|
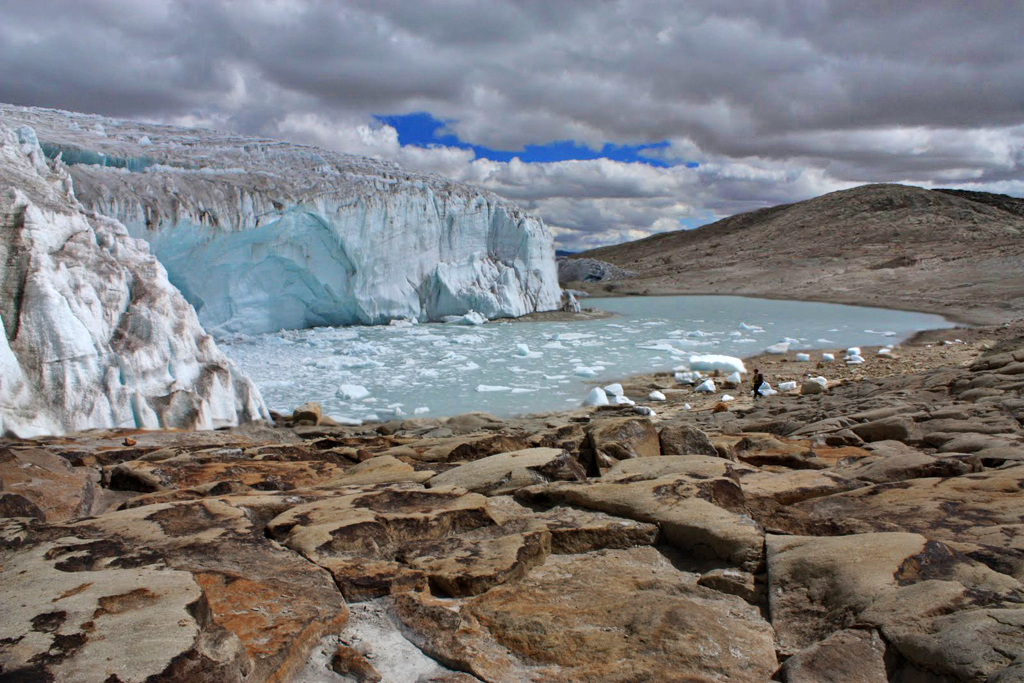
Starshot Glacier
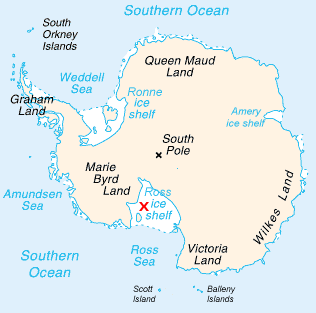
Starshot Glacier () is a glacier 50 nautical miles (90 km) long, flowing from the polar plateau eastward through the Churchill Mountains, then north along the west side of Surveyors Range, entering the Ross Ice Shelf south of Cape Parr. So named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition The New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) describes a series of scientific explorations of the continent Antarctica. The expeditions were notably active throughout the 1950s and 1960s. Features named by the expeditions 1957 ... (NZGSAE) (1960–61) because the area was surveyed with the use of star observations. Glaciers of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchill Mountains
The Churchill Mountains are a mountain range group of the Transantarctic Mountains System, located in the Ross Dependency region of Antarctica. They border on the western side of the Ross Ice Shelf, between Byrd Glacier and Nimrod Glacier. Several of the range's highest summits, including Mounts Egerton, Field, Nares, Wharton, and Albert Markham were first seen and named by the Discovery Expedition of 1901–1904 (aka: British National Antarctic Expedition), under Robert Falcon Scott The mountains were mapped in detail by the USGS from Tellurometer surveys during 1960–61, and by United States Navy air photos in 1960. They were named by the US-ACAN for Sir Winston Churchill. Mountains and peaks ;Mount Albert Markham Mount Albert Markham is a striking flat-topped mountain, standing midway between Mount Nares and Pyramid Mountain. Discovered by the Discovery Expedition and named for Admiral Sir Albert Hastings Markham, a member of the Ship Committee for the expedition. ;Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surveyors Range
Surveyors Range () is a long mountain range in the Churchill Mountains of Antarctica. Location Surveyors Range is long, extending north along the east side of Starshot Glacier from the Thompson Mountain area to the glacier's terminus at the Ross Ice Shelf. The Swithinbank Range is to the west, on the other side of the Starshot Glacier. The Dickey Glacier runs north along the east side of the range. The range was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) (1960–61) for the early pioneering surveyors of New Zealand and present day equivalents in Great Britain who contributed to work carried out in this area by Captain P.J. Hunt, Royal Engineers. Glaciers Starshot Glacier . A glacier long, flowing from the polar plateau eastward through the Churchill Mountains, then north along the west side of Surveyors Range, entering the Ross Ice Shelf south of Cape Parr. So named by the NZGSAE (1960-61) because the area was surveyed with the use of star ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Parr
Cape Parr () is a large snow-covered cape along the west side of the Ross Ice Shelf The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between hi ..., about 8 nautical miles (15 km) south of Gentile Point. Discovered by the ''Discovery'' expedition (1901–04) under Scott, who named it for Admiral Alfred Arthur Chase Parr, one of Scott's advisors who had served in Arctic exploration. Headlands of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition
The New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) describes a series of scientific explorations of the continent Antarctica. The expeditions were notably active throughout the 1950s and 1960s. Features named by the expeditions 1957–1958 expedition The 1957–1958 expedition went to the Ross Dependency and named the Borchgrevink Glacier. Other features named include: * Carter Ridge * Felsite Island * Halfway Nunatak * Hedgehog Island * Moraine Ridge 1958–1959 expedition * Cadwalader Beach * Cape Hodgson * Carter Ridge * Isolation Point * Mountaineer Range * Mount Aurora * Mount Hayward * Mount Henderson (White Island) * Mount Bird. 1960–1961 expedition * Deverall Island * Lonewolf Nunataks 1961–1962 expedition * Aurora Heights * The Boil * Ford Spur * Graphite Peak * Half Century Nunatak * Half Dome Nunatak * Hump Passage * Last Cache Nunatak * Lookout Dome * Montgomerie Glacier * Mount Fyfe * Mount Macdonald * Snowshoe Pass * Turret Nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciers Of The Ross Dependency
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |