|
Stalita Taenaria
''Stalita taenaria'' is an Araneomorphae, araneomorph spider species in the family Dysderidae. The species is classified as a member of troglofauna, more precisely a troglobiont species, meaning such spiders are obligate cave-dwellers adapted to living in dark surroundings. ''Stalita taenaria'' is a species of a few Europe, European countries. The spider is thought to be the first described species of true (eyeless) cave spider in the world. Taxonomy The species was first described and named by Danish entomologist Jørgen Matthias Christian Schiødte in 1847. In the same year Schiødte also named and described the genus ''Stalita'', while making ''Stalita taenaria'' its type species. Besides ''S. taenaria'' there are three more species in the same genus. Description Males Males of this species are approximately 6.7 millimetres long. They have densely haired and oval opisthosoma (abdomen) which is of bright Ivory (color), ivory colour. Their legs are reddish-brown and cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers , and has a population of 2.1 million (2,108,708 people). Slovenes constitute over 80% of the country's population. Slovene, a South Slavic language, is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. A sub-mediterranean climate reaches to the northern extensions of the Dinaric Alps that traverse the country in a northwest–southeast direction. The Julian Alps in the northwest have an alpine climate. Toward the northeastern Pannonian Basin, a continental climate is more pronounced. Ljubljana, the capital and largest city of Slovenia, is geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivory (color)
Ivory is an off-white color named after, and derived from, the material made from the tusks and teeth of certain animals, such as the elephant and the walrus. It has a very slight tint of yellow. The color is often associated with purity and elegance. In Western culture, it is also associated with weddings and other formal occasions. In Eastern cultures, ivory has been used for centuries in the creation of decorative objects and religious artifacts, such as Buddha statues and other sculptures. The cultural acceptance of the use of Ivory as a material has declined over time, with the practice being outlawed in much of the world. The first recorded use of ''ivory'' as a color name in English was in 1385. Maerz and Paul ''A Dictionary of Color'' New York:1930 McGraw-Hill Page 197; Color Sample of Ivory: Page 43 Plate 10 Color Sample B12 The color "ivory" was included as one of the X11 colors when they were formulated in 1987. Ivory in nature Plants *The ivory-colored cymbidiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of Italy
The fauna of Italy comprises all the animal species inhabiting the territory of the Italy, Italian Republic and its surrounding waters. Italy has one the highest level of faunal biodiversity in Europe, with over 57,000 species recorded, representing more than a third of all European fauna. This is due to various factors. The Italian peninsula is in the center of the Mediterranean Sea, forming a corridor between central Europe and North Africa, and it has of coastline. Italy also receives species from the Balkans, Eurasia, and the Middle East. Italy's varied geological structure, including the Italian Alps, Alps and the Apennines, Central Italian woodlands, and Southern Italian Garigue and Maquis shrubland, also contribute to high climate and habitat diversity. The fauna of Italy includes 4,777 Endemism, endemic animal species, which include the Sardinian long-eared bat, Corsican red deer, Sardinian red deer, spectacled salamander, brown cave salamander, Italian newt, Italian str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of Slovenia
Fauna of Slovenia includes: * List of birds of Slovenia * List of Lepidoptera of Slovenia * List of mammals of Slovenia * List of Odonata species of Slovenia The list of Odonata species of Slovenia includes 72 species of Odonata, dragonflies and damselflies ( sl, kačji pastirji) for which reliable records exist from the present-day territory of Slovenia, including one that has not been seen since the ... See also * Outline of Slovenia * :Fauna of Slovenia {{Slovenia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of Europe
The fauna of Europe is all the animals living in Europe and its surrounding seas and islands. Since there is no natural biogeographic boundary in the east and south between Europe and Asia, the term "fauna of Europe" is somewhat elusive. Europe is the western part of the Palearctic realm (which in turn is part of the Holarctic). Lying within the temperate region, (north of the equator) the wildlife is not as rich as in the hottest regions, but is nevertheless diverse due to the variety of habitats and the faunal richness of Eurasia as a whole. Before the arrival of humans European fauna was more diverse and widespread than today. The European megafauna of today is much reduced from its former numbers. The Holocene extinction drastically reduced numbers and distribution of megafauna and continues to (such as with wolves and bears). Many of these species still exist in smaller numbers, while others thrive in the developed continent free from natural predators, with the former threaten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg , image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg , anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland") , image_map = , map_caption = , capital = Zagreb , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Croatian , languages_type = Writing system , languages = Latin , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2021 , religion = , religion_year = 2021 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Zoran Milanović , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Andrej Plenković , leader_title3 = Speaker of Parliament , leader_name3 = Gordan Jandroković , legislature = Sabor , sovereignty_type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troglobite
A troglobite (or, formally, troglobiont) is an animal species, or population of a species, strictly bound to underground habitats, such as caves. These are separate from species that mainly live in above-ground habitats but are also able to live underground (eutroglophiles), and species that are only cave visitors ( subtroglophiles and trogloxenes). Land-dwelling troglobites may be referred to as troglofauna, while aquatic species may be called stygofauna, although for these animals the term ''stygobite'' is preferable. Troglobites typically have evolutionary adaptations to cave life. Examples of such adaptations include slow metabolism, reduced energy consumption, better food usage efficiency, decrease or loss of eyesight (anophthalmia), and depigmentation (absence of pigment in the integument). Conversely, as opposed to lost or reduced functions, many species have evolved elongated antenna and locomotory appendages, in order to better move around and respond to environmental s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerae
The chelicerae () are the mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as "jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated fangs, or similarly to pincers. Some chelicerae, such as those found on nearly all spiders, are hollow and contain (or are connected to) venom glands, and are used to inject venom into prey or a perceived threat. In ''Pisaurina mira'', also known as the nursery web spider, the chelicerae are utilized to snatch the prey once it becomes within reach, facilitating the "sit-and-wait ambush predator" behavior. Both pseudoscorpions and harvestmen have structures on their chelicerae that are used for grooming (papillae in pseudoscorpions, cheliceral teeth in Opiliones). Types Chelicerae can be divided into three kinds: jackknife chelicerae, scissor chelicerae, and 3-segmented chelate chelicerae. Jackknife chelicerae The jackknife chelicera is subchelate (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
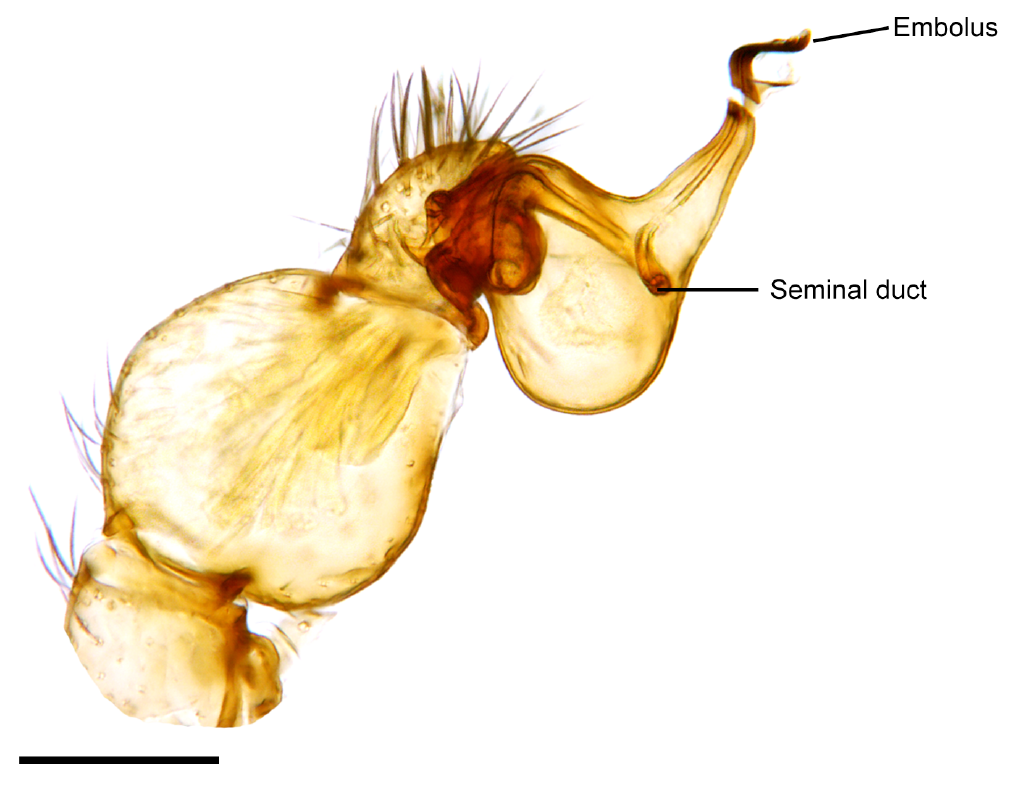
Embolus (spider Anatomy)
The two palpal bulbs – also known as palpal organs and genital bulbs – are the copulatory organs of a male spider. They are borne on the last segment of the pedipalps (the front "limbs" of a spider), giving the spider an appearance often described as like wearing boxing gloves. The palpal bulb does not actually produce sperm, being used only to transfer it to the female. Palpal bulbs are only fully developed in adult male spiders and are not completely visible until after the final moult. In the majority of species of spider, the bulbs have complex shapes and are important in identification. Structure The palpal bulb of a mature male spider is borne on the last segment of the pedipalp. This segment usually has touch-sensitive hairs (setae) with nerves leading to them. The bulb itself is entirely without nerves, and hence without sensory organs and muscles, since these depend on nerves for their functioning, although some spiders have one or two muscles external to the bulb and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpal Bulb
The two palpal bulbs – also known as palpal organs and genital bulbs – are the copulatory organs of a male spider. They are borne on the last segment of the pedipalps (the front "limbs" of a spider), giving the spider an appearance often described as like wearing boxing gloves. The palpal bulb does not actually produce sperm, being used only to transfer it to the female. Palpal bulbs are only fully developed in adult male spiders and are not completely visible until after the final moult. In the majority of species of spider, the bulbs have complex shapes and are important in identification. Structure The palpal bulb of a mature male spider is borne on the last segment of the pedipalp. This segment usually has touch-sensitive hairs (setae) with nerves leading to them. The bulb itself is entirely without nerves, and hence without sensory organs and muscles, since these depend on nerves for their functioning, although some spiders have one or two muscles external to the bulb and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |