|
Stencyl
Stencyl is a video game development tool that allows users to create 2D video games for computers, mobile devices, and the web. The software is available for free, with select publishing options available for purchase. The software was originally called "StencylWorks" while in development and for the initial release but was later shortened to just "Stencyl". Features Games created in Stencyl can be exported to the web via Adobe Flash Player or HTML5, and to personal computers as executable games, as well as onto various mobile devices as iOS and Android applications. Physics and collisions are managed by Box2D, which can be selectively or completely disabled to decrease any potential performance impact for games that don't require full physics simulation. Starting in version 3.0, projects in Stencyl use the Haxe programming language and OpenFL game framework to allow a flexible, write once, run anywhere style of game creation. IDE Stencyl is an authoring tool and an IDE. The ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
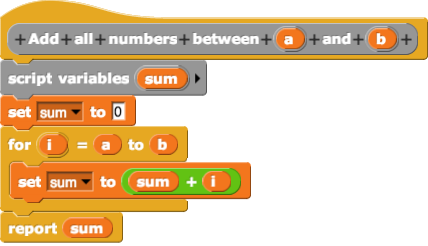
Visual Programming Language
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create computer program, programs by manipulating program elements rather than by specifying them . A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Box2D
Box2D is a free software, free Open-source software, open source Dimension, 2-dimensional Physics engine, physics simulator game engine, engine written in C (programming language), C by Erin Catto and published under the MIT license. It has been used in ''Crayon Physics Deluxe'', ''Limbo (video game), Limbo'', ''Rolando (video game), Rolando'', ''Incredibots'', ''Angry Birds (video game), Angry Birds'', ''Tiny Wings'', ''Shovel Knight'', ''Transformice'', ''Happy Wheels'', and many online Flash games, as well as iPhone, iPad and Android games using the Cocos2d or Moscrif game engine and Corona (software development kit), Corona framework. It has also been used in the Unity (game engine), Unity game engine. History Box2D was first released as "Box2D Lite", a demonstration engine to accompany a physics presentation given by Erin Catto at Game Developers Conference, GDC 2006. On September 11, 2007, it was released as open source on SourceForge. On January 17, 2010, Box 2D moved th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Haxe
Haxe is a high-level cross-platform programming language and compiler that can produce applications and source code for many different computing platforms from one code-base. It is free and open-source software, released under an MIT License. The compiler is written in OCaml. It can be run in server-mode to provide code completion for integrated development environments (IDEs). Haxe includes a set of features and a standard libraryIntroduction to the Haxe Standard Library Haxe Docs supported across all platforms, including numeric data types, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Write Once, Run Anywhere
''Write once, run anywhere'' (WORA), or sometimes ''Write once, run everywhere'' (WORE), was a 1995 slogan created by Sun Microsystems to illustrate the cross-platform benefits of the Java (programming language), Java programming language. Ideally, this meant that a Java program could be developed on any device, compiled into standard bytecode, and be expected to run on any device equipped with a Java virtual machine (JVM). The installation of a JVM or Java interpreter on chips, devices, or software packages became an industry standard practice. The catch is that since there are multiple JVM implementations, on top of a wide variety of different operating systems, there could be subtle differences in how a program executes on each JVM/OS combination, possibly requiring an application to be tested on each target platform. This gave rise to a joke among Java developers: ''Write once, debug everywhere''. In comparison, the Squeak Smalltalk programming language and environment boasts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Traditional Chinese
A tradition is a system of beliefs or behaviors (folk custom) passed down within a group of people or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or impractical but socially meaningful clothes (like court dress, lawyers' wigs or military officers' spurs), but the idea has also been applied to social norms and behaviors such as greetings, etc. Traditions can persist and evolve for thousands of years— the word ''tradition'' itself derives from the Latin word ''tradere'' literally meaning to transmit, to hand over, to give for safekeeping. While it is reportedly assumed that traditions have an ancient history, many traditions have been invented on purpose, whether it be political or cultural, over short periods of time. Various academic disciplines also use the word in a variety of ways. The phrase "according to tradition" or "by tradition" usually means that wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hard Coding
Hard coding (also hard-coding or hardcoding) is the software development practice of embedding data directly into the source code of a program or other executable object, as opposed to obtaining the data from external sources or generating it at runtime. Hard-coded data typically can be modified only by editing the source code and recompiling the executable, although it can be changed in memory or on disk using a debugger or hex editor. Data that is hard-coded is best suited for unchanging pieces of information, such as physical constants, version numbers, and static text elements. Soft-coded data, on the other hand, encodes arbitrary information through user input, text files, INI files, HTTP server responses, configuration files, preprocessor macros, external constants, databases, command-line arguments, and is determined at runtime. Overview Hard coding requires the program's source code to be changed any time the input data or desired format changes, when it might b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Boolean Data Type
In computer science, the Boolean (sometimes shortened to Bool) is a data type that has one of two possible values (usually denoted ''true'' and ''false'') which is intended to represent the two truth values of logic and Boolean algebra. It is named after George Boole, who first defined an algebraic system of logic in the mid 19th century. The Boolean data type is primarily associated with conditional statements, which allow different actions by changing control flow depending on whether a programmer-specified Boolean ''condition'' evaluates to true or false. It is a special case of a more general ''logical data type—''logic does not always need to be Boolean (see probabilistic logic). Generalities In programming languages with a built-in Boolean data type, such as Pascal, C, Python or Java, the comparison operators such as > and ≠ are usually defined to return a Boolean value. Conditional and iterative commands may be defined to test Boolean-valued expressions. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Drag And Drop
In computer graphical user interfaces, drag and drop is a pointing device gesture in which the user (computing), user selects a virtual object by "grabbing" it and dragging it to a different location or onto another virtual object. In general, it can be used to invoke many kinds of actions, or create various types of associations between two abstract objects. As a feature, drag-and-drop support is not found in all software, though it is sometimes a fast and easy-to-learn technique. However, it is not always clear to users that an item can be dragged and dropped, or what command is performed by the drag and drop, which can decrease usability. Actions The basic sequence involved in drag and drop is: * Move the pointer (computing WIMP), pointer to the object * Press, and hold down, the button on the computer mouse, mouse or other pointing device, to "grab" the object * "Drag" the object to the desired location by moving the pointer to this one * "Drop" the object by releasing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Syntax (programming Languages)
In computer science, the syntax of a computer language is the rules that define the combinations of symbols that are considered to be correctly structured Statement (computer science), statements or Expression (computer science), expressions in that language. This applies both to programming languages, where the document represents source code, and to markup languages, where the document represents data. The syntax of a language defines its surface form. Text-based user interface, Text-based computer languages are based on sequences of Character (computing), characters, while visual programming languages are based on the spatial layout and connections between symbols (which may be textual or graphical). Documents that are syntactically invalid are said to have a syntax error. When designing the syntax of a language, a designer might start by writing down examples of both legal and illegal String (computer science), strings, before trying to figure out the general rules from these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
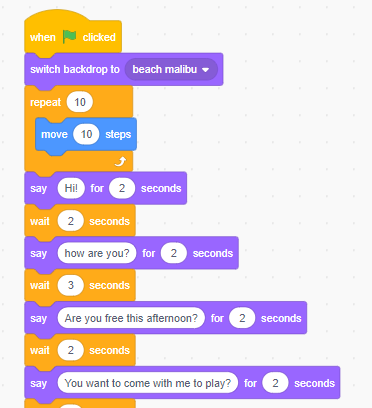
Scratch (programming Language)
Scratch is a High-level programming language, high-level, block-based visual programming language and website aimed primarily at children as an educational tool, with a target audience of ages 8 to 16. Users on the site can create projects on the website using a block-like interface. Scratch was conceived and designed through collaborative National Science Foundation grants awarded to Mitchel Resnick and Yasmin Kafai. Scratch is developed by the MIT Media Lab and has been translated into 70+ languages, being used in most parts of the world. Scratch is taught and used in after-school centers, schools, and colleges, as well as other public knowledge institutions. As of 15 February 2023, community statistics on the language's official website show more than 123 million projects shared by over 103 million users, and more than 95 million monthly website visits. Overall, more than 1.15 billion projects have been created in total, with the site reaching its one billionth project on A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
End-user Development
End-user development (EUD) or end-user programming (EUP) refers to activities and tools that allow end-users – people who are not professional software developers – to program computers. People who are not professional developers can use EUD tools to create or modify ''software artifacts'' (descriptions of automated behavior) and complex data objects without significant knowledge of a programming language. In 2005 it was estimated (using statistics from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics) that by 2012 there would be more than 55 million end-user developers in the United States, compared with fewer than 3 million professional programmers. Various EUD approaches exist, and it is an active research topic within the field of computer science and human-computer interaction. Examples include natural language programming, spreadsheets, scripting languages (particularly in an office suite or art application), visual programming, trigger-action programming and programming by examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Programming
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing source code, code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the Domain (software engineering), application domain, details of programming languages and generic code library (computing), libraries, specialized algorithms, and Logic#Formal logic, formal logic. Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include Requirements analysis, analyzing requirements, Software testing, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), imple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |