|
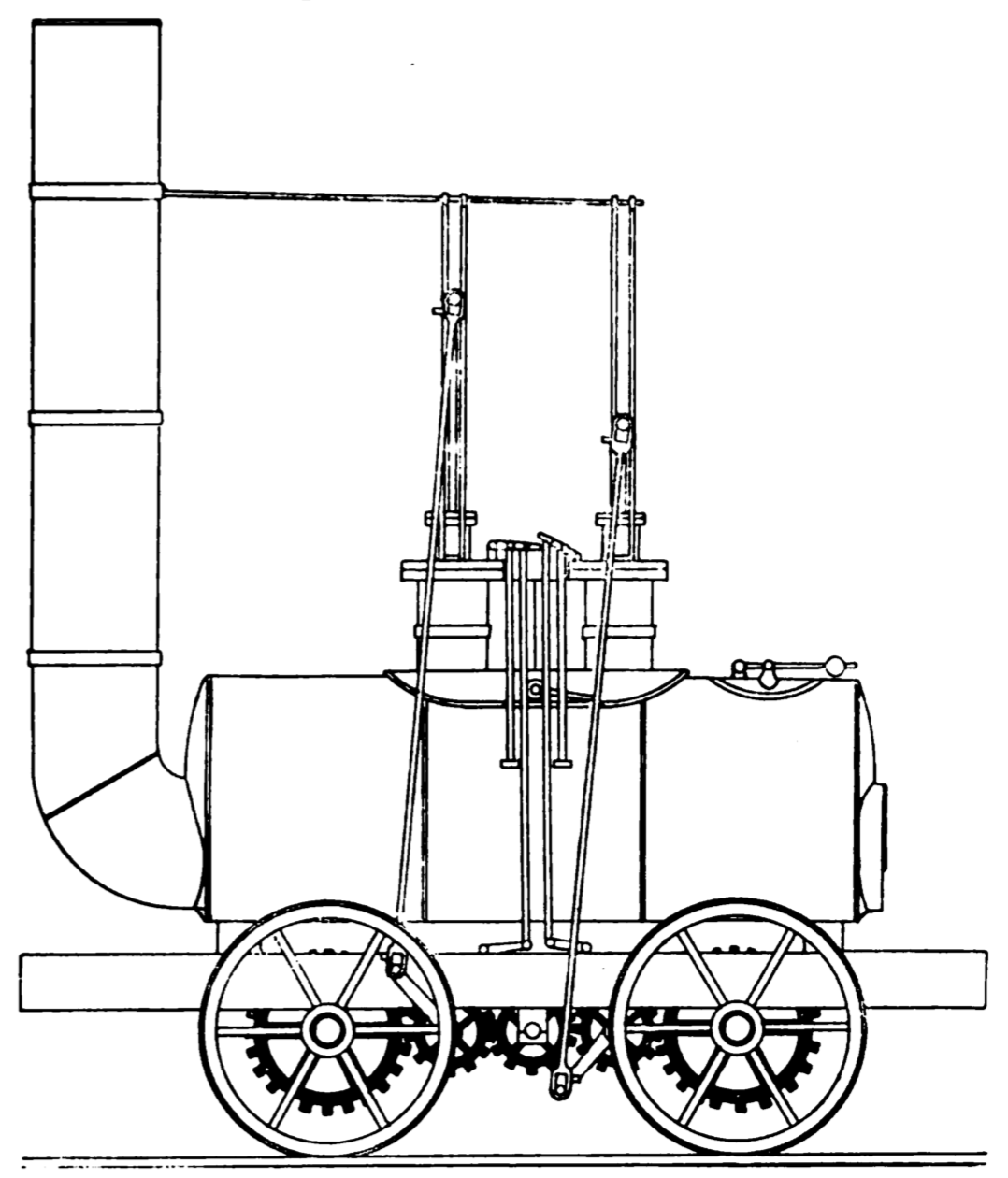
Steam Spring
Steam springs or steam suspension are a form of suspension used for some early steam locomotives designed and built by George Stephenson. They were only briefly used and may have been used for fewer than ten locomotives. Requirements for suspension Early railways used cast-iron fishbelly rails. These were brittle and prone to cracking under shock loads. The new steam locomotives of the 1820s were much heavier than the horse-drawn wagons of earlier plateways. Locomotives of this period also used vertical cylinders set within the boiler. The vertical forces of the moving pistons further gave rise to hammer blow, which increased the load on the rails. A further reason for suspension was to improve the frictional contact between the wheels and rail. This relied upon maintaining a good contact, thus requiring good suspension of the wheels over the uneven track. The ability of an 'adhesion-hauled' locomotive to draw a train was much questioned at this time, as it was thought that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Stephensons Patent Locomotive Engine LOC3c10386v (cropped)
G, or g, is the seventh letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''gee'' (pronounced ), plural ''gees''. History The letter 'G' was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ' C' to distinguish voiced from voiceless . The recorded originator of 'G' is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, who added letter G to the teaching of the Roman alphabet during the 3rd century BC: he was the first Roman to open a fee-paying school, around 230 BCE. At this time, ' K' had fallen out of favor, and 'C', which had formerly represented both and before open vowels, had come to express in all environments. Ruga's positioning of 'G' shows that alphabetic order related to the letters' values as Greek numerals was a concern even in the 3rd century BC. According to some records, the original seventh letter, 'Z', had been purged from the Latin alphabet somewhat ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Valve
A safety valve is a valve that acts as a fail-safe. An example of safety valve is a pressure relief valve (PRV), which automatically releases a substance from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system, when the pressure or temperature exceeds preset limits. Pilot-operated relief valves are a specialized type of pressure safety valve. A leak tight, lower cost, single emergency use option would be a rupture disk. Safety valves were first developed for use on steam boilers during the Industrial Revolution. Early boilers operating without them were prone to explosion unless carefully operated. Vacuum safety valves (or combined pressure/vacuum safety valves) are used to prevent a tank from collapsing while it is being emptied, or when cold rinse water is used after hot CIP (clean-in-place) or SIP (sterilization-in-place) procedures. When sizing a vacuum safety valve, the calculation method is not defined in any norm, particularly in the hot CIP / cold water scenario, but some manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spur Gear
Spur gears or straight-cut gears are the simplest type of gear. They consist of a cylinder or disk with teeth projecting radially. Viewing the gear at 90 degrees from the shaft length (side on) the tooth faces are straight and aligned parallel to the axis of rotation. Looking down the length of the shaft, a tooth's cross section is usually not triangular. Instead of being straight (as in a triangle) the sides of the cross section have a curved form (usually involute and less commonly cycloidal) to achieve a constant drive ratio. Spur gears mesh together correctly only if fitted to parallel shafts. No axial thrust is created by the tooth loads. Spur gears are excellent at moderate speeds but tend to be noisy at high speeds. Spur gear can be classified into two pressure angles, 20° being the current industry standard and 14½° being the former (often found in older equipment). Spur gear teeth are manufactured as either involute In mathematics, an involute (also known as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blücher (locomotive)
George Stephenson built a number of experimental steam locomotives to work in the Killingworth Colliery between 1814 and 1826. Background George Stephenson was appointed as engine-wright at Killingworth Colliery in 1812 and immediately improved the haulage of the coal from the mine using fixed engines. But he had taken an interest in Blenkinsop's engines in Leeds and Blackett's experiments at Wylam colliery, where he had been born. By 1814 he persuaded the lessees of the colliery to fund a "travelling engine" which first ran on 25 July. By experiment he confirmed Blackett's observation that the friction of the wheels was sufficient on an iron railway without cogs but still used a cogwheel system in transmitting power to the wheels. ''Blücher'' ''Blücher'' (often spelled ''Blutcher'') was built by George Stephenson in 1814; the first of a series of locomotives that he designed in the period 1814–16 which established his reputation as an engine designer and laid the foundati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coupling Rod
A coupling rod or side rod connects the driving wheels of a locomotive. Steam locomotives in particular usually have them, but some diesel and electric locomotives, especially older ones and shunters, also have them. The coupling rods transfer the power of drive to all wheels. Development Locomotion No. 1 was the first locomotive to employ coupling rods rather than chains. In the 1930s reliable roller bearing coupling rods were developed. Allowance for vertical motion In general, all railroad vehicles have spring suspension; without springs, irregularities in the track could lift wheels off the rail and cause impact damage to both rails and vehicles. Driving wheels are typically mounted so that they have around 1 inch (2.5 cm) of vertical motion. When there are only 2 coupled axles, this range of motion places only slight stress on the crank pins. With more axles, however, provision must be made to allow each axle to move vertically independently of the others without be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Wood
Nicholas Wood FGS FRS (24 April 1795 – 19 December 1865) was an English colliery and steam locomotive engineer. He helped engineer and design many steps forward in both engineering and mining safety, and helped bring about the North of England Institute of Mining and Mechanical Engineers, holding the position of President from its inauguration to his death. Early life Nicholas Wood was born at Sourmires, in the parish of Ryton, then in County Durham, the son of Nicholas and Ann (née Laws) Wood. Nicholas Senior was the mining engineer at Crawcrook colliery. Nicholas Junior attended the village school at Crawcrook and started work in 1811 at Killingworth Colliery as an apprentice colliery viewer under the guidance of Ralph Dodds. Wood eventually became the viewer, or colliery manager, of Killingworth Colliery in 1815. He was there a close associate of the colliery enginewright George Stephenson, helping him develop his version of the safety lamp and making considerable technic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tallow
Tallow is a rendering (industrial), rendered form of beef or mutton fat, primarily made up of triglycerides. In industry, tallow is not strictly defined as beef or mutton fat. In this context, tallow is animal fat that conforms to certain technical criteria, including its melting point. Commercial tallow commonly contains fat derived from other animals, such as lard from domestic pig, pigs, or even from plant sources. The adjacent diagram shows the chemical structure of a typical triglyceride molecule. The solid material remaining after rendering is called cracklings, greaves, or graves. It has been used mostly for animal feed, animal food, such as dog food#History, dog food. In the soap industry and among soap-making hobbyists, the name tallowate is used informally to refer to soaps made from tallow. soap, Sodium tallowate, for example, is obtained by reacting tallow with sodium hydroxide (lye, caustic soda) or sodium carbonate (washing soda). It consists chiefly of a varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oakum
Oakum is a preparation of tarred fibre used to seal gaps. Its main traditional applications were in shipbuilding, for caulking or packing the joints of timbers in wooden vessels and the deck planking of iron and steel ships; in plumbing, for sealing joints in cast iron pipe; and in log cabins for chinking. In ship caulking, it was forced into the seams using a hammer and a caulking iron, then sealed into place with hot pitch. It is also referenced frequently as a medical supply for medieval surgeons, often used along with bandages for sealing wounds. History The word oakum derives from Middle English ', from Old English ', from ' ( separative and perfective prefix) + ' (akin to Old English ', 'comb')—literally 'off-combings'. Oakum was at one time recycled from old tarry ropes and cordage, which were painstakingly unravelled and reduced to fibre, termed "picking". The task of picking and preparation was a common occupation in prisons and workhouses, where the young or th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
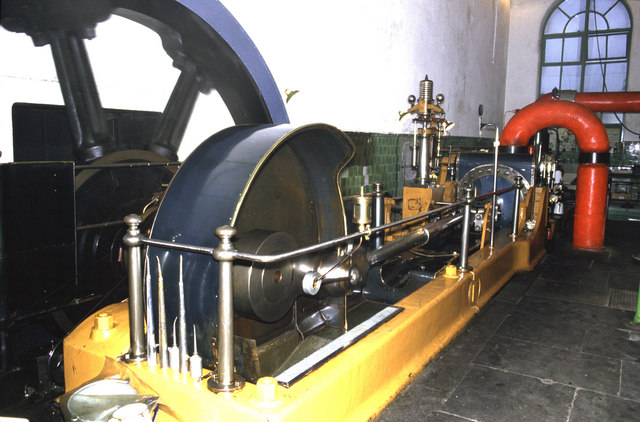
Stationary Steam Engine
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from locomotive engines used on railways, traction engines for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam cars (and other motor vehicles), agricultural engines used for ploughing or threshing, marine engines, and the steam turbines used as the mechanism of power generation for most nuclear power plants. They were introduced during the 18th century and widely made for the whole of the 19th century and most of the first half of the 20th century, only declining as electricity supply and the internal combustion engine became more widespread. Types of stationary steam engine There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by the layout of the cylinders and crankshaft: * Beam engines have a rocking beam providing the connection between the vertical cylinder and crankshaft. *Table engines have the crosshead above the vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder. __TOC__ Piston engines Internal combustion engines An internal combustion engine is acted upon by the pressure of the expanding combustion gases in the combustion chamber space at the top of the cylinder. This force then acts downwards through the connecting rod and onto the crankshaft. The connecting rod is att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flued Boiler
A shell or flued boiler is an early and relatively simple form of boiler used to make steam, usually for the purpose of driving a steam engine. The design marked a transitional stage in boiler development, between the early haystack boilers and the later multi-tube fire-tube boilers. A flued boiler is characterized by a large cylindrical boiler shell forming a tank of water, traversed by one or more large flues containing the furnace. These boilers appeared around the start of the 19th century and some forms remain in service today. Although mostly used for static steam plants, some were used in early steam vehicles, railway locomotives and ships. Flued boilers were developed in an attempt to raise steam pressures and improve engine efficiency. Early haystack designs of Watt's day were mechanically weak and often presented an unsupported flat surface to the fire. Boiler explosions, usually beginning with failure of this firebox plate, were common. It was known that an arched stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)