|
Statistical Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making predict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Of Study
Field may refer to: Expanses of open ground * Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes * Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport * Battlefield * Lawn, an area of mowed grass * Meadow, a grassland that is either natural or allowed to grow unmowed and ungrazed * Playing field, used for sports or games Arts and media * In decorative art, the main area of a decorated zone, often contained within a border, often the background for motifs ** Field (heraldry), the background of a shield ** In flag terminology, the background of a flag * ''FIELD'' (magazine), a literary magazine published by Oberlin College in Oberlin, Ohio * ''Field'' (sculpture), by Anthony Gormley Organizations * Field department, the division of a political campaign tasked with organizing local volunteers and directly contacting voters * Field Enterprises, a defunct private holding company ** Field Communications, a division of Field Enterprises * Field Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics encompasses a variety of statistical techniques from data mining, predictive modeling, and machine learning that analyze current and historical facts to make predictions about future or otherwise unknown events. In business, predictive models exploit patterns found in historical and transactional data to identify risks and opportunities. Models capture relationships among many factors to allow assessment of risk or potential associated with a particular set of conditions, guiding decision-making for candidate transactions. The defining functional effect of these technical approaches is that predictive analytics provides a predictive score (probability) for each individual (customer, employee, healthcare patient, product SKU, vehicle, component, machine, or other organizational unit) in order to determine, inform, or influence organizational processes that pertain across large numbers of individuals, such as in marketing, credit risk assessment, fraud det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Cells
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body ( soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebbian Theory
Hebbian theory is a neuroscientific theory claiming that an increase in synaptic efficacy arises from a presynaptic cell's repeated and persistent stimulation of a postsynaptic cell. It is an attempt to explain synaptic plasticity, the adaptation of brain neurons during the learning process. It was introduced by Donald Hebb in his 1949 book '' The Organization of Behavior.'' The theory is also called Hebb's rule, Hebb's postulate, and cell assembly theory. Hebb states it as follows: Let us assume that the persistence or repetition of a reverberatory activity (or "trace") tends to induce lasting cellular changes that add to its stability. ... When an axon of cell ''A'' is near enough to excite a cell ''B'' and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that ''A''’s efficiency, as one of the cells firing ''B'', is increased. The theory is often summarized as "Cells that fire together wire t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organization Of Behavior
''Organization of Behavior'' is a 1949 book by the psychologist Donald O. Hebb. Reception The author Richard Webster identifies ''Organization of Behavior'' as the most influential outline of Hebb's postulate. According to Webster, the hypothesis has classic status within science and is supported by recent research. References Bibliography ;Books * 1949 non-fiction books Books by Donald O. Hebb English-language books Neuroscience books {{learning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald O
Donald is a masculine given name derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers, and partly associated with the spelling of similar-sounding Germanic names, such as ''Ronald''. A short form of ''Donald'' is '' Don''. Pet forms of ''Donald'' include ''Donnie'' and ''Donny''. The feminine given name ''Donella'' is derived from ''Donald''. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh '' Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name '' Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations Kings and noblemen Domnall or Domhnall is the name of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadians
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Canadian''. Canada is a multilingual and multicultural society home to people of groups of many different ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World immigrants and their descendants. Following the initial period of French and then the much larger British colonization, different waves (or peaks) of immigration and settlement of non-indigenous peoples took place over the course of nearly two centuries and continue today. Elements of Indigenous, French, British, and more recent immigrant customs, languages, and religions have combined to form the culture of Canada, and thus a Canadian identity. Canada has also been strongly influenced by its linguistic, geographic, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components. A computer program in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be translated to machine instructions using the language's compiler. (Assembly language programs are translated using an assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within the language's interpreter. If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system loads it into memory and starts a process. The central processing unit will soon switch to this process so it can fetch, decode, and then execute each machine instruction. If the source code is requested for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Gaming
A personal computer game, also known as a PC game or computer game, is a type of video game played on a personal computer (PC) rather than a video game console or arcade machine. Its defining characteristics include: more diverse and user-determined gaming hardware and software; and generally greater capacity in input, processing, video and audio output. The uncoordinated nature of the PC game market, and now its lack of physical media, make precisely assessing its size difficult. In 2018, the global PC games market was valued at about $27.7 billion. Home computer games became popular following the video game crash of 1983, leading to the era of the "bedroom coder". In the 1990s, PC games lost mass-market traction to console games, before enjoying a resurgence in the mid-2000s through digital distribution on services such as Steam and GOG.com. Newzoo reports that the ''PC gaming sector'' is the third-largest category (and estimated in decline) across all platforms , with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probably Approximately Correct Learning
In computational learning theory, probably approximately correct (PAC) learning is a framework for mathematical analysis of machine learning. It was proposed in 1984 by Leslie Valiant.L. Valiant. A theory of the learnable.' Communications of the ACM, 27, 1984. In this framework, the learner receives samples and must select a generalization function (called the ''hypothesis'') from a certain class of possible functions. The goal is that, with high probability (the "probably" part), the selected function will have low generalization error (the "approximately correct" part). The learner must be able to learn the concept given any arbitrary approximation ratio, probability of success, or distribution of the samples. The model was later extended to treat noise (misclassified samples). An important innovation of the PAC framework is the introduction of computational complexity theory concepts to machine learning. In particular, the learner is expected to find efficient functions (tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
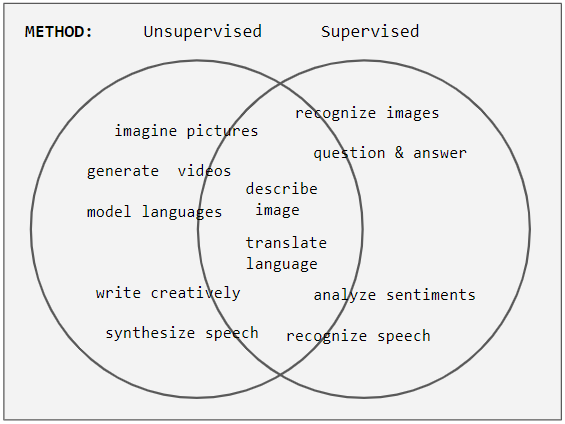
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning is a type of algorithm that learns patterns from untagged data. The hope is that through mimicry, which is an important mode of learning in people, the machine is forced to build a concise representation of its world and then generate imaginative content from it. In contrast to supervised learning where data is tagged by an expert, e.g. tagged as a "ball" or "fish", unsupervised methods exhibit self-organization that captures patterns as probability densities or a combination of neural feature preferences encoded in the machine's weights and activations. The other levels in the supervision spectrum are reinforcement learning where the machine is given only a numerical performance score as guidance, and semi-supervised learning where a small portion of the data is tagged. Neural networks Tasks vs. methods Neural network tasks are often categorized as discriminative (recognition) or generative (imagination). Often but not always, discriminative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploratory Data Analysis
In statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA) is an approach of analyzing data sets to summarize their main characteristics, often using statistical graphics and other data visualization methods. A statistical model can be used or not, but primarily EDA is for seeing what the data can tell us beyond the formal modeling and thereby contrasts traditional hypothesis testing. Exploratory data analysis has been promoted by John Tukey since 1970 to encourage statisticians to explore the data, and possibly formulate hypotheses that could lead to new data collection and experiments. EDA is different from initial data analysis (IDA), which focuses more narrowly on checking assumptions required for model fitting and hypothesis testing, and handling missing values and making transformations of variables as needed. EDA encompasses IDA. Overview Tukey defined data analysis in 1961 as: "Procedures for analyzing data, techniques for interpreting the results of such procedures, ways of planni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |