene epoch. It was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with '' Mammuthus subplanifrons'' in the early Pliocene. The woolly mammoth began to diverge from the steppe mammoth about 800,000 years ago in East Asia. Its closest extant relative is the Asian elephant. DNA studies show that the Columbian mammoth was a hybrid between woolly mammoths and another lineage descended from steppe mammoths. The appearance and behaviour of this species are among the best studied of any prehistoric animal because of the discovery of frozen carcasses in Siberia and North America, as well as skeletons, teeth, stomach contents, dung, and depiction from life in prehistoric cave paintings. Mammoth remains had long been known in Asia before they became known to Europeans in the 17th century. The origin of these remains was long a matter o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Puy-en-Velay
Le Puy-en-Velay (, literally ''Le Puy in Velay''; oc, Lo Puèi de Velai ) is the prefecture of the Haute-Loire department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of south-central France. Located near the river Loire, the city is famous for its cathedral, for a kind of lentil, for its lace-making, as well as for being the origin of the ''Chemin du Puy,'' one of the principal origin points of the pilgrimage route of Santiago de Compostela in France. In 2017, the commune had a population of 18,995. History Le Puy-en-Velay was a major bishopric by the early period of medieval France. Its foundation is largely legendary. According to a martyrology compiled by Ado of Vienne, published in many copies in 858, and supplemented in the mid-10th century by Gauzbert of Limoges, a priest named George accompanied a certain Front, the first Bishop of Périgueux, when they were sent to proselytize in Gaul. Front was added to the list of the apostles to Gaul, who in tradition are described as be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée Crozatier
The Musée Crozatier is a museum in Le Puy-en-Velay in the French Auvergne. Inaugurated in 1868, its collection comprises art and archaeological artifacts from Velay and the Haute-Loire region. The museum has undergone a major renovation from 2010 to 2018 (re opening in July 2018). Collection The diversity of the museum's collections (painting, sculpture, graphic arts, works of art, archaeology, natural history, mechanics, crafts, lace) allows a discovery of the history of Velay and an overview of art and sciences, through 4 galleries: historical, fine arts, scientific and local crafts.''Le musée Crozatier au Puy-en-Velay'', Archéologia, Hors-série n°22, 2018 See also * List of museums in France A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union ... References External ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dick Mol
Dick "Sir Mammoth" Mol (born June 26, 1955) is a Dutch paleontologist - a specialist in the field of mammoths for almost three decades. He is a research associate of several museums. Mol's primary focus is on mammals of the Quaternary period, including mammoths and extinct rhinoceros species. Biography Early life and education Dick Mol was born in Winterswijk, Gelderland (The Netherlands), in 1955, as one of nine children, Mol could not afford to attend higher education after high school, and so he joined customs service in 1974. As the Netherlands implemented the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), Dick Mol was trained to be a CITES specialist, spending much time on the job studying bones, eventually accumulating ample knowledge to compensate for an academic career. Career Dick has catalogued fossil remains dredged from the bottom of the North Sea, and published over fifty papers on his finds. Since 1990, he has been associated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Runton Mammoth
The West Runton Mammoth is a fossilized skeleton of a steppe mammoth (''Mammuthus trogontherii'') found in the West Runton Cliffs, cliffs of West Runton in the county of Norfolk, England in 1990. The find is the largest nearly complete mammoth skeleton known, and is the oldest found in the United Kingdom. Discovery, excavation and preservation Following a stormy night on 13 December 1990, local residents found that a large bone had been partially exposed at the base of the cliffs in the Cromer Forest Bed. They contacted Norfolk Museums Service who identified it as a pelvic bone of a large steppe mammoth. After another storm just over a year later, a local fossil hunter discovered more and in January 1992 the Norfolk Archaeological Unit undertook an exploratory excavation at the site. A more major three-month Excavation (archaeology), excavation by the Norfolk Archaeological Unit followed in 1995. Funding from the National Lottery (United Kingdom), Heritage lottery Fund and from A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest, and claims a border with Albania through the Political status of Kosovo, disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia without Kosovo has about 6.7 million inhabitants, about 8.4 million if Kosvo is included. Its capital Belgrade is also the List of cities in Serbia, largest city. Continuously inhabited since the Paleolithic Age, the territory of modern-day Serbia faced Slavs#Migrations, Slavic migrations in the 6th century, establishing several regional Principality of Serbia (early medieval), states in the early Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kikinda
Kikinda ( sr-Cyrl, Кикинда, ; hu, Nagykikinda) is a city and the administrative center of the North Banat District in Serbia . The city urban area has 38,069 inhabitants, while the city administrative area has 59,453 inhabitants. The city was founded in the 18th century. From 1774 to 1874 Kikinda was the seat of the District of Velika Kikinda, an autonomous administrative unit of Habsburg monarchy. In 1893 Kikinda was granted the status of a city. The city became part of the Kingdom of Serbia (and Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes) in 1918, and it lost the city status. The status was re-granted in 2016. In 1996, the well-preserved archaeological remnants of a half a million-year-old mammoth were excavated on the outer edge of the town area. The mammoth called "Kika" has become one of the symbols of the town. Today it is exhibited in the National Museum of Kikinda. Other attractions of the city are the Suvača – a unique horse-powered dry mill, the annual Pumpkin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body, and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal skeleton supported by fluid pressure. Vertebrates are animals with a vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bone and cartilage. Invertebrates are animals that lack a vertebral column. The skeletons of invertebrates vary, including hard exoskeleton shells, plated endoskeletons, or Sponge spicule, spicules. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invertebrates. Etymology The term ''skeleton'' comes . ''Sceleton'' is an archaic form of the word. Classification Skeletons can be defined by several attributes. Solid skeletons consist of hard substances, such as bone, cartilage, or cuticle. These can be further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |