|
Stensioella
''Stensioella heintzi'' is an enigmatic placoderm of arcane affinity. It is only known from the Lower Devonian Hunsrück slate of Germany. The genus is named after Erik Stensiö, the species name honours Anatol Heintz. Anatomy ''Stensioella heintzi'' has an elongated body, a whip-like tail, and long, wing-like pectoral fins. In life, the animal would have looked vaguely like an elongated Chimaeridae, ratfish. Like the sympatric ''Gemuendina'', ''S. heintzi'' had armor made up of a complex mosaic of small, scale-like tubercles. Taxonomy ''Stensioella'' is tentatively placed within Placodermi as being among the most basal of all placoderms, as from what can be discerned from the only whole specimen found, the shoulder joints of its armor appear to be very similar to other placoderms. Despite this detail, coupled with superficial similarities in skull plates, and gross, superficial similarities between its tubercles, and the tubercles of the rhenanids, some paleontologists believ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderms Of Europe
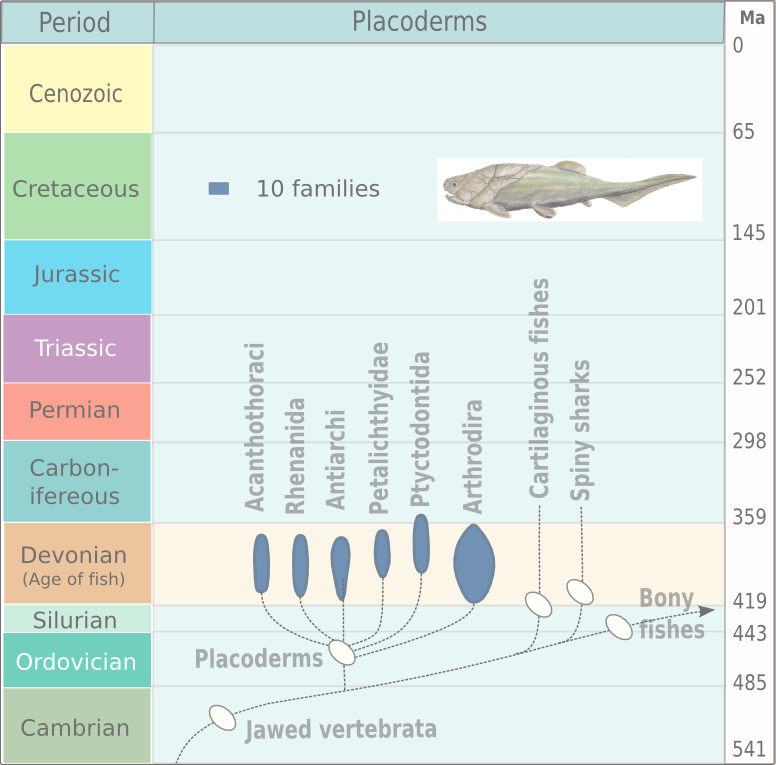
Placoderms (from Ancient Greek πλάξ [''plax'', ''plakos''] 'Plate (animal anatomy), plate' and δέρμα [''derma''] 'skin') are vertebrate animals of the class (biology), class Placodermi, an extinct group of prehistoric fish known from Paleozoic fossils during the Silurian and the Devonian geological period, periods. While their endoskeletons are mainly cartilaginous, their head and thorax were covered by articulated armour (zoology), armoured plates (hence the name), and the rest of the body was scale (zoology), scaled or naked depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish (their fish jaw, jaws likely Evolution, evolved from the first pair of gill arches), as well as the first vertebrates to have true tooth, teeth. They were also the first fish clade to develop pelvic fins, the second set of paired fins and the homology (biology), homologous precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods. 380-million-year-old fossils of three other genera, ''Incisoscutum'', ''M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderm Genera
Placoderms (from Ancient Greek πλάξ 'plax'', ''plakos''' plate' and δέρμα 'derma'''skin') are vertebrate animals of the class Placodermi, an extinct group of prehistoric fish known from Paleozoic fossils during the Silurian and the Devonian periods. While their endoskeletons are mainly cartilaginous, their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates (hence the name), and the rest of the body was scaled or naked depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish (their jaws likely evolved from the first pair of gill arches), as well as the first vertebrates to have true teeth. They were also the first fish clade to develop pelvic fins, the second set of paired fins and the homologous precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods. 380-million-year-old fossils of three other genera, '' Incisoscutum'', '' Materpiscis'' and '' Austroptyctodus'', represent the oldest known examples of live birth. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderm
Placoderms (from Ancient Greek πλάξ [''plax'', ''plakos''] 'Plate (animal anatomy), plate' and δέρμα [''derma''] 'skin') are vertebrate animals of the class (biology), class Placodermi, an extinct group of prehistoric fish known from Paleozoic fossils during the Silurian and the Devonian geological period, periods. While their endoskeletons are mainly cartilaginous, their head and thorax were covered by articulated armour (zoology), armoured plates (hence the name), and the rest of the body was scale (zoology), scaled or naked depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish (their fish jaw, jaws likely Evolution, evolved from the first pair of gill arches), as well as the first vertebrates to have true tooth, teeth. They were also the first fish clade to develop pelvic fins, the second set of paired fins and the homology (biology), homologous precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods. 380-million-year-old fossils of three other genera, ''Incisoscutum'', ''M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
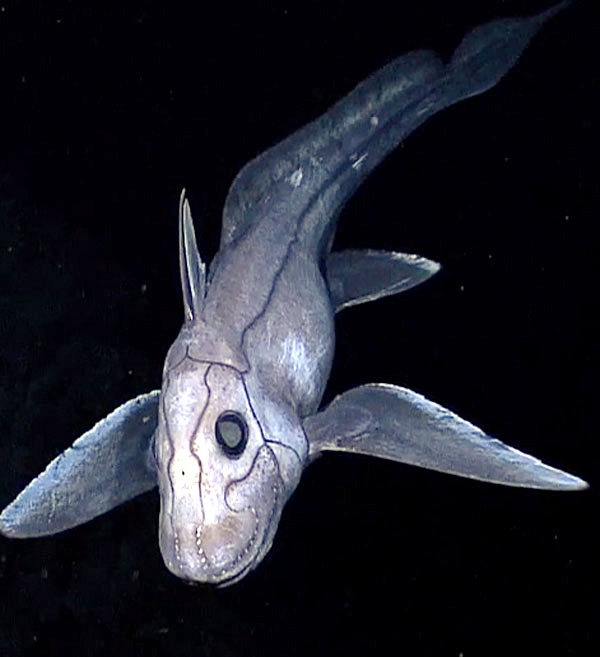
Holocephali
Holocephali (Sometimes spelled Holocephala; Romanization of Greek, Greek for "complete head" in reference to the fusion of Palatoquadrate, upper jaw with the rest of the skull) is a Subclass (biology), subclass of Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish. While the only living holocephalans are three families within a single Order (biology), order which together are commonly known as chimaeras, the group includes many extinct orders and was far more diverse during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Era (geology), eras. The earliest known fossils of holocephalans date to the Middle Devonian period, and the group likely reached its peak diversity during the following Carboniferous period. Molecular clock studies suggest that the subclass diverged from its closest relatives, Elasmobranchii, elasmobranchs such as sharks and Batomorphi, rays, during the Early Devonian or Silurian period. Extinct holocephalans are typically divided into a number of orders, although the interrelationships of these gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erik Stensiö
Prof Erik Helge Osvald Stensiö HFRSE (2 October 1891 – 11 January 1984), né Andersson, was an influential Swedish paleozoologist and founder of the so-called "Stockholm School" of vertebrate paleontology. He later took his new surname, Stensiö, from his place of origin and is occasionally referred to with both names (as Erik Andersson Stensiö, Erik A. Stensiö or Erik A:son Stensiö) Life Erik Helge Oswald Andersson, as his original name was, was born in the village of Stensjö by in Döderhult parish in Kalmar County, the son of Johan Fredrik Andersson (d.1907), a farmer, and his wife, Otilia Maria Erlandson (d.1940). He was educated at Linköping Gymnasium. He then studied science at the University of Uppsala, graduating BSc in 1912. He received his Ph.D. and a docentship in paleontology from Uppsala University in 1921 and became professor and keeper at the Zoopaleontological (later called the Paleozoological) department of the Swedish Museum of Natural History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimaeridae
The Chimaeridae, or short-nosed chimaeras, are a family (biology), family of cartilaginous fish. They resemble other Chimaeriformes, chimaeras in general form and habits, but have short, rounded snouts, without the modifications found in related families. Many species have long, tapering tails, giving them an alternative name of ratfish. Shortnose Chimaera, chimaeras have a venomous spine on their backs, which is sufficiently dangerous to injure humans. They are found in temperate and tropical marine waters worldwide. Most species are restricted to depths below , but a few, notably the spotted ratfish and rabbit fish, can locally be found at relatively shallow depths. They range from in maximum total length, depending on species. Species The species are grouped into two genera and include: Family Chimaeridae * Genus ''Chimaera (genus), Chimaera'' Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus, 10th edition of Systema Naturae, 1758 (Eocene-Recent) ** ''Chimaera argiloba'' Peter R. Last, Last, Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimaera
Chimaeras are Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish in the order (biology), order Chimaeriformes (), known informally as ghost sharks, rat fish (not to be confused with rattails), spookfish, or rabbit fish; the last two names are also applied to Barreleye, Opisthoproctidae and Rabbitfish, Siganidae, respectively. At one time a "diverse and abundant" group (based on the fossil record), their closest living relatives are sharks and ray (fish), rays, though their last common ancestor with them lived nearly 400 million years ago. Living species (aside from plough-nose chimaeras) are largely confined to deep water. Anatomy Chimaeras are soft-bodied, shark-like fish with bulky heads and long, tapered tails; measured from the tail, they can grow up to in length. Like other members of the class Chondrichthyes, chimaera skeletons are entirely cartilaginous, or composed of cartilage. Males use forehead denticles to grasp a female by a fin during copulation. The Branchial arch, gill arche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iniopterygians
Iniopterygiformes (Originally spelled Iniopterygia and sometimes informally abbreviated as "iniops") is an extinct order of cartilaginous fish known only from the Carboniferous period of the United States. Iniopterygians are characterized by large, superficially wing-like pectoral fins positioned upwards behind the head, from which the name of the group (translated as "nape fin") is derived. Iniopterygians are also noted to possess proportionally large skulls and eyes, armor plates composed of dentin, and "tooth-whorls" of fused teeth. Their elongated pectoral fins bore large, denticle-covered spines, and they are thought to have used them to swim using a "flying" motion. The iniopterygians were comparatively small chondrichthyans, with the largest species reaching only in length. The group is regarded as a relative of modern chimaeras, and is placed in the subclass Holocephali Holocephali (Sometimes spelled Holocephala; Romanization of Greek, Greek for "complete head" in refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petalodont
Petalodontiformes ("thin-plate teeth") is an extinct order of marine cartilaginous fish related to modern day chimaera found in what is now the United States of America and Europe.Lund, Richard, E. D. Grogan, and M. Fath. "On the relationships of the Petalodontiformes (Chondrichthyes)." Paleontological Journal 48.9 (2014): 1015-1029. Most species are known only from isolated teeth.Dalla Vecchia, Fabio Marco, and Museo Paleontologico Cittadino. "A new petalodont tooth (Chondrichthyes, Petalodontiformes) from the Lower Permian of the Carnic Alps (Friuli, NE Italy)." Bollettino della Società Paleontologica Italiana 39 (2000): 225-228. All fossils range from the Carboniferous to the Permian, where they are presumed to have died out during the Permian/Triassic extinction event. The two best known species are '' Belantsea montana'', from the Carboniferous Bear Gulch, Montana Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emsian
The Emsian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 410.62 ±1.95 million years ago to 393.47 ±0.99 million years ago. It was preceded by the Pragian Stage and followed by the Eifelian Stage. It is named after the Ems river in Germany. The GSSP is located in the Zinzil'ban Gorge in the Kitab State Geological Reserve of Uzbekistan , image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg , image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg , symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem , national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ..., above the contact with the Madmon Formation. In North America the Emsian Stage is represented by Sawkill or Sawkillian time. Biological events During this period, earliest known agoniatitid ammonoid fossils began appearing within this stage after first appearing in previous stage and began to evolutionarily radiate within this stage, in which a new ammonoid or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrichthyan
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class (biology), class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are aquatic animal, aquatic vertebrates with paired fins, paired Nostril, nares, placoid scales, conus arteriosus in the heart, and a lack of operculum (fish), opercula and swim bladders. Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates. The class is divided into two subclasses: Elasmobranchii (sharks, Batoidea, rays, skate (fish), skates and sawfish) and Holocephali (chimaeras, sometimes called ghost sharks, which are sometimes separated into their own class). Extant chondrichthyans range in size from the finless sleeper ray to the over whale shark. Anatomy Skeleton The skeleton is cartilaginous. The notochord is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at million years ago (Megaannum, Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at Ma. It is the fourth period of both the Paleozoic and the Phanerozoic. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant evolutionary radiation of history of life#Colonization of land, life on land occurred during the Devonian, as free-spore, sporing land plants (pteridophytes) began to spread across dry land, forming extensive coal forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of vascular plants had evolved leaf, leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants (Pteridospermatophyta, pteridospermatophyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |