|
Statistical Potential
In protein structure prediction, statistical potentials or knowledge-based potentials are scoring functions derived from an analysis of known protein structures in the Protein Data Bank (PDB). The original method to obtain such potentials is the ''quasi-chemical approximation'', due to Miyazawa and Jernigan. It was later followed by the ''potential of mean force'' (statistical PMF ), developed by Sippl. Although the obtained scores are often considered as approximations of the free energy—thus referred to as ''pseudo-energies''—this physical interpretation is incorrect. Nonetheless, they are applied with success in many cases, because they frequently correlate with actual Gibbs free energy differences. Overview Possible features to which a pseudo-energy can be assigned include: * interatomic distances, * torsion angles, * solvent exposure, * or hydrogen bond geometry. The classic application is, however, based on pairwise amino acid contacts or distances, thus producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann Distribution
In statistical mechanics and mathematics, a Boltzmann distribution (also called Gibbs distribution Translated by J.B. Sykes and M.J. Kearsley. See section 28) is a probability distribution or probability measure that gives the probability that a system will be in a certain state as a function of that state's energy and the temperature of the system. The distribution is expressed in the form: :p_i \propto e^ where is the probability of the system being in state , is the energy of that state, and a constant of the distribution is the product of the Boltzmann constant and thermodynamic temperature . The symbol \propto denotes proportionality (see for the proportionality constant). The term ''system'' here has a very wide meaning; it can range from a collection of 'sufficient number' of atoms or a single atom to a macroscopic system such as a natural gas storage tank. Therefore the Boltzmann distribution can be used to solve a very wide variety of problems. The distrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Assessment Of Techniques For Protein Structure Prediction
Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP), sometimes called Critical Assessment of Protein Structure Prediction, is a community-wide, worldwide experiment for protein structure prediction taking place every two years since 1994. CASP provides research groups with an opportunity to objectively test their structure prediction methods and delivers an independent assessment of the state of the art in protein structure modeling to the research community and software users. Even though the primary goal of CASP is to help advance the methods of identifying protein three-dimensional structure from its amino acid sequence many view the experiment more as a “world championship” in this field of science. More than 100 research groups from all over the world participate in CASP on a regular basis and it is not uncommon for entire groups to suspend their other research for months while they focus on getting their servers ready for the experiment and on performing the detailed predic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
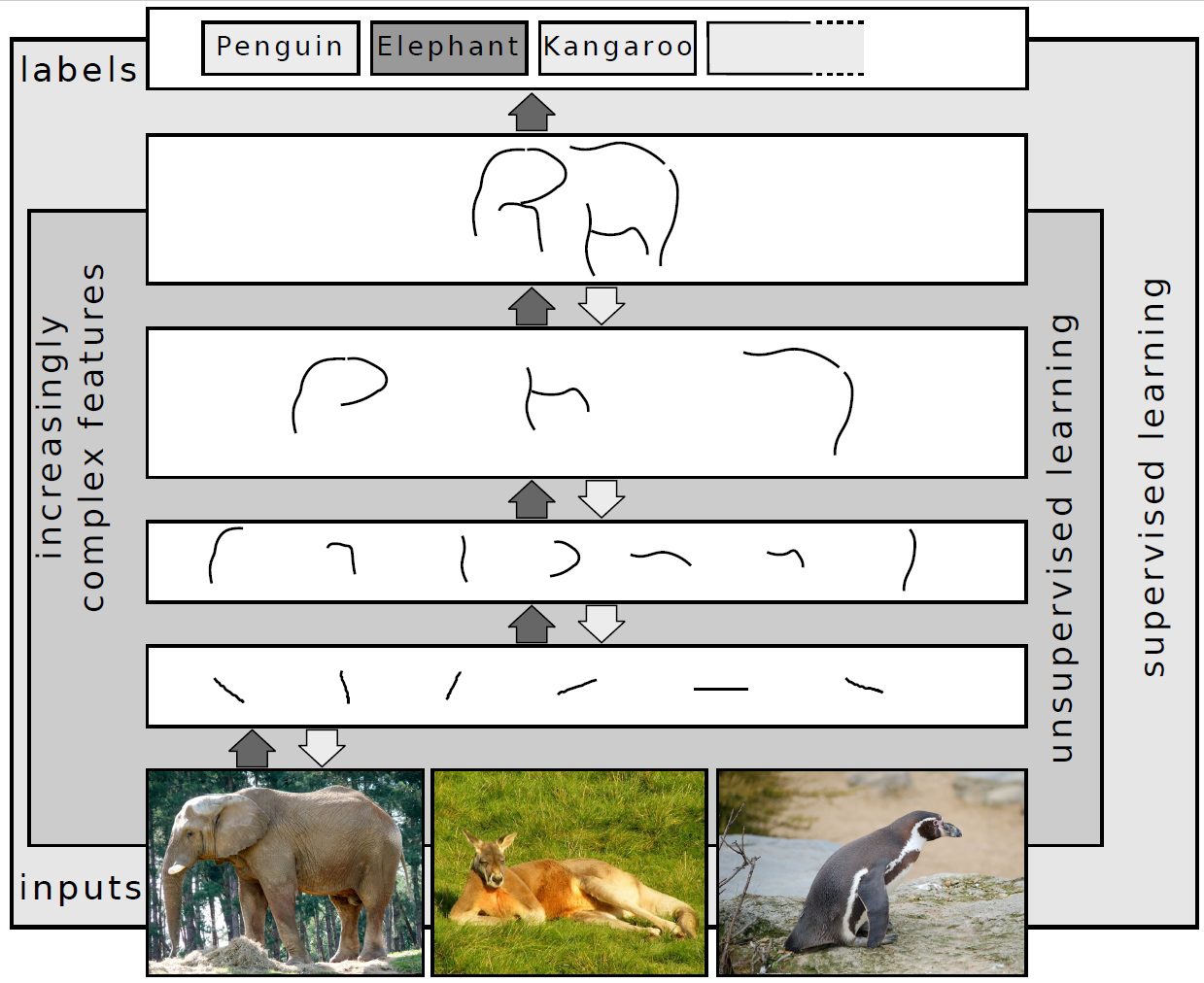
Deep Learning
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be Supervised learning, supervised, Semi-supervised learning, semi-supervised or Unsupervised learning, unsupervised. Deep-learning architectures such as #Deep_neural_networks, deep neural networks, deep belief networks, deep reinforcement learning, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks and Transformer (machine learning model), Transformers have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, Climatology, climate science, material inspection and board game programs, where they have produced results comparable to and in some cases surpassing human expert performance. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) were inspired by information processing and distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeepMind
DeepMind Technologies is a British artificial intelligence subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. and research laboratory founded in 2010. DeepMind was acquired by Google in 2014 and became a wholly owned subsidiary of Alphabet Inc, after Google's restructuring in 2015. The company is based in London, with research centres in Canada, France, and the United States. DeepMind has created a neural network that learns how to play video games in a fashion similar to that of humans, as well as a Neural Turing machine, or a neural network that may be able to access an external memory like a conventional Turing machine, resulting in a computer that mimics the short-term memory of the human brain. DeepMind made headlines in 2016 after its AlphaGo program beat a human professional Go player Lee Sedol, a world champion, in a five-game match, which was the subject of a documentary film. A more general program, AlphaZero, beat the most powerful programs playing go, chess and shogi (Japanese chess) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Network
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons, which loosely model the neurons in a biological brain. Each connection, like the synapses in a biological brain, can transmit a signal to other neurons. An artificial neuron receives signals then processes them and can signal neurons connected to it. The "signal" at a connection is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs. The connections are called ''edges''. Neurons and edges typically have a ''weight'' that adjusts as learning proceeds. The weight increases or decreases the strength of the signal at a connection. Neurons may have a threshold such that a signal is sent only if the aggregate signal crosses that threshold. Typically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Support Vector Machines
In machine learning, support vector machines (SVMs, also support vector networks) are supervised learning models with associated learning algorithms that analyze data for classification and regression analysis. Developed at AT&T Bell Laboratories by Vladimir Vapnik with colleagues (Boser et al., 1992, Guyon et al., 1993, Cortes and Vapnik, 1995, Vapnik et al., 1997) SVMs are one of the most robust prediction methods, being based on statistical learning frameworks or VC theory proposed by Vapnik (1982, 1995) and Chervonenkis (1974). Given a set of training examples, each marked as belonging to one of two categories, an SVM training algorithm builds a model that assigns new examples to one category or the other, making it a non-probabilistic binary linear classifier (although methods such as Platt scaling exist to use SVM in a probabilistic classification setting). SVM maps training examples to points in space so as to maximise the width of the gap between the two categories. New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arieh Ben-Naim
Arieh Ben-Naim ( he, אריה בן-נאים; Jerusalem, 11 July 1934) is a professor of physical chemistry who retired in 2003 from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. He has made major contributions over 40 years to the theory of the structure of water, aqueous solutions and hydrophobic- hydrophilic interactions. He is mainly concerned with theoretical and experimental aspects of the general theory of liquids and solutions. In recent years, he has advocated the use of information theory to better understand and advance statistical mechanics and thermodynamics. Contributions to the theory of liquids Books written by Arieh Ben-Naim: * Water and Aqueous Solutions: Introduction to a Molecular Theory. 1974, (out of print). * Hydrophobic Interactions. 1980, . * Molecular Theory of Solutions. 2006, . * Molecular Theory of Water and Aqueous Solutions: Understanding Water. 2009, . * Molecular Theory of Water and Aqueous Solutions, Part II: The role of Water in Protein Folding, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Angle X-ray Scattering
Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is a small-angle scattering technique by which nanoscale density differences in a sample can be quantified. This means that it can determine nanoparticle size distributions, resolve the size and shape of (monodisperse) macromolecules, determine pore sizes, characteristic distances of partially ordered materials, and much more. This is achieved by analyzing the elastic scattering behaviour of X-rays when travelling through the material, recording their scattering at small angles (typically 0.1 – 10°, hence the "Small-angle" in its name). It belongs to the family of small-angle scattering (SAS) techniques along with small-angle neutron scattering, and is typically done using hard X-rays with a wavelength of 0.07 – 0.2 nm.. Depending on the angular range in which a clear scattering signal can be recorded, SAXS is capable of delivering structural information of dimensions between 1 and 100 nm, and of repeat distances in partially ordered sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Distribution Function
In statistical mechanics, the radial distribution function, (or pair correlation function) g(r) in a system of particles (atoms, molecules, colloids, etc.), describes how density varies as a function of distance from a reference particle. If a given particle is taken to be at the origin O, and if \rho =N/V is the average number density of particles, then the local time-averaged density at a distance r from O is \rho g(r). This simplified definition holds for a homogeneous and isotropic system. A more general case will be considered below. In simplest terms it is a measure of the probability of finding a particle at a distance of r away from a given reference particle, relative to that for an ideal gas. The general algorithm involves determining how many particles are within a distance of r and r+dr away from a particle. This general theme is depicted to the right, where the red particle is our reference particle, and blue particles are those whose centers are within the cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential Of Mean Force
When examining a system computationally one may be interested in knowing how the free energy changes as a function of some inter- or intramolecular coordinate (such as the distance between two atoms or a torsional angle). The free energy surface along the chosen coordinate is referred to as the potential of mean force (PMF). If the system of interest is in a solvent, then the PMF also incorporates the solvent effects. General description The PMF can be obtained in Monte Carlo or molecular dynamics simulations to examine how a system's energy changes as a function of some specific reaction coordinate parameter. For example, it may examine how the system's energy changes as a function of the distance between two residues, or as a protein is pulled through a lipid bilayer. It can be a geometrical coordinate or a more general energetic (solvent) coordinate. Often PMF simulations are used in conjunction with umbrella sampling, because typically the PMF simulation will fail to adequately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |